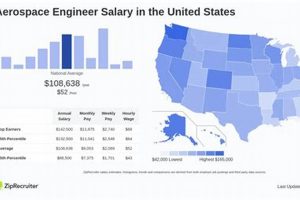
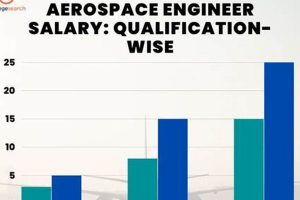
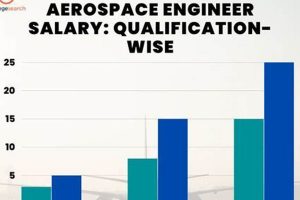
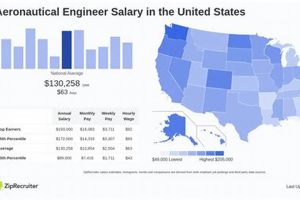
Compensation for professionals specializing in aircraft and spacecraft design, development, and testing within the French Republic varies considerably. This remuneration is affected by factors such as experience level, education, specialization, and the specific company or organization employing the engineer. For instance, an entry-level position at a smaller firm may offer a different compensation package than a senior role at a major aerospace corporation.
Understanding the financial aspects of a career path within the aerospace field in this European nation is vital for both prospective and current engineers. It allows individuals to make informed decisions about education, career choices, and negotiation strategies. Furthermore, comprehending the economic landscape assists in evaluating the overall attractiveness and sustainability of pursuing a career in this sector within the country.
The following discussion will delve into the specifics of typical compensation ranges, influential factors, regional variations, and a comparison with similar roles in other nations. Additionally, the influence of education, skills, and industry demand will be explored, providing a holistic view of earning potential within this specialized profession.
Insights on Maximizing Remuneration
Strategic career planning and proactive skill development can substantially influence earnings within the specialized field. The following insights offer guidance on enhancing financial prospects.
Tip 1: Acquire Advanced Certifications: Obtaining specialized certifications relevant to aerospace engineering, such as those related to specific software or industry standards, can demonstrably increase earning potential.
Tip 2: Pursue Continuous Education: Master’s degrees or doctorates in specialized areas, like propulsion systems or avionics, often correlate with higher compensation levels, especially in research and development roles.
Tip 3: Develop Niche Expertise: Focusing on in-demand areas, such as sustainable aviation or space exploration technologies, makes candidates more attractive to employers and justifies higher salary expectations.
Tip 4: Enhance Language Proficiency: Fluency in multiple languages, particularly English in addition to French, broadens employment opportunities and can lead to roles with international companies offering competitive compensation.
Tip 5: Cultivate Strong Negotiation Skills: Researching industry salary benchmarks and effectively communicating one’s value during salary negotiations is crucial for securing optimal compensation packages.
Tip 6: Seek Opportunities in High-Demand Regions: Relocating to regions with significant aerospace industry activity, such as Toulouse or areas near major aerospace hubs, can improve job prospects and associated remuneration.
Tip 7: Gain International Experience: Working on projects abroad, even for short periods, demonstrates adaptability and global perspective, enhancing appeal to multinational corporations.
By strategically focusing on continuous learning, specialization, and professional development, individuals can significantly improve their earning potential. This proactive approach positions candidates for greater financial success.
The subsequent sections will address regional variations in compensation and a comparative analysis with international standards, further enriching understanding of the overall economic landscape.
1. Experience Level
Experience level is a primary determinant of remuneration for aerospace engineers in France. Compensation structures typically reflect a progressive increase corresponding to accumulated years of professional practice and demonstrated expertise. This correlation is foundational to career advancement and financial stability within the sector.
- Entry-Level Positions (0-3 years)
Entry-level positions, such as junior engineers or graduate trainees, offer foundational experience. These roles typically involve supporting senior engineers and contributing to well-defined project tasks. Compensation at this level reflects the initial investment in professional development, with a focus on skill acquisition and integration into the industry’s technical workflows. For instance, a recent engineering graduate might begin with tasks like CAD modeling or assisting in system testing under the supervision of more experienced colleagues.
- Mid-Career Professionals (3-10 years)
Mid-career professionals demonstrate increasing autonomy and technical proficiency. These engineers often manage smaller projects or lead specific sub-teams within larger initiatives. They are expected to exhibit problem-solving skills, contribute to design reviews, and participate in technical decision-making. The salary range at this level acknowledges the value of practical experience and the ability to deliver results independently. For example, an engineer with five years of experience might be responsible for designing and testing a specific component of an aircraft’s control system.
- Senior Engineers (10+ years)
Senior engineers possess extensive experience and deep expertise in specialized areas. They typically lead large-scale projects, mentor junior engineers, and contribute to strategic planning. Senior roles involve significant responsibility for technical innovation, risk management, and project outcomes. Compensation reflects the value of their knowledge, leadership, and ability to drive complex engineering solutions. An example of a senior engineer’s role would be to lead the development of an entirely new propulsion system or manage a team designing a next-generation satellite.
- Expert/Principal Engineer (15+ years)
Expert or Principal Engineers possess a very high level of specialized knowledge, often functioning as technical authorities within their organizations. They are responsible for solving the most complex engineering problems, guiding technological direction, and contributing to the overall strategic goals of the company. Their expertise commands the highest salary ranges, reflecting the critical impact of their contributions to innovation and success. An example may be leading the development of a new aircraft wing design, or overseeing a complex international collaboration for a space mission.
The progression through these experience levels directly influences compensation within the aerospace engineering field in France. As engineers gain experience, their expertise and contributions become more valuable, leading to commensurate increases in salary and responsibilities. This structured career trajectory provides a clear framework for professional growth and financial advancement.
2. Education & Specialization
Academic qualifications and specialized expertise significantly influence earning potential within the aerospace engineering sector in France. A direct correlation exists between the level of education attained and the subsequent remuneration offered by employers. A Master’s degree or doctorate, particularly from a prestigious institution or in a highly specialized field such as propulsion, aerodynamics, or avionics, often translates to a higher starting salary and faster career advancement than a Bachelor’s degree alone. For instance, an engineer with a doctorate specializing in composite materials might command a premium due to the increasing demand for lightweight and fuel-efficient aircraft designs.
Specialization further enhances an engineer’s value proposition in the French aerospace market. The industry increasingly demands experts in niche areas like unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), satellite technology, or sustainable aviation practices. An engineer with expertise in a cutting-edge field is likely to receive more competitive offers compared to generalist candidates. The specific degree of specialization allows for higher-level contribution to more specific tasks. Example, an aerospace engineer who is specialized in fluid dynamics is more valuable than generalist candidate.
In summary, advanced education and specialization are pivotal drivers of elevated salaries within the aerospace engineering profession in France. Investment in higher education and the development of specialized skill sets position professionals for greater career opportunities and enhanced earning power. Such factors also allow engineer to be assigned to higher-level tasks.
3. Company Size & Type
The size and type of aerospace company significantly influence compensation levels for engineers in France. Larger organizations, often multinational corporations, typically offer more competitive salaries and comprehensive benefits packages compared to smaller enterprises. This disparity arises from the greater financial resources, established salary scales, and hierarchical structures characteristic of larger firms. For instance, a senior engineer at a major aerospace manufacturer like Airbus might receive a substantially higher salary and benefits package than an engineer with comparable experience at a small or medium-sized enterprise (SME) specializing in a niche area of aerospace technology.
Furthermore, the type of companywhether it is a research institution, a manufacturing firm, a government agency, or a consulting firmimpacts compensation structures. Research institutions may prioritize academic credentials and publications, offering lower base salaries but providing opportunities for research grants and intellectual property royalties. Manufacturing firms, focused on production efficiency and product development, tend to offer competitive salaries tied to performance metrics and project milestones. Government agencies often adhere to standardized pay scales based on experience and education, potentially providing job security and benefits but with less flexibility in salary negotiation. Consulting firms may offer high compensation packages contingent on project success and client billings, reflecting the specialized expertise and market demand for their services.
In summary, the combined effect of company size and type creates a diverse compensation landscape for aerospace engineers in France. Understanding these factors enables professionals to strategically target employment opportunities that align with their career goals and financial expectations. Larger, multinational corporations and specialized consulting firms tend to offer the most lucrative compensation packages, while research institutions and government agencies provide alternative benefits such as job security and opportunities for intellectual contribution.
4. Geographic Location
Geographic location exerts a considerable influence on compensation levels for aerospace engineers in France. Certain regions, particularly those with significant aerospace industry presence, exhibit higher salary benchmarks. This phenomenon arises from increased demand for skilled professionals, a concentration of major aerospace companies, and a generally higher cost of living compared to other areas. For instance, Toulouse, a prominent aerospace hub and home to Airbus headquarters, commands some of the highest salaries for aerospace engineers in the country. The concentration of job opportunities and the competitive labor market in such regions drive up compensation to attract and retain qualified personnel.
Conversely, regions with less developed aerospace sectors may offer lower salaries due to reduced demand and a lower cost of living. While the core skill set remains the same, the economic dynamics within a specific geographic area significantly affect the financial remuneration for the same role. For example, an aerospace engineer working on research and development in a smaller city with fewer industry connections may earn less than a counterpart in Toulouse or Paris, even with similar experience and qualifications. The availability of alternative employment opportunities and the overall economic vitality of the region play a crucial role in shaping salary expectations.
In summary, geographic location represents a critical determinant of salary variations within the aerospace engineering profession in France. The concentration of aerospace activity in specific regions, coupled with the cost of living and local economic conditions, drives significant differences in compensation. Understanding this spatial dynamic is essential for both prospective and current aerospace engineers seeking to maximize their earning potential and make informed career decisions based on regional opportunities.
5. Industry Demand
Industry demand constitutes a fundamental driver of compensation levels within the aerospace engineering sector in France. Increased demand for aerospace products and services directly translates to a greater need for qualified engineers, leading to upward pressure on salaries. This correlation is particularly evident during periods of economic expansion and technological advancement, when companies actively seek to expand their workforce and innovate to maintain a competitive edge. For example, the heightened interest in sustainable aviation technologies has fueled demand for engineers specializing in electric propulsion systems and alternative fuel sources, thereby increasing salaries for professionals with these specialized skills.
Conversely, periods of economic downturn or reduced investment in aerospace projects can lead to decreased demand for engineers, potentially resulting in salary stagnation or even reductions. The cyclical nature of the aerospace industry makes it susceptible to fluctuations in demand based on global economic conditions, government spending, and technological disruptions. Furthermore, government initiatives aimed at promoting the aerospace sector can also stimulate demand for engineers. For instance, investments in space exploration or the development of next-generation aircraft can generate numerous job opportunities and elevate salaries for specialized roles within these projects. Consider the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the aviation industry. This led to job insecurity and reduced salaries for many, highlighting the vulnerability of the sector to external shocks.
In summary, industry demand serves as a key determinant of aerospace engineer salary in France. The interplay between market forces, technological advancements, and government policies shapes the overall demand landscape, impacting both job availability and compensation levels. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for aerospace engineers to make informed career decisions and navigate the ever-changing economic environment. By monitoring industry trends and aligning skill sets with emerging demands, professionals can position themselves for greater career opportunities and enhanced earning potential within the French aerospace sector.
6. Skills & Certifications
The demonstrable skill set and possession of relevant certifications are critical determinants of remuneration for aerospace engineers in France. Employers place a premium on individuals who possess both a strong theoretical foundation and practical abilities aligned with industry needs, thus influencing salary offers and career progression.
- Technical Proficiency
Proficiency in industry-standard software, such as CATIA, MATLAB, and ANSYS, is highly valued. Employers seek candidates with demonstrable abilities in computer-aided design (CAD), computational fluid dynamics (CFD), and finite element analysis (FEA). For instance, an engineer proficient in simulating aircraft performance using CFD software will be more attractive to employers and command a higher salary than a candidate without this skill.
- Specialized Knowledge
In-depth knowledge of specific aerospace domains, such as aerodynamics, propulsion, avionics, or structural analysis, is a significant asset. Employers often seek candidates with specialized expertise that directly aligns with their project requirements. An engineer with expertise in composite materials used in aircraft construction, for instance, will be highly sought after and rewarded accordingly.
- Project Management Skills
Effective project management skills, including the ability to plan, execute, and monitor aerospace projects, are increasingly important. Employers value candidates who can manage project budgets, timelines, and resources effectively. An engineer certified in project management methodologies, such as PMP or PRINCE2, will demonstrate a commitment to professional development and command a higher salary.
- Industry Certifications
Relevant industry certifications, such as those related to aircraft maintenance, airworthiness standards, or safety regulations, can significantly enhance earning potential. Employers often require specific certifications for certain roles and responsibilities. An engineer certified as a Part 66 Aircraft Maintenance Engineer, for example, will possess the requisite skills and knowledge to perform maintenance tasks and therefore be a valuable asset.
In summary, the possession of relevant skills and certifications is pivotal in determining remuneration for aerospace engineers in France. A combination of technical proficiency, specialized knowledge, project management skills, and industry certifications significantly enhances a candidate’s value proposition and earning potential. Continuous professional development and acquisition of in-demand skills are therefore essential for maximizing career opportunities and salary growth in the French aerospace sector.
7. Economic Conditions
Economic conditions exert a significant influence on the remuneration of aerospace engineers in France. The overall health and stability of the French economy, as well as the global economic climate, directly impact the aerospace industry’s performance, which in turn affects the demand for engineers and their corresponding salaries. Periods of economic expansion typically lead to increased investment in aerospace projects, resulting in greater job opportunities and upward pressure on compensation. Conversely, economic recessions or downturns can trigger budget cuts, project cancellations, and workforce reductions, leading to salary stagnation or even declines.
Consider the impact of governmental fiscal policy. Tax incentives encouraging aerospace innovation, for example, can stimulate growth within the sector, boosting employment rates and driving up salaries to attract skilled engineers. Conversely, austerity measures or shifts in government priorities away from aerospace can negatively affect the industry’s financial health and the earnings potential of its workforce. The interconnectedness of these elements makes economic awareness crucial for engineers to adjust financial and career expectations.
In conclusion, economic conditions serve as a crucial external factor shaping the financial landscape for aerospace engineers in France. Macroeconomic trends, government policies, and the overall health of the aerospace industry collectively influence job availability, compensation levels, and career opportunities. Understanding these dynamics is vital for engineers seeking to navigate the complexities of the labor market and make informed decisions about their professional trajectory. Remaining informed of the broader economic situation enhances career navigation.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following section addresses common inquiries regarding the financial aspects of a career as an aerospace engineer in France, providing concise and informative answers.
Question 1: What is the average annual income for a recent aerospace engineering graduate in France?
Entry-level positions generally offer annual salaries ranging from 30,000 to 40,000, contingent upon the institution from which the degree was obtained and the specific company.
Question 2: How does experience level affect earning potential in this profession?
Compensation increases commensurate with experience. Senior engineers with over ten years of experience can expect salaries significantly exceeding those of entry-level counterparts, often reaching 60,000 to 90,000 or more, depending on their role and specialization.
Question 3: Do specific specializations command higher salaries?
Yes. Specializations in high-demand areas such as sustainable aviation, avionics, and composite materials often result in higher compensation due to the specialized expertise required and the competition for skilled professionals.
Question 4: Which regions in France offer the most lucrative opportunities for aerospace engineers?
Toulouse, renowned as a major aerospace hub, typically offers the most competitive salaries due to the concentration of aerospace companies and research institutions.
Question 5: Are there specific skills or certifications that can significantly boost earning potential?
Proficiency in industry-standard software like CATIA and ANSYS, coupled with certifications in project management or quality assurance, can enhance a candidate’s value and command a higher salary.
Question 6: How do economic conditions influence salaries in the aerospace engineering sector?
Economic downturns can lead to reduced investment in aerospace projects, potentially impacting salaries and job security. Conversely, periods of economic growth and increased government investment can drive up demand and boost compensation.
Understanding these key factors provides valuable insights into the financial prospects for aerospace engineers in France.
The subsequent section will provide a conclusion, summarizing the key findings and offering final thoughts on navigating the aerospace engineering career path in France.
Conclusion
This exploration of aerospace engineer salary in france has illuminated the multifaceted factors influencing compensation within this specialized profession. Experience level, education, company size, geographic location, industry demand, and individual skills collectively determine earning potential. Strategic career planning, continuous skill development, and a keen awareness of economic conditions are essential for maximizing financial rewards.
The insights presented underscore the significance of informed decision-making for both aspiring and practicing aerospace engineers. By understanding the dynamics of the French aerospace labor market, individuals can effectively navigate their career paths and contribute to the continued advancement of this vital sector. Further research and engagement with industry resources remain crucial for staying abreast of evolving trends and optimizing career prospects.