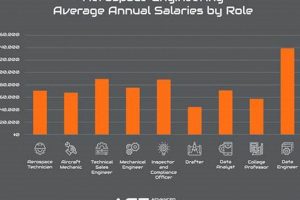
The projected availability of positions in the aerospace engineering field constitutes a significant consideration for individuals pursuing this career path. It reflects the anticipated demand for professionals skilled in designing, developing, testing, and maintaining aircraft, spacecraft, and related systems. Factors such as technological advancements, government spending on space exploration and defense, and the growth of the commercial aviation sector all influence the opportunities available to graduates and experienced engineers alike.
Understanding the expected demand is crucial for several reasons. It aids prospective students in making informed decisions about their education and career goals, allowing them to assess the potential return on investment in an aerospace engineering degree. It assists universities in tailoring their programs to meet the evolving needs of the industry. Furthermore, it enables current professionals to anticipate future trends and proactively develop the skills necessary to remain competitive.
This analysis will delve into the key drivers affecting the demand for these skilled professionals, examine relevant data from reputable sources, and discuss potential challenges and opportunities that may arise in the coming years. It will also address specific areas of specialization within the field and their corresponding prospects.
Strategic career planning is essential for aspiring and practicing aerospace engineers. The following tips can enhance prospects within this competitive field.
Tip 1: Prioritize Relevant Education. A strong foundation in mathematics, physics, and engineering principles is paramount. Advanced degrees or specialized certifications can significantly improve job prospects.
Tip 2: Cultivate In-Demand Skills. Proficiency in CAD/CAM software, computational fluid dynamics (CFD), and finite element analysis (FEA) is highly valued by employers. Furthermore, skills in systems engineering and project management are increasingly important.
Tip 3: Seek Internship Opportunities. Practical experience gained through internships or co-op programs provides invaluable insight into the industry and allows for the development of professional networks.
Tip 4: Network Strategically. Attending industry conferences, joining professional organizations like the American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics (AIAA), and connecting with engineers on professional networking platforms can expand career opportunities.
Tip 5: Tailor Resumes and Cover Letters. Emphasize skills and experiences that directly align with the requirements of specific job postings. Quantifiable achievements and contributions should be highlighted.
Tip 6: Stay Abreast of Technological Advancements. The aerospace industry is constantly evolving. Continuously updating knowledge through professional development courses, industry publications, and online resources is crucial for long-term success.
Tip 7: Consider Government Service. Government agencies offer stable opportunities and involvement in significant technological programs. Familiarize oneself with available roles and necessary qualifications.
These proactive measures, combined with a strong academic foundation and a commitment to continuous learning, can significantly enhance career prospects in the dynamic field of aerospace engineering.
The subsequent sections will explore specific career paths and emerging trends that impact opportunities for professionals in this discipline.
1. Government spending
Government expenditure plays a pivotal role in shaping the employment landscape for aerospace engineers. As a major funding source for research and development, defense programs, and space exploration initiatives, governmental allocations directly influence the demand for skilled professionals in this sector. An increase in government funding typically translates to more projects, expanded research efforts, and the creation of new positions for engineers in various specialties, including design, testing, and systems integration. For instance, a significant investment in a new generation of military aircraft or a renewed focus on lunar missions necessitates a surge in the employment of aerospace engineers.
Conversely, reductions in government spending can lead to project cancellations, hiring freezes, and potential layoffs. The cyclical nature of government appropriations, often influenced by political priorities and economic conditions, introduces an element of uncertainty. The Space Shuttle program’s eventual termination, for example, led to considerable job losses in specific areas of aerospace engineering, illustrating the direct impact of policy shifts. Therefore, monitoring government budgets and policy decisions is critical for understanding the near-term prospects in the field.
In summary, governmental financial commitment serves as a substantial determinant of the employment situation. Its influence is multifaceted, shaping the direction of technological innovation and the availability of career pathways. Staying informed about relevant government actions is thus imperative for both aspiring and current aerospace professionals navigating the evolving job market.
2. Technological advancements
Technological advancements function as a primary driver influencing the demand for aerospace engineers. Innovations across various domains within the aerospace industry directly create new opportunities and reshape existing roles. The development of novel materials, propulsion systems, and avionics technologies necessitates specialized expertise in design, manufacturing, and testing. For example, the growing adoption of composite materials in aircraft construction requires engineers with knowledge of composite mechanics, manufacturing processes, and non-destructive testing techniques. Similarly, advancements in electric propulsion systems for aircraft and spacecraft are creating a need for engineers with expertise in electrical engineering, battery technology, and power electronics. These developments expand the scope of work for aerospace engineers, requiring adaptation and the acquisition of new skills.
The rise of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) or drones provides another compelling example. The design, development, and deployment of UAVs across diverse applications, including surveillance, delivery, and agriculture, has led to a significant increase in demand for aerospace engineers specializing in areas such as aerodynamics, control systems, and autonomous navigation. Furthermore, the increasing emphasis on sustainability within the aviation sector is fostering innovation in areas such as fuel-efficient aircraft designs and alternative fuels, generating opportunities for engineers focused on environmental considerations and green technologies. These examples highlight how ongoing technological progress directly translates into a changing skill set needed in the field and the creation of specialized job roles.
In conclusion, technological advancements are not merely external factors influencing the profession; they are integral components shaping the qualifications and required expertise of aerospace engineers. A proactive approach to learning and adapting to emerging technologies is essential for sustained career success. The capacity to embrace innovation and develop expertise in cutting-edge areas will be a key differentiator in a competitive job market, ensuring continued relevance and contribution to the field.
3. Industry growth
Industry expansion directly correlates with the availability of positions for aerospace engineers. As the aerospace sector experiences increased demand for its products and services, a corresponding need for skilled professionals to design, develop, and maintain these systems arises. This growth can stem from various sources, including increased air travel, rising defense spending, the expansion of the space industry, and the development of new aerospace technologies. When airlines order new aircraft, for example, manufacturers require additional engineers to meet production demands. Similarly, increased investment in space exploration initiatives drives the hiring of engineers specializing in spacecraft design and propulsion systems. Therefore, the overall health and trajectory of the aerospace industry serve as a primary indicator of employment prospects for engineers in this field.
The specific sectors experiencing growth within the aerospace industry can also influence the types of engineering roles in demand. For instance, the burgeoning commercial space sector, with companies like SpaceX and Blue Origin, has created opportunities for engineers specializing in reusable rocket technology and space-based manufacturing. The increased focus on sustainable aviation is also driving demand for engineers with expertise in alternative fuels, electric propulsion, and fuel-efficient aircraft designs. Understanding which sub-sectors are expanding allows individuals to tailor their skills and education to meet the specific needs of the job market. Monitoring industry reports, company announcements, and technological trends is crucial for identifying these growth areas and positioning oneself for emerging opportunities.
In summary, the expansion of the aerospace industry is a critical factor determining the employment outlook for engineers in this field. The overall growth of the sector, as well as the specific areas experiencing increased activity, directly impact the availability of jobs and the types of skills that are most highly sought after. By staying informed about industry trends and proactively developing expertise in relevant areas, aerospace engineers can significantly enhance their career prospects and contribute to the continued advancement of this vital sector.
4. Globalization impacts
Globalization exerts considerable influence on the employment prospects of aerospace engineers. The interconnected nature of the modern aerospace industry necessitates understanding the multifaceted effects of global economic and political dynamics.
- Offshoring and Outsourcing
Globalization facilitates the movement of aerospace manufacturing and engineering services to locations with lower labor costs. This can result in a decrease in certain types of engineering positions in developed countries as companies seek to reduce expenses. Conversely, it can create new opportunities in emerging economies with growing aerospace sectors, impacting the geographic distribution of jobs.
- International Collaboration
Large-scale aerospace projects, such as the development of new aircraft or space exploration initiatives, increasingly involve collaboration between companies and governments from multiple countries. This necessitates aerospace engineers to possess strong communication and cross-cultural skills to effectively work within international teams. It also creates opportunities for engineers to gain international experience and exposure to diverse engineering practices.
- Global Competition
Globalization intensifies competition among aerospace companies worldwide. To remain competitive, companies must innovate and improve efficiency, driving the demand for engineers with expertise in areas such as advanced manufacturing, automation, and data analytics. Engineers who can contribute to streamlining processes, reducing costs, and developing cutting-edge technologies are highly valued in this globalized environment.
- Supply Chain Complexity
The globalization of aerospace supply chains means that components and materials are sourced from various countries around the world. This requires engineers to have a deep understanding of global supply chain management, including logistics, quality control, and risk mitigation. Engineers with expertise in these areas are essential for ensuring the efficient and reliable operation of complex aerospace systems.
In summary, globalization has fundamentally reshaped the environment, creating both challenges and opportunities for professionals. Adapting to the dynamics of the global market requires developing skills in international collaboration, advanced technologies, and supply chain management to ensure continued success in this evolving landscape.
5. Competition intensity
A heightened level of rivalry among aerospace firms directly influences the availability of employment for aerospace engineers. Intense competition within the industry necessitates that companies prioritize innovation, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness to maintain market share. This drive compels firms to seek out highly skilled and specialized engineers capable of contributing to these objectives. Consequently, while competition can lead to pressure on wages or staffing levels in certain areas, it also fosters demand for top-tier talent possessing cutting-edge technical expertise. For instance, the race to develop more fuel-efficient aircraft engines has spurred significant hiring in the fields of thermodynamics, materials science, and computational fluid dynamics.
The effect of competitive dynamics on job prospects is not uniform across all sectors within aerospace. Areas experiencing intense competition, such as commercial aviation or the development of unmanned aerial systems (UAS), tend to exhibit greater demand for engineers with specific skillsets aligned with the competitive priorities. Conversely, more consolidated or regulated sectors may present fewer opportunities for rapid career advancement or significant job growth. The rise of new entrants and disruptive technologies, such as electric propulsion or reusable launch systems, further intensifies competition, leading established firms to invest heavily in research and development, thereby creating new roles for engineers capable of driving innovation. Understanding these competitive pressures is crucial for engineers seeking to navigate the job market effectively.
In conclusion, the degree of competition within the aerospace industry is a key determinant of the employment landscape for its engineering workforce. While competition can create challenges related to job security and wage pressures, it also acts as a catalyst for innovation and technological advancement, leading to demand for specialized skills and expertise. Aerospace engineers who possess the qualifications and adaptability to thrive in a competitive environment are well-positioned to capitalize on the opportunities that arise from this dynamic landscape.
6. Economic cycles
Economic cycles, characterized by periods of expansion and contraction, exert a demonstrable influence on the employment prospects for aerospace engineers. Periods of economic growth typically correlate with increased demand for air travel, heightened defense spending, and greater investment in space exploration. This heightened activity leads to an expansion of aerospace industry operations, resulting in a greater need for engineers across various specializations, including design, testing, and manufacturing. The commercial aviation sector, for instance, experiences increased aircraft orders during economic booms, driving demand for aerospace engineers to support production and development efforts. Conversely, economic recessions often lead to reduced air travel, decreased defense budgets, and curtailed investment in space programs. This contraction of activity typically translates to hiring freezes, project cancellations, and potential layoffs within the aerospace engineering workforce.
The susceptibility of the aerospace industry to economic fluctuations underscores the importance of understanding these cyclical patterns. During periods of economic uncertainty, aerospace companies may postpone or cancel long-term projects, impacting job stability for engineers. The 2008 financial crisis, for example, resulted in significant cutbacks in aircraft production and delays in space exploration programs, leading to job losses for aerospace engineers across the industry. While some sectors, such as defense, may be relatively insulated from economic downturns due to ongoing national security needs, the overall impact of economic cycles on the aerospace engineering job market remains significant. The ability to anticipate and adapt to these fluctuations is thus critical for professionals in this field. Staying informed about macroeconomic indicators, industry trends, and company performance can enable aerospace engineers to make informed career decisions and proactively manage their professional development.
In summary, economic cycles are a fundamental determinant of the availability for professionals. Fluctuations in economic activity directly impact demand for aerospace products and services, thereby shaping the hiring landscape for engineers. While the aerospace industry can be subject to these cycles, understanding their patterns and proactively adapting to changing conditions remains a key strategy for individuals seeking to navigate the aerospace engineering job market successfully. A long-term perspective, combined with adaptability and continuous learning, can help aerospace engineers weather economic downturns and capitalize on opportunities that arise during periods of growth.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding the Prospects for Aerospace Engineering Positions
This section addresses common inquiries concerning the employment opportunities available to qualified aerospace engineering professionals. The answers provided are intended to offer clarity and guidance based on current industry trends and expert projections.
Question 1: What factors primarily influence availability within aerospace engineering?
Government spending on defense and space exploration, technological advancements in areas such as sustainable aviation and electric propulsion, and the overall health of the commercial aviation sector are key determinants. Economic cycles and global competition also play significant roles.
Question 2: Does the demand differ across various specializations within aerospace engineering?
Yes. Specializations such as propulsion systems, aerodynamics, structural design, and avionics may experience varying degrees of demand depending on current industry priorities and technological advancements. Emerging fields like unmanned aerial systems (UAS) and space-based manufacturing are also creating new opportunities.
Question 3: How can aspiring aerospace engineers enhance job prospects upon graduation?
A strong academic foundation in mathematics, physics, and engineering principles is essential. Pursuing internships, developing proficiency in industry-standard software (e.g., CAD/CAM, CFD), and networking with professionals in the field can significantly improve job prospects. Acquiring specialized certifications or advanced degrees may also be beneficial.
Question 4: What role does globalization play in the employment landscape for aerospace engineers?
Globalization influences job distribution, as companies may offshore or outsource engineering services to lower-cost locations. It also necessitates strong communication and cross-cultural skills due to international collaborations. Furthermore, globalization intensifies competition, driving demand for engineers with expertise in advanced manufacturing and data analytics.
Question 5: Are government positions a viable career path for aerospace engineers?
Yes. Government agencies such as NASA and the Department of Defense offer stable opportunities and involvement in significant technological programs. These positions often require specific security clearances and may involve contributing to national security objectives.
Question 6: How important is it for aerospace engineers to stay updated on technological advancements?
Continuous learning and professional development are crucial for long-term success. The aerospace industry is constantly evolving, and engineers must stay abreast of emerging technologies and industry trends to remain competitive and contribute effectively. Failure to do so may result in skills becoming obsolete.
In summary, understanding the multifaceted factors influencing aerospace engineering positions requires staying informed about industry trends, economic conditions, and technological advancements. Proactive career planning and continuous skill development are essential for navigating this dynamic job market.
The following section will delve into strategies for adapting to potential challenges and capitalizing on opportunities in the aerospace engineering field.
Concluding Remarks on Aerospace Engineering Employment
This analysis has explored the multifaceted dimensions of “what is the job outlook for aerospace engineers,” considering the influence of government spending, technological advancements, industry growth, globalization, competition, and economic cycles. The availability is demonstrably shaped by these interconnected factors, demanding proactive adaptation and strategic career planning from aspiring and practicing professionals.
The aerospace engineering field presents both significant opportunities and potential challenges. Continuous monitoring of industry trends, acquisition of in-demand skills, and adaptability to evolving technological landscapes remain paramount for sustained career success. While economic uncertainties and global competition necessitate vigilance, the pursuit of innovation and commitment to excellence will define the future trajectory of professionals within this vital sector. The ongoing advancement of aerospace technology hinges on the expertise and dedication of its engineering workforce.