The earnings potential for professionals in aircraft and spacecraft design, development, and testing can be significantly influenced by the employer. Specifically, when considering compensation for these engineers at a high-profile manufacturing company known for luxury automobiles and aerospace systems, it’s essential to understand the intersection of industry sector and company reputation. For example, an engineer at this company might command a higher salary than one at a smaller or less specialized firm.
The significance of this association lies in the company’s commitment to innovation, its global presence, and its involvement in advanced engineering projects. These factors often translate into competitive remuneration packages designed to attract and retain top talent. Historically, this organization has been a leader in its field, investing heavily in research and development, which in turn supports higher compensation levels for its engineering staff. Benefits beyond base salary, such as stock options, comprehensive health insurance, and retirement plans, often contribute to the overall attractiveness of these employment opportunities.
Therefore, understanding the interplay between an aerospace engineer’s qualifications, experience, and the specific dynamics of working for such a prominent corporation offers crucial insights into salary expectations within the aerospace engineering field. Further analysis will delve into the specific factors affecting pay scales for these roles, including educational background, geographical location, and specific area of expertise.
Insights into Aerospace Engineer Compensation at a Distinguished Firm
The following points offer guidance for aerospace engineers seeking employment and competitive remuneration within a prestigious aerospace and automotive manufacturing environment.
Tip 1: Target Relevant Skill Sets: Developing expertise in areas highly valued by the specific company, such as advanced materials, propulsion systems, or computational fluid dynamics, can significantly enhance earning potential.
Tip 2: Seek Advanced Education: Possessing a Master’s degree or a Ph.D. in a relevant engineering discipline can lead to higher starting salaries and accelerated career advancement opportunities.
Tip 3: Gain Industry-Specific Experience: Prior internships or work experience within the aerospace or automotive industries, particularly those focusing on high-performance systems, can increase marketability and salary negotiation power.
Tip 4: Cultivate Strong Communication Skills: Effectively conveying technical information to both technical and non-technical audiences is crucial for collaboration and leadership roles, which often correlate with higher compensation.
Tip 5: Network Strategically: Attending industry conferences, joining professional organizations, and connecting with company employees can provide valuable insights into salary ranges and potential career paths.
Tip 6: Research Geographic Locations: Salary levels can vary significantly based on location, with higher costs of living generally corresponding to higher pay. Consider the company’s major facilities and their respective compensation norms.
Tip 7: Prepare for Salary Negotiations: Research industry benchmarks and salary data, and be prepared to articulate one’s skills, experience, and value proposition to justify desired compensation.
By focusing on acquiring specialized skills, gaining relevant experience, and developing strong communication abilities, aerospace engineers can position themselves for higher earning potential within a prestigious manufacturing organization.
Further sections will address the long-term career prospects and advancement opportunities available within this sector.
1. Company Prestige
The reputation and standing of an employer significantly impact the earning potential of its aerospace engineering staff. Company prestige, therefore, acts as a key determinant in salary considerations for individuals working within the aerospace engineering field, especially within renowned organizations.
- Brand Recognition and Market Position
A company with strong brand recognition and a dominant market position often commands higher revenues and profit margins. This financial stability allows for more competitive compensation packages for employees, including aerospace engineers. For example, a firm celebrated for its advanced engine technology and luxurious brand image can leverage its financial strength to attract top engineering talent with premium salaries.
- Investment in Research and Development
Prestigious companies typically invest heavily in cutting-edge research and development to maintain their competitive edge. These investments create opportunities for aerospace engineers to work on groundbreaking projects, which can lead to increased compensation. An aerospace manufacturer recognized for its commitment to innovation in sustainable aviation may attract and reward engineers specializing in novel propulsion systems.
- Talent Acquisition and Retention Strategies
High-prestige companies employ comprehensive talent acquisition and retention strategies to secure and maintain a skilled workforce. These strategies frequently include offering competitive salaries and benefits packages. To retain skilled engineers crucial for a complex project, like the development of advanced turbine blades, a reputable firm would be motivated to ensure attractive compensation.
- Global Reach and Project Scale
Companies with global reach and involvement in large-scale, international projects often offer higher salaries to compensate for the challenges and responsibilities associated with these endeavors. An aerospace engineer managing international compliance and certification for a multi-billion dollar project at a world-renowned firm might expect a salary reflecting the scale and complexity of their role.
In conclusion, the influence of company prestige on the remuneration of aerospace engineers is multifaceted. A firm’s market position, investment in innovation, talent strategies, and global operations collectively create an environment where competitive salaries are offered to attract and retain top engineering professionals, ultimately influencing overall earning potential within the aerospace engineering sector.
2. Project Complexity
The intricacy and scale of aerospace endeavors significantly influence the remuneration of engineers involved. Project complexity demands specialized knowledge, advanced skills, and heightened problem-solving capabilities, which directly correlate with increased compensation levels.
- Technological Innovation Requirements
Projects pushing the boundaries of technological innovation necessitate engineers with expertise in cutting-edge fields such as advanced materials, hypersonic propulsion, or autonomous systems. Developing a novel engine component, for example, requiring intricate simulations and analyses, merits higher compensation due to the specialized knowledge and skills demanded, impacting salary considerations within the aerospace sector.
- Stringent Regulatory Compliance
Aerospace projects are subject to rigorous safety standards and regulatory frameworks, demanding meticulous attention to detail and adherence to strict protocols. Engineers responsible for ensuring compliance with international aviation regulations or environmental standards face significant pressure and liability, justifying higher salaries to reflect the critical nature of their responsibilities and impact on product safety.
- Integration of Multidisciplinary Systems
Modern aerospace systems involve the integration of diverse and complex components, requiring engineers to possess a broad understanding of various disciplines, including aerodynamics, avionics, and structural mechanics. Managing the seamless integration of complex subsystems in a new aircraft design, for instance, demands exceptional coordination and problem-solving skills, leading to increased salary expectations.
- Risk Mitigation and Safety Assurance
Given the high-stakes nature of aerospace operations, engineers play a crucial role in identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential risks throughout the project lifecycle. Implementing comprehensive safety measures and conducting rigorous testing procedures to ensure the reliability and integrity of critical systems requires specialized expertise and carries significant responsibility, thus influencing salary negotiations within the aerospace sector.
These facets of project complexity underscore the increased value and corresponding compensation levels associated with aerospace engineering roles involving challenging and technically demanding projects. The need for specialized skills, regulatory compliance, multidisciplinary integration, and robust risk mitigation collectively contribute to the premium salaries commanded by engineers working on projects that push the boundaries of aerospace technology.
3. Skill Demand
The labor market’s demand for specific competencies significantly influences compensation structures within the aerospace engineering sector, particularly for engineers associated with high-profile organizations known for both automotive and aerospace excellence. As skill demands evolve, so too does the financial recognition afforded to those possessing critical expertise. The value placed on certain skill sets directly impacts salary expectations and hiring practices within these leading companies.
- Expertise in Advanced Materials
Aerospace engineering heavily relies on advanced materials science. Engineers proficient in the design, testing, and implementation of novel materials, such as composites, alloys, and nanomaterials, are highly sought after. For instance, expertise in developing lightweight, high-strength materials for aircraft structures contributes directly to fuel efficiency and performance. A company like the one mentioned, committed to high performance and luxury, would place a premium on engineers who can optimize material usage, influencing compensation positively.
- Specialization in Propulsion Systems
The design, development, and optimization of propulsion systems are critical to aerospace engineering. Engineers specializing in gas turbine engines, rocket propulsion, or electric propulsion systems are in high demand. With growing emphasis on sustainability, expertise in alternative fuels and hybrid propulsion is particularly valuable. For an organization that produces both high-performance vehicles and aircraft engines, engineers with advanced propulsion expertise are crucial assets, impacting salary positively.
- Proficiency in Systems Engineering
The integration and management of complex aerospace systems necessitate strong systems engineering skills. Engineers capable of defining system requirements, managing interfaces, and ensuring system reliability are essential. With complex projects requiring multidisciplinary collaboration, expertise in systems engineering ensures that disparate components function harmoniously. This skill is highly prized, especially in companies known for their intricate engineering designs, impacting earnings favorably.
- Competency in Aerodynamics and Fluid Dynamics
An understanding of aerodynamic principles and fluid dynamics is fundamental to aerospace engineering. Engineers skilled in computational fluid dynamics (CFD), wind tunnel testing, and aircraft design are crucial for optimizing performance. Improving lift-to-drag ratios, reducing turbulence, and enhancing stability are all vital for aircraft efficiency. Companies that push boundaries in aerodynamic design, such as firms specializing in high-speed vehicles or advanced aircraft, value these skills greatly, impacting salary structures.
In summary, the demand for specific skills within aerospace engineering plays a crucial role in determining compensation levels, especially for professionals associated with high-profile firms. Expertise in advanced materials, propulsion systems, systems engineering, and aerodynamics are highly valued, translating to increased earning potential for engineers possessing these competencies. As technology continues to evolve, the demand for engineers with specialized knowledge in these areas will continue to drive salary growth within the aerospace sector.
4. Location Influence
Geographic location exerts a considerable influence on compensation for aerospace engineers, particularly those employed by prominent manufacturing entities known for luxury automobiles and aerospace systems. The cost of living, regional industry demand, and the presence of competing aerospace firms directly impact salary scales. Metropolitan areas with a high concentration of aerospace activity, such as Los Angeles, Seattle, or regions near major military installations, often exhibit higher salary benchmarks due to increased competition for skilled personnel and the elevated expense of housing and daily living.
Furthermore, tax implications at the state and local levels can affect the net income of aerospace engineers. States with lower income tax rates may, in effect, provide greater financial benefit, even if the gross salary is nominally lower compared to locations with higher tax burdens. For example, an aerospace engineer in Washington State, which has no state income tax, might experience a similar standard of living as an engineer earning a higher gross salary in California, considering California’s income tax. The proximity to specific company facilities also plays a role. Relocation incentives or bonuses may be offered to attract engineers to locations that are critical to the company’s operations but may not be inherently desirable due to climate, culture, or other factors.
In conclusion, the correlation between geographic location and aerospace engineer salaries at a specific, well-regarded firm is multi-faceted. Cost of living, regional industry presence, tax implications, and company-specific incentives all contribute to variations in compensation. Aerospace engineers should carefully consider these location-based factors when evaluating job offers and negotiating salary expectations to ensure a financially sound decision aligned with their career goals. Understanding location’s influence offers a strategic advantage for maximizing earning potential in this specialized engineering field.
5. Experience Level
The correlation between experience level and compensation for aerospace engineers at a renowned firm specializing in both automotive and aerospace systems is direct and substantial. Increased experience translates to a greater capacity to handle complex projects, a deeper understanding of industry best practices, and a demonstrated track record of problem-solving, all of which contribute to higher earning potential. Entry-level engineers typically receive lower salaries reflecting their initial training phase, while seasoned professionals, possessing decades of practical application and leadership capabilities, command significantly higher remuneration packages. For example, a recent graduate might focus on component-level design, whereas a principal engineer with 15 years of experience could oversee the development of an entire aircraft engine.
Specific examples illustrate the practical impact of experience. An engineer with five years of experience specializing in computational fluid dynamics could lead simulations to optimize aircraft wing designs. This mid-career professional’s experience makes them invaluable in enhancing aircraft performance and fuel efficiency. A senior engineer, having over ten years of aerospace experience, may manage multidisciplinary teams, ensure regulatory compliance, and represent the company in technical discussions with clients. Their breadth of knowledge allows them to make critical decisions that impact project timelines and budgets. Experience also dictates eligibility for promotions, leadership roles, and specialized certifications, further driving compensation upwards.
In summary, experience level functions as a cornerstone of the compensation structure for aerospace engineers. While education, specialization, and location influence salary, experience serves as a primary indicator of an engineer’s ability to contribute to the success of complex aerospace projects. Aerospace engineers seeking career advancement and increased compensation must prioritize continuous professional development, seek opportunities for leadership roles, and demonstrate a commitment to staying current with industry trends. The firm’s commitment to innovation and high standards further reinforces the value placed on the demonstrated expertise that comes with years of dedicated service.
6. Performance Rewards
Performance-based incentives form a critical component of the total compensation package for aerospace engineers, particularly within prestigious organizations known for automotive and aerospace excellence. These rewards, designed to recognize and incentivize exceptional contributions, directly influence the overall earning potential and career progression of engineers within such firms.
- Individual Merit Bonuses
Merit bonuses represent a direct financial reward tied to individual performance against predetermined goals and objectives. An aerospace engineer instrumental in developing a novel wing design that significantly improves fuel efficiency might receive a substantial merit bonus. Such bonuses not only recognize past achievements but also incentivize continued innovation and excellence, affecting future compensation possibilities.
- Project Completion Incentives
Many aerospace projects are structured with completion incentives, rewarding engineering teams for delivering projects on time, within budget, and to specified performance criteria. For instance, successfully completing the development and testing of a new aircraft engine within a tight deadline can trigger significant financial rewards for the entire engineering team involved. These incentives foster collaboration, efficiency, and a focus on achieving critical project milestones, thereby influencing the team’s collective income.
- Stock Options and Equity Grants
Stock options and equity grants provide aerospace engineers with a stake in the company’s overall success. As the company’s value increases, so does the value of the engineer’s stock options or equity grants, providing a direct financial incentive to contribute to the organization’s long-term growth. For engineers at a high-profile firm, stock options can represent a substantial portion of their overall compensation, aligning their interests with those of the company’s shareholders and impacting long-term wealth accumulation.
- Recognition and Awards Programs
Formal recognition and awards programs, such as “Engineer of the Year” awards or innovation prizes, provide both financial and reputational rewards for outstanding contributions. Winning such awards not only enhances an engineer’s professional standing but also often includes monetary prizes and increased opportunities for career advancement, thereby influencing future salary negotiations. Moreover, such programs cultivate a culture of excellence and innovation, fostering continuous improvement within the engineering workforce.
The integration of performance rewards into the compensation structure significantly influences the overall appeal and competitiveness of aerospace engineering roles. These incentives, ranging from individual merit bonuses to project-based incentives and equity grants, motivate engineers to excel, innovate, and contribute to the organization’s success. These performance-driven components elevate potential earnings, thus influencing the attractiveness of working at a prestigious firm within the aerospace industry.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following questions address common inquiries regarding the salary landscape for aerospace engineers employed by a distinguished manufacturer with a presence in both the automotive and aerospace sectors.
Question 1: What is the general salary range for an aerospace engineer working at a corporation renowned for both luxury vehicles and aircraft engines?
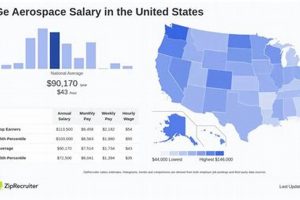
Salaries vary widely depending on factors such as experience, education, specialization, and geographic location. Entry-level positions may start in the $70,000 to $90,000 range, while senior engineers with extensive experience can earn upwards of $150,000 to $200,000 or more. Specific compensation packages are contingent upon the candidate’s qualifications and the specific role requirements.
Question 2: How does the company’s reputation for luxury and high performance affect aerospace engineer salaries?
The company’s emphasis on innovation, quality, and advanced technology typically translates into competitive salaries and comprehensive benefits packages designed to attract top talent. The organization’s global presence and involvement in cutting-edge projects also contribute to higher compensation levels compared to smaller or less specialized firms.
Question 3: What specific skills or expertise command the highest salaries within this particular company?
Expertise in areas such as advanced materials, propulsion systems, aerodynamics, and systems engineering is highly valued. Engineers with proficiency in computational fluid dynamics (CFD), finite element analysis (FEA), or control systems design are also in high demand. Specialized knowledge and certifications related to aerospace regulations and safety standards enhance earning potential.
Question 4: Are there geographic locations where aerospace engineers are paid more within this company?
Salary levels often correlate with the cost of living and the demand for aerospace engineers in specific regions. Locations near major company facilities or aerospace hubs may offer higher compensation to attract and retain qualified personnel. Relocation assistance or bonuses may also be provided to engineers who accept positions in less desirable locations.
Question 5: How does experience level impact salary progression for aerospace engineers at this organization?
Experience is a primary driver of salary growth. As engineers gain experience, demonstrate proficiency, and take on increasingly complex responsibilities, their compensation typically increases accordingly. Senior engineers with a proven track record of success can command significantly higher salaries and opportunities for advancement into leadership roles.
Question 6: What types of performance-based incentives are offered to aerospace engineers, and how do these influence overall compensation?
Performance-based incentives may include merit bonuses, project completion bonuses, stock options, and recognition awards. These incentives are designed to reward exceptional contributions and motivate engineers to exceed expectations. The availability and magnitude of these incentives can significantly impact an engineer’s overall compensation package.
In summary, while the factors previously detailed can influence salary, specific compensation packages depend on individual qualifications and role requirements.
Further sections will explore career development and long-term growth opportunities within the aerospace engineering sector.
Aerospace Engineer Salary Rolls Royce
This exploration has illuminated the multifaceted determinants of compensation for aerospace engineers, particularly within the context of a high-profile manufacturing firm with interests in both luxury automotive and advanced aerospace systems. Factors such as company prestige, project complexity, skill demand, geographic location, experience level, and performance-based rewards all contribute to the overall remuneration landscape for professionals in this field. Understanding these elements enables a more informed assessment of career opportunities and salary expectations.
The insights presented should serve as a foundation for future investigation and strategic career planning. Continuous professional development, coupled with a keen awareness of industry trends and company-specific compensation practices, remains essential for aerospace engineers seeking to maximize their earning potential and contribute meaningfully to advancements in aerospace technology. Further research is encouraged to refine understanding of this complex and evolving field, with proactive preparation paving the way for sustained success.