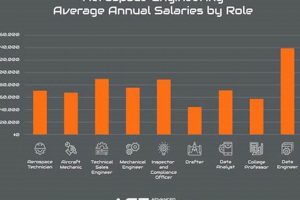
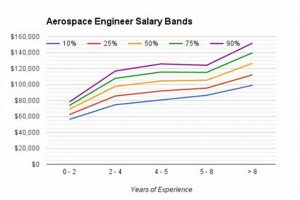
The standing of the University of Texas at Austin’s aerospace engineering program reflects its perceived quality and competitiveness relative to similar programs at other institutions. These evaluations, often published by reputable organizations, take into account factors such as research output, faculty expertise, student selectivity, and employer reputation. A high position typically signifies a program that offers rigorous academic training and prepares graduates for successful careers in the aerospace industry.
A favorable assessment can be crucial for attracting top students, securing research funding, and enhancing the program’s overall prestige. Historically, consistently high evaluations have allowed the program to build strong relationships with industry partners and government agencies, facilitating opportunities for internships, research collaborations, and career placement for graduates. The reputation stemming from this assessment also contributes to the university’s overall academic standing.
The subsequent sections will delve into the specific criteria used in these assessments, provide an overview of recent standings, and explore the factors that contribute to the program’s placement, including faculty research, student outcomes, and industry connections.
Strategies for Aspiring Aerospace Engineers
The standing of an aerospace engineering program provides insights for prospective students and faculty. Analyzing the criteria contributing to a program’s high assessment can inform strategies for academic and professional success in the field.
Tip 1: Prioritize a Strong Foundation in Mathematics and Physics: A rigorous understanding of fundamental scientific principles is essential for success in aerospace engineering. Coursework in calculus, differential equations, linear algebra, and physics should be prioritized to build a solid foundation for advanced topics.
Tip 2: Seek Research Opportunities: Active participation in research projects provides invaluable experience in applying theoretical knowledge to real-world problems. Engage with faculty, attend research seminars, and explore opportunities to contribute to ongoing research initiatives.
Tip 3: Develop Expertise in Computational Tools: Proficiency in software packages used for modeling, simulation, and data analysis is highly valued in the aerospace industry. Familiarize yourself with tools such as MATLAB, ANSYS, and SolidWorks through coursework, independent study, and project work.
Tip 4: Cultivate Strong Communication Skills: Effective communication is crucial for collaborating with engineers from diverse backgrounds and presenting technical information to both technical and non-technical audiences. Practice written and oral communication skills through coursework, presentations, and group projects.
Tip 5: Pursue Internships and Industry Experience: Gaining practical experience through internships provides valuable insights into the aerospace industry and allows for the application of classroom knowledge in a professional setting. Seek out internships at aerospace companies, government agencies, and research institutions.
Tip 6: Participate in Extracurricular Activities: Involvement in aerospace-related clubs and organizations provides opportunities to network with peers, attend industry events, and gain hands-on experience through design projects and competitions. Consider joining organizations such as AIAA or the Society of Women Engineers.
Tip 7: Focus on Specialization Areas: Aerospace engineering encompasses a broad range of disciplines, including aerodynamics, propulsion, structures, and control systems. Identify areas of interest and pursue specialized knowledge through elective coursework and research projects.
Consistently demonstrating these attributes throughout academic and professional pursuits strengthens one’s qualifications, mirroring factors that contribute to a top-ranked aerospace engineering program. Prioritization of fundamentals, research, communication, practical experience, and specialization enhances career prospects.
The next section explores the potential career paths available to graduates of highly regarded aerospace engineering programs.
1. Reputation
In the context of university programs, reputation significantly influences evaluations. For the University of Texas at Austin’s aerospace engineering program, a favorable reputation acts as a catalyst for attracting resources, talented individuals, and collaborative opportunities, all impacting its standing.
- Survey-Based Assessments
Reputation is often gauged through surveys of academics and industry professionals. Positive perceptions among these groups contribute to a higher standing. Consistently high marks in surveys suggest a program is well-regarded within its field.
- Employer Recognition
The perception of employers regarding the quality of graduates heavily impacts a program’s reputation. If graduates are consistently sought after and perform well in the aerospace industry, the programs assessment will likely improve. This is due to employer feedback factoring into the ranking methodologies used by evaluators.
- Influence on Funding
A strong reputation can attract funding from both public and private sources. Funding enables programs to invest in facilities, faculty, and research, which in turn strengthens the program and potentially improves its assessment. A positive image can lead to greater philanthropic contributions, governmental grants, and research contracts.
- Attraction of Top Students and Faculty
A program with a stellar reputation tends to attract highly qualified students and faculty. These individuals contribute to the program’s overall intellectual environment and research output, further enhancing its reputation and potentially improving its standing. High-caliber faculty attract more research grants and students contribute to a thriving environment.
The interconnectedness of reputation, funding, faculty, students, and employer perceptions creates a feedback loop that significantly influences program standing. The University of Texas at Austin’s aerospace engineering ranking is thus deeply intertwined with its established and maintained reputation within the academic and professional communities.
2. Faculty Expertise
The expertise of the faculty within the University of Texas at Austin’s aerospace engineering program is a critical determinant of its evaluations. The knowledge, experience, and research contributions of faculty members directly influence the quality of education, research output, and the overall reputation of the program. The program’s standing is inextricably linked to the collective expertise of its faculty.
- Research Contributions and Publications
Faculty research productivity, measured by publications in reputable journals and presentations at conferences, reflects the cutting-edge nature of the program. High publication rates and impactful research findings elevate the institution’s standing. For instance, faculty involvement in advanced propulsion systems research and their peer-reviewed publications in related journals enhance the program’s standing.
- Industry Experience and Collaborations
Faculty members with practical experience in the aerospace industry provide students with real-world insights and connections. Collaborations with industry partners often lead to research funding, internship opportunities for students, and curriculum development that aligns with industry needs. A faculty member who has previously worked at NASA, for example, will bring significant practical experience and industry connections that benefit the program.
- Teaching Excellence and Mentorship
Effective teaching and mentorship are essential for developing skilled aerospace engineers. Faculty members who are dedicated to student success, provide engaging instruction, and offer personalized guidance contribute to a positive learning environment. This commitment fosters student achievement, which is often considered in program evaluations.
- National and International Recognition
Faculty awards, honors, and leadership positions in professional organizations reflect their standing within the aerospace engineering community. National recognition, such as being elected to the National Academy of Engineering, enhances the program’s prestige and attracts top students and faculty. Faculty expertise, validated through awards and recognition, thus contributes directly to UT Austin aerospace engineering ranking.
In conclusion, faculty expertise, manifested through research, industry involvement, teaching, and recognition, significantly contributes to UT Austin’s aerospace engineering standing. The collective achievements of the faculty translate into a high-quality educational experience, impactful research outcomes, and a strong reputation, all of which are reflected in the program’s evaluation.
3. Research Output
Research output is a cornerstone of academic program assessment. For the aerospace engineering program at the University of Texas at Austin, the volume, quality, and impact of research directly influence evaluations. This section explores key facets of research output and their specific relevance to the program’s standing.
- Peer-Reviewed Publications
The number of publications in high-impact, peer-reviewed journals serves as a primary indicator of research productivity. A higher volume of publications signals a commitment to advancing knowledge within the field. Publications authored by UT Austin aerospace engineering faculty in journals such as the “AIAA Journal” or “Acta Astronautica” demonstrate the program’s contribution to the scientific literature and positively impact the rankings.
- Citations and Impact Factor
Beyond the sheer number of publications, the frequency with which these publications are cited by other researchers indicates their influence and significance within the scientific community. High citation counts and impact factors signify that the research conducted at UT Austin is influential and contributes significantly to the progression of aerospace engineering. These metrics are carefully considered during evaluations.
- Funded Research Projects
The amount of funding secured through competitive grants and contracts reflects the program’s ability to attract external support for its research endeavors. Funding from agencies like NASA, the Department of Defense, and industry partners validates the program’s research agenda and provides resources for conducting cutting-edge research. A significant portfolio of funded research projects at UT Austin bolsters its assessment.
- Patents and Technology Transfer
The creation of new technologies and intellectual property, as evidenced by patents awarded and licensing agreements, demonstrates the program’s commitment to innovation and its potential for translating research findings into practical applications. Successful technology transfer to industry partners indicates that the research conducted at UT Austin has real-world value and contributes to economic development. These innovation metrics have increasing weight in assessments.
The interplay between publications, citations, funding, and innovation showcases the multifaceted nature of research output. Consistently high performance across these indicators underscores the robust research environment at the University of Texas at Austin’s aerospace engineering program and directly enhances its evaluations by demonstrating tangible contributions to the field.
4. Student Selectivity
Student selectivity, defined as the rigor of the admissions process and the academic qualifications of admitted students, significantly impacts the perceived quality of an aerospace engineering program. A highly selective program, such as that at the University of Texas at Austin, can attract a pool of academically gifted and highly motivated individuals. This, in turn, creates a more challenging and stimulating learning environment, fostering higher achievement and innovation within the program. Student selectivity is often measured by metrics such as average standardized test scores (SAT/ACT) and high school GPA of incoming students, as well as the acceptance rate of the program.
The connection between student selectivity and program ranking is multifaceted. Highly selective programs benefit from a student body that is better prepared to tackle advanced coursework and research projects, leading to increased research output and a stronger reputation among faculty and industry professionals. This enhanced academic environment and the increased likelihood of student success contribute directly to a higher program assessment. For example, if the University of Texas at Austin’s aerospace engineering program consistently admits students with high standardized test scores and GPAs, it signals to ranking organizations that the program is attracting top talent, which can improve its assessment.
In conclusion, student selectivity is a crucial component of a program’s quality and is directly linked to its evaluation. Selective programs tend to foster an environment of academic rigor and high achievement, which contributes to the overall reputation and research output, and leads to greater success for its graduates, ultimately impacting the overall standing. The practical significance of understanding this link lies in the strategic focus institutions may place on attracting and admitting highly qualified students to enhance their program’s perceived quality and improve placement.
5. Funding Resources
Funding resources are a critical determinant of the evaluation for the University of Texas at Austin’s aerospace engineering program. The availability of financial support influences a program’s capacity to attract and retain high-caliber faculty, invest in advanced facilities, and support cutting-edge research endeavors. Enhanced funding directly translates to improved resources, contributing to a more robust academic environment and positively affecting the evaluation. For example, substantial grants from federal agencies, like NASA, enable the program to engage in large-scale research projects, yielding significant findings and elevating its reputation. Conversely, inadequate funding can lead to faculty attrition, outdated equipment, and reduced research output, ultimately hindering progress and impacting the rankings.
The allocation of funding resources within the program also plays a crucial role. Investments in graduate student support, such as fellowships and research assistantships, attract top applicants and foster a research-intensive culture. Moreover, funding earmarked for specialized laboratories and computational resources enables faculty and students to pursue innovative projects and develop expertise in emerging areas of aerospace engineering. Consider the Cockrell School of Engineering’s emphasis on interdisciplinary research. Sufficient funding encourages this collaboration between departments, leading to innovative projects that garner national recognition and boost the overall assessment. The practical application of this understanding lies in strategic resource allocation, prioritizing investments that maximize the program’s research capabilities and educational offerings.
In summary, funding resources are inextricably linked to the success and evaluation of the aerospace engineering program at the University of Texas at Austin. Adequate and strategically allocated funding enables the program to attract top talent, invest in state-of-the-art infrastructure, and produce impactful research. The availability and deployment of these resources are essential components in enhancing the program’s reputation and maintaining a competitive assessment among its peers. The proactive pursuit of funding opportunities and efficient resource management are therefore critical to the program’s continued success and standing.
6. Industry Connections
A strong network of connections with the aerospace industry directly enhances a university’s program evaluation. For the University of Texas at Austin, these connections serve as a conduit for internships, research collaborations, and employment opportunities for graduates. The presence of robust industry partnerships signals to assessment bodies that the program is producing graduates who are well-prepared to enter the workforce and contribute to the aerospace sector. A program with close ties to companies like Lockheed Martin or Boeing demonstrates practical relevance and alignment with industry needs, factors that positively influence its assessment.
These industry collaborations often lead to sponsored research projects, providing funding and real-world context for faculty and students. For example, a partnership with a space exploration company could involve collaborative research on advanced propulsion systems, generating valuable data and potentially leading to innovative technologies. Moreover, advisory boards comprising industry leaders can provide guidance on curriculum development, ensuring that the program remains current and relevant to the evolving needs of the aerospace sector. Such engagement benefits students by offering exposure to industry practices, enhancing their skills, and creating networking opportunities that facilitate career placement upon graduation. A concrete outcome of such collaboration is high employment rate of graduates.
In summary, robust industry connections are a significant factor in enhancing the assessment of an aerospace engineering program. These connections enable the program to provide practical experiences, conduct relevant research, and produce graduates who are highly sought after by employers. The University of Texas at Austin’s aerospace engineering program’s standing is therefore intrinsically linked to the strength and breadth of its relationships with industry partners, highlighting the importance of fostering and maintaining these collaborations to ensure continued program success and positive evaluation outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following questions address common inquiries regarding the evaluation and standing of the aerospace engineering program at the University of Texas at Austin. These answers are intended to provide clarity and context regarding the factors influencing its assessment.
Question 1: What specific criteria are used to determine the UT Austin Aerospace Engineering ranking?
Evaluations typically consider factors such as faculty expertise and research productivity, student selectivity and graduate outcomes, program reputation among academics and employers, and the availability of resources and funding. Methodologies may vary among ranking organizations.
Question 2: How frequently is the UT Austin Aerospace Engineering ranking updated?
Ranking organizations generally release updated assessments on an annual basis, although the exact timing may differ. These updates reflect changes in program performance, faculty accomplishments, and evolving evaluation criteria.
Question 3: Where can official UT Austin Aerospace Engineering ranking information be found?
Information is published by ranking organizations such as U.S. News & World Report, QS World University Rankings, and others. The University of Texas at Austin’s official website may also provide summaries of its rankings.
Question 4: How does the UT Austin Aerospace Engineering ranking impact career opportunities for graduates?
A favorable evaluation can enhance the program’s reputation among employers, potentially increasing the demand for its graduates and improving their access to competitive job opportunities in the aerospace industry.
Question 5: What steps does the University of Texas at Austin take to improve its Aerospace Engineering ranking?
The university may invest in faculty recruitment and development, enhance research facilities, increase student support, and strengthen industry partnerships to improve its program’s overall quality and evaluation.
Question 6: Does a high UT Austin Aerospace Engineering ranking guarantee admission to the program?
A high evaluation is not a guarantee of admission. Admission remains highly competitive, and decisions are based on a holistic review of each applicant’s qualifications, including academic record, standardized test scores, and extracurricular activities.
In summary, the ranking of the aerospace engineering program at UT Austin is a complex reflection of various factors, all of which contribute to the program’s overall quality and reputation. Understanding these factors can provide valuable insights for prospective students, current students, and alumni.
The subsequent section explores resources for prospective students interested in learning more about the UT Austin Aerospace Engineering program.
Conclusion
This exploration of the UT Austin aerospace engineering ranking has illuminated the multifaceted elements influencing its standing. Factors such as faculty expertise, research output, student selectivity, funding resources, and industry connections collectively shape the program’s overall evaluation. Understanding these determinants provides a framework for assessing the program’s strengths and areas for potential improvement.
The UT Austin aerospace engineering ranking serves as a vital benchmark for prospective students, faculty, and stakeholders. Continued dedication to academic excellence and strategic investment in key areas will be critical for maintaining and enhancing the program’s standing in the future, thus solidifying its position as a leader in aerospace education and research.


![Top Aerospace Engineering Masters Programs [Ranked] Innovating the Future of Flight with Reliable Aviation Solutions Top Aerospace Engineering Masters Programs [Ranked] | Innovating the Future of Flight with Reliable Aviation Solutions](https://mixaerospace.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/th-459-300x200.jpg)