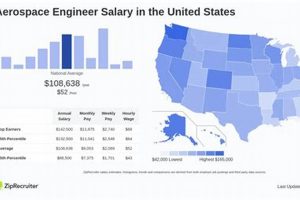
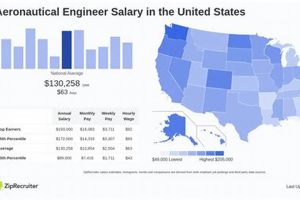
Compensation for professionals specializing in the design, development, and testing of aircraft and spacecraft in the San Francisco metropolitan area represents a key factor for both job seekers and employers. This financial consideration reflects the high cost of living and the demand for specialized skills within the region’s technology and engineering sectors.
Understanding the typical earnings for these engineering roles in this specific geographic location offers numerous advantages. For candidates, it provides a benchmark for salary negotiation and career planning. For companies, it informs competitive compensation packages necessary to attract and retain qualified personnel. Factors influencing this compensation include experience level, educational background, specific skill sets, and the size and profitability of the employing organization. The historical growth of the technology sector in the Bay Area has consistently impacted the demand and, consequently, the earning potential for engineers.
This analysis will delve into the various elements affecting remuneration for aerospace engineers in the Bay Area, exploring salary ranges, influencing factors, and available resources for further research. It will also touch upon the competitive landscape and the overall economic climate impacting compensation trends.
Securing optimal compensation in the field of aerospace engineering within the competitive San Francisco job market requires a strategic approach. The following tips provide guidance for both aspiring and experienced professionals.
Tip 1: Research the Market Thoroughly: Before entering salary negotiations, conduct comprehensive research using industry salary surveys and online resources to determine the prevailing rates for similar roles with comparable experience levels in the San Francisco Bay Area. Utilize websites such as Glassdoor, Salary.com, and Payscale to gather data points.
Tip 2: Highlight Specialized Skills and Expertise: Emphasize specific skills and areas of expertise that are in high demand. This may include proficiency in particular software programs (e.g., MATLAB, ANSYS), experience with specific types of aircraft or spacecraft, or certifications relevant to the industry. Quantify these skills with demonstrable achievements.
Tip 3: Leverage Educational Credentials: Advanced degrees, such as a Master’s or Ph.D. in Aerospace Engineering or a related field, can significantly increase earning potential. Clearly articulate how advanced knowledge contributes to improved performance and innovation.
Tip 4: Negotiate Beyond Base Salary: Consider negotiating benefits beyond base compensation, such as stock options, performance-based bonuses, relocation assistance, professional development opportunities, and comprehensive health insurance plans. These benefits can substantially increase the overall compensation package.
Tip 5: Understand the Employer’s Financial Position: Research the financial health and profitability of potential employers. Companies with strong financial performance are typically better positioned to offer competitive salaries and benefits.
Tip 6: Document Accomplishments and Contributions: Maintain a detailed record of achievements and contributions throughout one’s career. This documentation provides concrete evidence of value and strengthens negotiating power during salary discussions. Utilize quantifiable metrics to demonstrate impact.
Tip 7: Explore Opportunities in High-Demand Sub-Sectors: Certain sub-sectors within aerospace engineering, such as those focused on space exploration, autonomous systems, or sustainable aviation, may offer higher compensation due to specialized skill requirements and industry growth.
By implementing these strategies, aerospace engineers can effectively navigate the complexities of compensation in San Francisco and maximize their earning potential. Understanding the market dynamics and proactively showcasing value are crucial for achieving financial success in this competitive field.
The subsequent sections will provide additional insights into factors impacting earnings and resources available for further exploration of this topic.
1. Cost of Living
The cost of living in the San Francisco Bay Area exerts a significant upward pressure on compensation across all professions, and aerospace engineering is no exception. This region’s exceptionally high expenses for housing, transportation, and general goods and services necessitate commensurate salaries to attract and retain qualified professionals.
- Housing Costs
Rental and purchase prices for housing in San Francisco are among the highest in the United States. This substantial expense directly impacts the income required for aerospace engineers to maintain a reasonable standard of living. Consequently, employers must offer salaries that account for this significant financial burden.
- Transportation Expenses
While public transportation options exist, many professionals rely on personal vehicles to commute. The costs associated with vehicle ownership, including insurance, fuel, and maintenance, further contribute to the overall cost of living. Parking fees and bridge tolls within the Bay Area can also be substantial.
- General Goods and Services
The prices of everyday goods and services, such as groceries, utilities, and healthcare, are notably higher in San Francisco compared to other regions. This price inflation impacts the disposable income of aerospace engineers and necessitates higher salaries to offset these increased expenses.
- Taxation
California has a progressive state income tax system, and San Francisco’s local taxes further contribute to the overall tax burden. These tax obligations reduce the net income available to aerospace engineers, requiring employers to factor in these deductions when determining competitive salaries.
The combined impact of these high living expenses results in a pronounced demand for competitive remuneration for aerospace engineers in San Francisco. Employers must carefully consider these factors to attract and retain top talent in this highly competitive market. Failure to address the high cost of living could lead to difficulty recruiting and retaining qualified professionals, ultimately impacting the organization’s ability to thrive in the region.
2. Experience Level
Experience level is a primary determinant in the compensation structure for aerospace engineers within the San Francisco job market. As proficiency and expertise grow, so too does the earning potential, reflecting increased responsibility and specialized knowledge application.
- Entry-Level Positions
Entry-level aerospace engineering roles, typically requiring a bachelor’s degree and limited practical experience, command the lowest salaries. These positions focus on foundational tasks and skill development under the guidance of experienced engineers. Example: A recent graduate assisting with design validation or data analysis within a larger project team. The starting compensation reflects the limited experience and training necessary to perform the required duties.
- Mid-Career Professionals
Aerospace engineers with several years of experience often transition into roles requiring more independent work and specialized skill application. Responsibilities may include leading small teams, managing project components, and contributing to complex design solutions. Example: An engineer with five years of experience leading a subsystem development effort or performing advanced simulations. Increased responsibilities and specialized skills lead to a notable salary increase compared to entry-level positions.
- Senior Engineers and Technical Specialists
Senior aerospace engineers and technical specialists possess extensive experience and deep expertise in specific areas of aerospace engineering. These individuals may lead large teams, develop innovative technologies, and serve as technical advisors. Example: A lead engineer with ten or more years of experience directing the design and testing of a new aircraft component or a specialist in a niche area like hypersonic aerodynamics providing expert consultation. The high level of expertise and leadership abilities associated with these roles command significant salaries.
- Management and Leadership Roles
Aerospace engineers who transition into management or leadership positions assume responsibilities for project management, team supervision, and strategic decision-making. These roles require a combination of technical expertise and leadership skills. Example: An engineering manager overseeing multiple project teams or a program manager responsible for the overall execution of a complex aerospace project. The additional responsibilities and required management skills are reflected in higher compensation levels.
In summary, experience level directly correlates with the earning potential for aerospace engineers in San Francisco. As engineers progress through their careers and acquire specialized skills and leadership abilities, their compensation reflects their increased value and contributions to the organization. The specific salary levels within each experience bracket are also subject to other factors, such as company size, industry sector, and educational attainment, further influencing the overall compensation package.
3. Company Size
Company size significantly impacts compensation for aerospace engineers in the San Francisco Bay Area. Larger corporations, possessing greater financial resources, generally offer more competitive salaries and comprehensive benefits packages than smaller firms or startups. This discrepancy stems from several factors. Larger companies often handle more complex and high-value projects, requiring specialized skillsets that command premium compensation. Their established infrastructure and human resources departments also facilitate standardized salary scales and performance-based bonus systems. For instance, a multinational aerospace corporation with a San Francisco office might offer a significantly higher starting salary than a local, privately-owned aerospace engineering firm due to its larger revenue streams and global reach.
Conversely, smaller companies may offer alternative advantages, such as greater opportunities for rapid career advancement, more direct involvement in diverse projects, and a more flexible work environment. However, their limited financial capacity often restricts their ability to match the salary levels offered by larger competitors. As an example, a startup focusing on drone technology might compensate with equity options or profit-sharing plans to offset a lower base salary. The decision to prioritize compensation over other potential benefits represents a critical consideration for aerospace engineers evaluating employment opportunities in the Bay Area.
In summary, company size functions as a pivotal determinant in salary negotiations for aerospace engineers in San Francisco. While larger companies typically offer more competitive financial packages, smaller companies may provide unique career development opportunities and alternative compensation structures. A comprehensive assessment of both financial and non-financial benefits remains essential when evaluating prospective employers and maximizing earning potential within this dynamic and competitive job market. Understanding this relationship allows engineers to better navigate the employment landscape and make informed career choices.
4. Industry Sector
The specific industry sector within the broader aerospace field exerts a considerable influence on compensation levels for aerospace engineers in San Francisco. The variations stem from differences in project funding, revenue generation, and specialized skill requirements across various sectors. Distinct aerospace sectors operating in and around San Francisco may include commercial aviation, defense contracting, space exploration, and emerging fields like unmanned aerial systems (UAS) or electric vertical takeoff and landing (eVTOL) aircraft. Each sector presents unique financial dynamics that directly impact the remuneration offered to engineers. For example, defense contractors may secure substantial government funding for long-term projects, potentially leading to more stable and higher-paying positions compared to startups in the nascent eVTOL sector still seeking venture capital.
Consider the contrast between a seasoned aerospace engineer working on flight control systems for a major commercial aircraft manufacturer based near San Francisco International Airport, versus a counterpart at a venture-backed space technology firm in Silicon Valley. The commercial aviation position, supported by consistent revenue streams from aircraft sales and maintenance, typically offers a predictable salary trajectory and comprehensive benefits. The space technology engineer, while potentially benefiting from stock options with high growth potential, might face greater uncertainty regarding long-term compensation and job security due to the volatile nature of startup funding. Similarly, an engineer involved in developing autonomous navigation systems for drones might encounter a different salary scale reflecting the evolving regulatory landscape and market demand within that specific sector.
In summary, the aerospace sector plays a key role in determining aerospace engineer salary within San Francisco. Industry Sector exerts influence on project funding, revenue generation, and specialized skills required. The choice of industry sector significantly impacts engineers’ long-term financial prospects. Those seeking high and predictable income might favor established commercial or defense sectors, while those willing to accept greater risk for potential high rewards may gravitate towards emerging fields. Comprehending these sector-specific compensation dynamics enables aerospace engineers to make informed career decisions aligned with their financial goals and risk tolerance levels.
5. Skill Specialization
Within the San Francisco Bay Area’s competitive job market, specialized skills wield a considerable influence on the compensation commanded by aerospace engineers. The demand for specific expertise directly impacts the earning potential, as employers are willing to offer higher salaries to secure individuals with capabilities aligned with their most pressing technological needs. For instance, proficiency in areas like computational fluid dynamics (CFD), autonomous systems development, or advanced materials science demonstrably elevates an engineer’s market value. An aerospace engineer possessing expertise in designing and optimizing airfoils using CFD software may find opportunities that command higher earnings, reflecting the organization’s need for precise aerodynamic analysis.
The concentration of technology companies and research institutions in the Bay Area further amplifies the importance of specialization. Companies engaged in developing cutting-edge technologies such as electric aircraft or space propulsion systems actively seek engineers with expertise in niche areas. This competition for talent drives up compensation for individuals who possess specialized knowledge. Furthermore, engineers with specialized skills often contribute directly to project innovation and efficiency, resulting in increased revenue or cost savings for their employers. The ability to quantify these contributions during salary negotiations strengthens the engineer’s position. A specialist who decreases design cycle time or improves system performance through the application of their expertise becomes a highly sought-after asset.
The practical significance of understanding the link between specialized skills and compensation lies in its ability to inform career planning and professional development. Aerospace engineers aspiring to maximize their earning potential in San Francisco should prioritize acquiring in-demand skills through advanced education, targeted training, and hands-on project experience. While the market rewards specialization, continuously updating and expanding skill sets remains crucial, as technology evolves and new areas of expertise emerge. Challenges exist in predicting which skills will be most valuable in the future, however, remaining adaptable and actively seeking opportunities to learn new technologies are strategies for maintaining career relevance and maximizing compensation opportunities within the dynamic Bay Area aerospace sector.
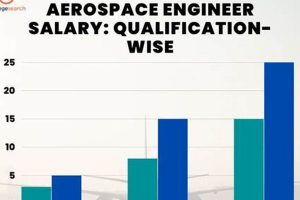
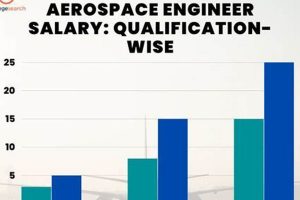
6. Education
Educational attainment serves as a significant factor influencing the compensation levels of aerospace engineers, particularly within the competitive San Francisco job market. Higher levels of education often correlate with more advanced skill sets and specialized knowledge, making candidates more attractive to employers and commanding higher salaries.
- Bachelor’s Degree
A bachelor’s degree in Aerospace Engineering, or a closely related field, represents the foundational requirement for entry into the profession. While a bachelor’s degree qualifies individuals for entry-level positions, the salary commanded may be comparatively lower than those with advanced degrees. Tasks may involve assisting senior engineers with design tasks or data analysis. The Bay Area market increasingly favors candidates with advanced degrees, positioning a bachelor’s as a baseline qualification rather than a differentiator.
- Master’s Degree
A master’s degree in Aerospace Engineering or a specialized sub-discipline, such as aerodynamics or propulsion, can significantly enhance earning potential. The advanced coursework and research experience gained through a master’s program equip engineers with specialized knowledge applicable to more complex projects and leadership roles. Examples include leading design teams for specialized subsystems. The Bay Area’s concentration of technology firms often incentivizes higher salaries for master’s-level engineers due to their enhanced analytical and problem-solving abilities.
- Doctoral Degree (Ph.D.)
A Ph.D. in Aerospace Engineering signifies the highest level of academic achievement and typically leads to positions involving research, development, and innovation. Individuals with doctorates often pursue careers in academia, research institutions, or advanced technology companies. A Ph.D. holder’s compensation reflects the specialized knowledge and ability to contribute novel solutions to complex engineering problems. In the San Francisco area, Ph.D. graduates may find higher salaries in research-intensive roles or management positions requiring advanced analytical skills.
- Specialized Certifications and Training
Beyond formal degrees, specialized certifications and training programs can also enhance an aerospace engineer’s earning potential. These certifications demonstrate proficiency in specific software, tools, or methodologies relevant to the field, such as certifications in computational fluid dynamics software or project management methodologies. Acquiring and maintaining these credentials signals commitment to professional development and increased competency in relevant areas, leading to potentially higher compensation levels.
In summary, higher levels of education, from master’s degrees to Ph.D.s, often correlate with elevated salaries for aerospace engineers within the San Francisco job market. The region’s emphasis on innovation and advanced technology drives the demand for engineers with specialized knowledge and advanced analytical skills, making educational attainment a crucial factor in determining compensation.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding compensation for aerospace engineers within the San Francisco metropolitan area. The information presented aims to provide clarity and realistic expectations concerning salary ranges and influencing factors.
Question 1: What is the typical salary range for an entry-level aerospace engineer in San Francisco?
The salary range for entry-level aerospace engineers in San Francisco typically falls between $80,000 and $100,000 annually. This range is influenced by the candidate’s educational background, internship experience, and the specific requirements of the position. High cost of living also factors into this compensation range.
Question 2: How does experience level impact the salary of an aerospace engineer in San Francisco?
Experience level significantly impacts compensation. Mid-career aerospace engineers with 5-10 years of experience can expect salaries ranging from $120,000 to $160,000 annually. Senior engineers with over 10 years of experience and specialized expertise may command salaries exceeding $180,000 per year.
Question 3: Do specific skills or certifications affect aerospace engineer salaries in San Francisco?
Yes, possessing specialized skills such as proficiency in computational fluid dynamics (CFD), finite element analysis (FEA), or systems engineering demonstrably increases earning potential. Relevant certifications, such as a Professional Engineer (PE) license, can also lead to higher compensation.
Question 4: How does the company size influence aerospace engineer salaries in San Francisco?
Larger corporations generally offer more competitive salaries and comprehensive benefits packages compared to smaller companies or startups. Multinational aerospace companies often have standardized salary scales and established compensation structures, leading to higher overall earnings for their employees.
Question 5: What impact does the aerospace industry sector have on compensation in San Francisco?
The specific sector within the aerospace industry affects salary levels. Positions in commercial aviation, defense contracting, or space exploration may offer varying levels of compensation. Emerging sectors such as unmanned aerial systems (UAS) or electric vertical takeoff and landing (eVTOL) aircraft may present unique compensation structures and growth opportunities.
Question 6: Are there resources available to research aerospace engineer salaries in San Francisco?
Yes, several online resources provide salary data for aerospace engineers in San Francisco. Websites such as Glassdoor, Salary.com, and Payscale offer salary ranges based on job title, experience level, and location. Industry-specific salary surveys conducted by professional organizations may also provide valuable insights.
In conclusion, understanding these factors enables both employers and job seekers to navigate the intricacies of aerospace engineer compensation in San Francisco effectively. Careful research and strategic planning are crucial for achieving mutually beneficial outcomes.
The next section will provide information about resources and further exploration of the topic.
Aerospace Engineer Salary San Francisco
This examination has provided a detailed overview of compensation structures for aerospace engineers in San Francisco. Factors such as cost of living, experience level, company size, industry sector, skill specialization, and educational attainment significantly impact earning potential. Understanding these elements empowers both employers and prospective employees to navigate the job market effectively.
Prospective aerospace engineers and employers are encouraged to leverage this information as a starting point for comprehensive research. As the aerospace industry continues to evolve, continued due diligence will be crucial for securing competitive and equitable compensation in this high-demand field. The future of engineering compensation relies on the continuous evaluation of skills and benefits.