Opportunities for specialists in the design, development, and testing of aircraft and spacecraft within the greater Houston metropolitan area are the focus of this overview. This includes positions at NASA’s Johnson Space Center, as well as various private aerospace firms and related industries located throughout the region. These roles typically demand a strong background in engineering principles, mathematics, and physics, with a specialized focus on aerospace disciplines.
The availability of these specialized roles is significantly influenced by the region’s prominent position within the aerospace sector, particularly due to NASA’s presence and the support it provides to a network of contractors. The benefits of pursuing such a career in this location extend beyond the immediate job scope, often including access to professional networks, specialized training, and the potential for career advancement within a thriving aerospace ecosystem. Historically, the area has been a hub for space exploration and aeronautical innovation, creating a deeply rooted culture of engineering excellence.
The following sections will provide a more detailed examination of specific roles available, the required qualifications, salary expectations, and key employers in the Houston area relevant to individuals seeking positions in this specialized field.
The subsequent guidance is intended to assist qualified professionals in effectively pursuing and securing positions related to aircraft and spacecraft engineering in the Houston metropolitan area. The information provided is focused on optimizing candidacy and ensuring a strategic approach to the job search.
Tip 1: Tailor Application Materials: Adapt resumes and cover letters to align precisely with the requirements specified in each job description. Highlight relevant experience, technical skills, and specific projects that demonstrate proficiency in areas sought by the employer.
Tip 2: Emphasize NASA-Related Experience: If applicable, clearly articulate any previous experience working directly with NASA or its contractors. Detail the specific contributions made and the technologies utilized during such engagements.
Tip 3: Network Strategically: Attend industry events, conferences, and workshops to establish connections with professionals in the field. Leverage online platforms like LinkedIn to connect with recruiters and engineers working at target companies.
Tip 4: Obtain Relevant Certifications: Pursue certifications that demonstrate expertise in specific aerospace engineering domains, such as FAA Airframe and Powerplant licenses or specialized software proficiency. This can enhance credibility and marketability.
Tip 5: Research Key Employers: Conduct thorough research on major aerospace companies in the Houston area, including their mission, values, and current projects. This knowledge will enable candidates to articulate their interest and suitability for the organization.
Tip 6: Demonstrate Problem-Solving Abilities: When describing past projects and experiences, focus on the problem-solving skills employed. Provide concrete examples of challenges overcome and the methodologies used to achieve successful outcomes.
Tip 7: Prepare for Technical Interviews: Expect rigorous technical interviews that assess fundamental engineering principles, as well as knowledge of specific aerospace technologies. Practice answering common interview questions and be prepared to solve technical problems on the spot.
Implementing these strategies should contribute to a more focused and effective approach to securing a relevant career in the dynamic engineering landscape.
The following sections will provide a comprehensive overview of the skills, required educational attainment, and other critical factors which shape prospects within this field.
1. Location Advantage
The presence of NASA’s Johnson Space Center is the primary driver of the location advantage for specialist positions in the Houston metropolitan area. This government facility serves as a central hub for manned spaceflight activities, mission control, and astronaut training, generating a significant demand for engineers with expertise in related fields. This proximity fosters a concentration of private aerospace companies and contractors who provide specialized services and technologies to NASA, further amplifying employment opportunities in the region. The Johnson Space Center serves as the cause, while the proliferation of related positions is the effect.
The existence of a robust aerospace cluster near Johnson Space Center also facilitates collaboration and knowledge sharing among engineers. This leads to a higher level of innovation and specialized skill development among the workforce. Several examples reinforce this point, including Boeing, Lockheed Martin, and Jacobs Engineering, all of whom maintain a significant presence in Houston to support NASA programs. The location advantage means access to cutting-edge projects and technologies, allowing for engineers to continually expand their capabilities and contribute to advancements in space exploration and aeronautics.
In summary, the location advantage afforded by the concentration of aerospace activities in Houston, specifically due to the presence of the Johnson Space Center, is a fundamental factor in understanding the employment prospects available to specialists. While challenges may exist in terms of competition for desirable roles, the presence of a vibrant and established aerospace ecosystem creates a dynamic and rewarding environment for qualified candidates. This aspect is intrinsically linked to the broader theme of career opportunity within the relevant sector.
2. NASA Proximity
The geographical adjacency to NASA’s Johnson Space Center (JSC) fundamentally shapes the landscape for specialist roles in the Houston area. Its influence is not merely physical; it permeates the entire ecosystem, affecting job availability, specialization focus, and career trajectories.
- Direct Employment Opportunities
NASA JSC directly employs a significant number of aerospace engineers across various disciplines. These positions involve design, development, testing, and operational support for manned spaceflight missions, including the International Space Station and future exploration programs. Examples include thermal engineers, propulsion specialists, and structural analysts, each contributing to critical aspects of space exploration. A direct appointment provides unparalleled access to groundbreaking research and technological advancements.
- Contractor and Subcontractor Roles
A vast network of contractors and subcontractors surrounds NASA JSC, providing essential support services and specialized expertise. These companies employ numerous engineers in roles closely aligned with NASA’s needs, such as developing mission-critical software, designing spacecraft components, and conducting research on advanced materials. Lockheed Martin, Boeing, and Jacobs Engineering are examples of major contractors with a substantial presence in Houston. These positions offer opportunities to work on cutting-edge projects while operating within a more commercially oriented environment.
- Specialized Skill Development
The concentration of aerospace activities near NASA JSC fosters a culture of specialized skill development. Engineers in the area have access to advanced training programs, professional networks, and mentorship opportunities that enhance their technical capabilities. The constant demand for innovative solutions to complex engineering challenges encourages continuous learning and adaptation. This concentrated expertise makes the Houston area a prime location for companies seeking highly skilled individuals.
- Economic Impact and Growth
NASA’s presence stimulates the regional economy and drives growth in related industries. The influx of federal funding supports research and development initiatives, creating new job opportunities and attracting talent from across the nation. The economic benefits extend beyond the aerospace sector, impacting supporting industries such as manufacturing, logistics, and technology. This contributes to a stable and thriving job market for aerospace engineers.
In conclusion, the close proximity to NASA JSC is a defining characteristic shaping the specialist field in Houston. It provides a diverse range of employment opportunities, facilitates specialized skill development, and stimulates economic growth. This geographical advantage positions Houston as a central hub for aerospace innovation and career advancement.
3. Technical Expertise
Technical proficiency is a foundational pillar supporting the landscape of specialist positions in Houston. The high-technology nature of the aerospace industry demands a rigorous skill set and deep understanding of complex engineering principles. This expertise is not merely an advantage, but a necessity for success in this highly competitive field.
- Propulsion Systems Design and Analysis
This facet encompasses the knowledge and application of principles related to rocket engines, jet propulsion, and other thrust-producing systems. It requires an understanding of thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, and combustion processes. For example, positions at companies involved in developing the next generation of rocket engines for lunar or Martian missions demand expertise in designing efficient and reliable propulsion systems. The ability to analyze performance characteristics and optimize designs is crucial.
- Aerodynamics and Flight Mechanics
Proficiency in aerodynamics is essential for engineers involved in aircraft and spacecraft design. This includes understanding airflow patterns, lift and drag characteristics, and stability and control principles. These skills are indispensable for optimizing vehicle performance, ensuring safe flight characteristics, and predicting the impact of environmental factors. Example: engineers designing reentry vehicles for returning astronauts must possess a strong understanding of hypersonic aerodynamics to mitigate the effects of extreme heat and pressure.
- Structural Analysis and Materials Science
Aerospace engineers must possess a strong understanding of structural mechanics, materials science, and finite element analysis to ensure the structural integrity of aircraft and spacecraft. This includes selecting appropriate materials, analyzing stress distributions, and predicting the response of structures to various loads. For example, designing the lightweight yet robust structures needed for lunar landers requires expert knowledge of materials science and structural analysis. The safety and reliability of these vehicles depend heavily on this expertise.
- Systems Engineering and Integration
This encompasses the ability to integrate various engineering disciplines and components into a cohesive system. This demands a holistic understanding of the entire aerospace system, from requirements definition to testing and operation. Specialist roles in systems engineering require the ability to manage complexity, coordinate teams, and ensure that all components work together seamlessly. This is evident in the integration of complex avionics and flight control systems, essential for safe and efficient flight operations.
The aforementioned areas of proficiency are not isolated skills, but rather interconnected facets of a comprehensive skill set demanded by employers within Houston. The demand for individuals equipped with expertise in these domains underpins the robust and highly competitive job market for aerospace professionals in the region. These competencies, supported by practical experience and formal education, are critical for navigating and succeeding in the specialist arena.
4. Industry Growth
The expansion and evolution of the aerospace sector are intrinsically linked to the availability and nature of specialist positions in the Houston metropolitan area. Industry growth acts as a primary catalyst, directly influencing the demand for engineers with expertise in diverse sub-disciplines. An expanding sector necessitates a larger workforce to support ongoing projects, research initiatives, and future endeavors. This creates a positive feedback loop: growth generates opportunities, which attract talent, further fueling innovation and development.
A clear example of this dynamic can be observed in the surge of private spaceflight companies. As these entities pursue ambitious goals such as commercial space tourism and lunar resource extraction, they require a skilled engineering workforce to design and build spacecraft, develop advanced propulsion systems, and manage mission operations. The increased investment and activity within these organizations directly translates into more open roles. Furthermore, the growing focus on sustainable aviation and electric aircraft technologies presents new avenues for engineering specialization and career advancement. This is particularly relevant for those with backgrounds in areas like battery technology, advanced materials, and electric propulsion.
Understanding the correlation between industry growth and the specialist employment landscape is crucial for both job seekers and educators. Monitoring industry trends, emerging technologies, and government funding priorities allows individuals to anticipate future skill demands and tailor their education and training accordingly. Furthermore, it enables educators to develop curricula that meet the evolving needs of the sector, ensuring a pipeline of qualified engineers ready to contribute to advancements. While economic downturns or shifts in government policy can introduce uncertainty, the long-term outlook for the aerospace sector remains positive, making it a promising field for those with the necessary technical expertise and adaptability. The constant evolution of the aerospace sphere ensures a consistent flow of new and exciting opportunities for specialist roles, making industry growth a central component of the specialist field.
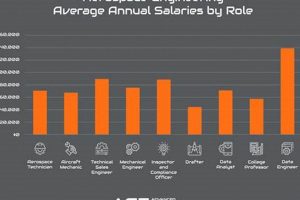
5. Competitive Salaries
The compensation offered for specialist roles in the Houston area is a significant component of the overall employment landscape. The promise of competitive salaries acts as a primary incentive, attracting qualified engineers from across the nation and internationally. This financial draw is directly linked to the concentration of high-profile aerospace organizations and government agencies in the region, most notably NASA’s Johnson Space Center. The demand for skilled personnel, coupled with the technical complexity inherent in aerospace engineering, necessitates attractive compensation packages to secure top talent. The effect is clear: competitive wages create a highly skilled and motivated workforce within the specialist arena.
The presence of a competitive salary structure also contributes to employee retention and job satisfaction. Professionals are more likely to remain with a company when they feel adequately compensated for their contributions and expertise. This reduces turnover rates, fosters a more stable work environment, and allows companies to invest in the long-term development of their employees. For example, major aerospace contractors such as Boeing and Lockheed Martin offer comprehensive benefits packages and performance-based bonuses, supplementing base salaries to incentivize excellence and dedication. The significance extends to attracting early-career engineers, solidifying the talent pipeline for future projects. This aspect demonstrates the practical application of this element in the relevant industry.
Understanding the role of compensation is critical for individuals navigating the specialist job market in Houston. While salaries are not the sole determining factor, they represent a tangible measure of the value placed on expertise and contributions within the aerospace sector. Navigating salary negotiations effectively, researching industry standards, and showcasing relevant skills are essential strategies for securing a competitive compensation package. However, cost of living adjustments may be required when comparing these benefits to similar sectors across the nation. In summary, a competitive salary structure is a fundamental aspect of the environment, directly impacting the ability to attract, retain, and motivate skilled professionals. This, in turn, supports the continued innovation and success of the Houston aerospace community.
6. Specialized Skills
A highly refined skillset is a prerequisite for securing relevant positions in the Houston area. The aerospace industry demands expertise that extends beyond general engineering principles, requiring proficiencies honed through specialized training and experience. This expertise directly impacts an engineer’s marketability and career trajectory within the sector.
- Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD)
Proficiency in CFD is essential for simulating and analyzing airflow around aircraft and spacecraft. This skill enables engineers to optimize aerodynamic designs, predict performance characteristics, and assess the impact of various environmental factors. For example, engineers designing reentry vehicles utilize CFD to model the extreme heat and pressure encountered during atmospheric entry. Positions requiring CFD expertise are prevalent at NASA and its contracting partners in Houston.
- Finite Element Analysis (FEA)
FEA is a crucial tool for evaluating the structural integrity of aerospace components and systems. This skill allows engineers to simulate stress distributions, predict failure modes, and optimize designs for weight and strength. For example, FEA is used to analyze the structural response of spacecraft during launch and landing, ensuring that components can withstand the extreme forces involved. Expertise in FEA is highly sought after by companies involved in spacecraft and aircraft manufacturing in Houston.
- Embedded Systems Development
A significant number of aerospace systems rely on embedded software and hardware for control, navigation, and communication. Expertise in embedded systems development is crucial for engineers working on flight control systems, avionics, and other critical components. For example, engineers developing autonomous flight systems for unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) require in-depth knowledge of embedded programming, sensor integration, and real-time operating systems. This is also true for many specialist roles.
- Materials Science and Engineering
The selection and application of advanced materials are critical for optimizing the performance and reliability of aircraft and spacecraft. Expertise in materials science and engineering is essential for engineers working on lightweight structures, thermal protection systems, and propulsion components. For example, engineers developing heat shields for reentry vehicles require a deep understanding of high-temperature materials and their behavior under extreme conditions. Research and development relating to aerospace are commonly performed in this market.
These specialized skills represent a subset of the expertise sought by aerospace employers in Houston. Possessing these, and other related proficiencies, enhances an engineer’s competitiveness and opens doors to a wide range of opportunities within the thriving local aerospace sector. The demand for such capabilities underpins the specialist market.
7. Project Variety
The breadth of projects available to aerospace engineers in the Houston area is a significant factor influencing the attractiveness and dynamism of the local job market. This project variety stems directly from the presence of NASA’s Johnson Space Center and the concentration of aerospace contractors supporting its mission. The effect is a diverse range of opportunities for engineers to apply their skills and expertise across different domains, preventing stagnation and promoting continuous learning. This abundance of disparate endeavors is not merely a perk; it’s a critical component shaping the professional trajectory for specialists.
Examples of this project variety include involvement in the design and development of spacecraft for lunar and Martian exploration, the maintenance and upgrades of the International Space Station, and the development of advanced propulsion systems. Furthermore, engineers in Houston may contribute to the development of commercial space vehicles, autonomous aircraft, and innovative aerospace technologies. The opportunity to work on projects ranging from manned spaceflight to unmanned aerial systems broadens an engineer’s skill set and enhances their adaptability. This flexibility is essential for navigating a rapidly evolving technological landscape and ensuring long-term career security. This is often manifested as “Engineer I” or “Engineer II” level roles, working under guidance of senior professionals.
In conclusion, the diversity of projects available in Houston is a key differentiator for the city’s aerospace job market. This project variety allows engineers to gain experience across multiple disciplines, expanding their knowledge base and enhancing their career prospects. While the demands of working on cutting-edge projects can be challenging, the opportunity to contribute to advancements in space exploration and aeronautics makes Houston a desirable location for specialist professionals. Understanding the correlation between project diversity and specialist is, therefore, fundamental for both job seekers and employers seeking to thrive in this innovative environment.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Opportunities for Aerospace Engineers in Houston
The following questions and answers address common inquiries and concerns pertaining to the job market for specialists involved in the design, development, and testing of aircraft and spacecraft within the Houston metropolitan area.
Question 1: What are the primary employers for aerospace engineers in Houston?
Key employers include NASA’s Johnson Space Center, as well as major aerospace contractors such as Boeing, Lockheed Martin, Jacobs Engineering, and numerous smaller firms supporting NASA’s missions. Opportunities may also exist within the growing private spaceflight sector.
Question 2: What educational qualifications are generally required?
A bachelor’s degree in aerospace engineering or a closely related field is typically the minimum requirement. Advanced degrees (master’s or doctorate) may be preferred for research-oriented positions or specialized roles.
Question 3: What types of skills are most in demand?
Skills in computational fluid dynamics (CFD), finite element analysis (FEA), systems engineering, propulsion systems design, and materials science are highly valued. Familiarity with industry-standard software and tools is also essential.
Question 4: What is the typical salary range for specialist positions in Houston?
Salary ranges vary depending on experience, education, and specific job responsibilities. Entry-level positions may start around \$70,000 per year, while experienced engineers can earn upwards of \$150,000 or more.
Question 5: How important is it to have NASA-related experience?
Prior experience working directly with NASA or its contractors is highly advantageous. Such experience demonstrates familiarity with NASA’s processes, standards, and technologies, making candidates more competitive.
Question 6: What resources are available to assist in the job search?
Online job boards (e.g., LinkedIn, Indeed, Glassdoor), professional organizations (e.g., AIAA), and networking events can provide valuable resources and connections. Targeted resume preparation and interview practice are also crucial.
These FAQs provide a concise overview of key considerations related to the specialist field in Houston. However, individual circumstances and career goals may necessitate further research and exploration.
The following sections will provide an action plan to help secure a specialist career.
Conclusion
This exploration of aerospace engineer jobs houston has detailed critical factors influencing career prospects within this sector. From the strategic advantage conferred by NASA’s Johnson Space Center to the imperative of specialized technical proficiency and the influence of industry growth, a comprehensive understanding of this environment is essential for prospective professionals. The significance of competitive salaries, the demand for specialized skills, and the diversity of available projects each contribute to a complex but potentially rewarding career path.
Success in securing aerospace engineer jobs houston necessitates proactive preparation, continuous skill development, and strategic networking. The future of aerospace in Houston, driven by both government initiatives and private sector innovation, presents significant opportunities for qualified individuals. However, continued awareness of industry trends and adaptability to evolving technological demands are crucial for sustained career advancement within this highly competitive and dynamic field.