The rigorous academic discipline concerned with the design, development, testing, and production of aircraft and spacecraft is a cornerstone of the educational experience offered at a specific military institution. This highly technical field blends principles from aerodynamics, propulsion, structures, and control systems to prepare individuals for leadership roles within the armed forces and related industries. The United States Air Force Academy, as an example, offers this specialization to cadets aspiring to become officers and contribute to national security.
Mastery of the foundational principles, combined with specialized training, provides significant advantages. Graduates possess a deep understanding of complex systems, enabling them to contribute to innovation and technological advancement. Historically, this academic path has served as a critical pipeline for producing highly skilled engineers and leaders capable of addressing evolving challenges in defense and aerospace sectors. The knowledge gained ensures that graduates are well-prepared to tackle the technological demands of modern warfare and contribute to advancements in air and space power.
The subsequent sections will delve into specific aspects of this program, examining the curriculum, research opportunities, and the impact graduates have on the broader aerospace community. Focus will be placed on the unique opportunities and challenges associated with pursuing this field of study within a military academy setting. Furthermore, details about career paths and the long-term benefits of this specialized education will be examined.
Tips for Aspiring Professionals
For individuals considering a career path that merges rigorous engineering principles with military service, careful preparation and strategic planning are essential. The following tips offer guidance for maximizing success in this demanding field.
Tip 1: Cultivate a Strong Foundation in Mathematics and Science: A robust understanding of calculus, differential equations, physics, and chemistry is paramount. Dedicate significant time to mastering these subjects, as they form the bedrock of all subsequent aerospace engineering coursework.
Tip 2: Develop Exceptional Problem-Solving Skills: Aerospace engineering inherently involves complex challenges. Practice tackling intricate problems through coursework, independent study, and participation in engineering competitions. Focus on analytical thinking and innovative solutions.
Tip 3: Seek Research Opportunities Early: Engage in undergraduate research projects related to aerospace topics. This provides invaluable hands-on experience and allows for deeper exploration of specialized areas, demonstrating initiative and passion to admission committees.
Tip 4: Prioritize Leadership and Teamwork: Military academies emphasize leadership development. Actively seek leadership roles in extracurricular activities, academic clubs, or community service organizations. Collaboration is crucial in engineering projects and military operations.
Tip 5: Understand the Demands of Military Service: Research the specific requirements and expectations of serving as an officer in the United States Air Force. This includes physical fitness standards, commitment timelines, and the potential for deployment to various locations.
Tip 6: Network with Professionals in the Field: Attend conferences, workshops, and career fairs to connect with aerospace engineers and military officers. Informational interviews can provide valuable insights into career paths and required qualifications.
Tip 7: Demonstrate a Genuine Passion for Aerospace: Express genuine enthusiasm for flight, space exploration, and technological innovation in all application materials and interviews. This passion can differentiate an applicant from the competition and demonstrate a long-term commitment to the field.
Adherence to these recommendations will significantly enhance an applicant’s competitiveness and preparedness for the rigors of aerospace engineering studies within a military academy setting.
The following sections will explore the practical application of these skills in a professional environment, highlighting career opportunities and pathways for advancement.
1. Technical Specialization
Within the context of this academy, the pursuit of engineering expertise represents a core objective. This rigorous focus is not merely academic; it is a strategic imperative directly influencing national defense capabilities. Students undergo intensive training in diverse subjects such as aerodynamics, propulsion, materials science, and control systems. The curriculum’s intensity reflects the advanced technological challenges inherent in modern aerospace operations. For instance, coursework pertaining to hypersonic flight dynamics equips future officers to design and analyze advanced aircraft that can operate at speeds exceeding Mach 5. The deliberate construction of such specialized knowledge directly contributes to the development of innovative aerospace solutions.
The importance of rigorous training is evident in various real-world applications. Consider the development of advanced satellite constellations used for global communication and surveillance. Engineers with specialized knowledge of orbital mechanics, spacecraft design, and signal processing are crucial to the success of these complex systems. Similarly, the design and maintenance of high-performance military aircraft demand a deep understanding of aerodynamics, structural integrity, and advanced materials. Graduates of the academy often contribute to these areas, ensuring that the Air Force maintains a technological advantage over potential adversaries. This specialized expertise guarantees the ongoing refinement of the U.S. Air Force’s technological capabilities.
In conclusion, the emphasis on specialized knowledge at the academy is fundamental to its mission. By providing students with an in-depth understanding of aerospace engineering principles, the program equips them to tackle the complex technological challenges facing the military and the broader aerospace industry. The commitment to technical excellence directly impacts the Air Force’s ability to maintain its technological edge and safeguard national security, ensuring that graduates remain at the forefront of innovation.
2. Military Leadership
Military leadership, as an integral component of the Air Force Academy’s aerospace engineering program, extends beyond conventional notions of command. Its importance stems from the inherent complexities of modern aerospace operations, which demand not only technical expertise but also the ability to effectively manage resources, coordinate teams, and make critical decisions under pressure. The curriculum is designed to instill leadership qualities essential for officers who will be responsible for overseeing the design, development, and maintenance of sophisticated aerospace systems. For instance, a graduate might lead a team of engineers working on the development of unmanned aerial vehicles, requiring a nuanced understanding of both engineering principles and leadership strategies to ensure project success and adherence to military objectives.
The practical application of military leadership principles within the context of aerospace engineering can be observed in the management of complex projects such as the development of new satellite constellations or the maintenance of existing aircraft fleets. Effective leadership ensures that projects are completed on time and within budget while adhering to stringent safety and performance standards. Moreover, military leaders in aerospace engineering roles must possess the ability to motivate and inspire their teams, fostering a culture of innovation and continuous improvement. This involves creating an environment where engineers feel empowered to contribute their ideas and are recognized for their achievements. Furthermore, graduates may be required to negotiate contracts with external vendors and manage relationships with other government agencies, requiring exceptional interpersonal and communication skills.
In summary, the incorporation of military leadership training within the Air Force Academy’s aerospace engineering curriculum addresses the multifaceted demands of modern aerospace operations. It equips graduates with the skills necessary to not only excel as engineers but also to lead and manage teams effectively in challenging and dynamic environments. This combination of technical expertise and leadership acumen is critical for ensuring the continued technological superiority of the Air Force and the success of its aerospace missions. The challenge remains in continuously adapting the leadership curriculum to reflect the evolving needs of the aerospace sector and the changing nature of warfare.
3. Curriculum Rigor
The demanding nature of the aerospace engineering program within a military academy setting necessitates a rigorous curriculum. This ensures graduates possess the comprehensive technical knowledge and problem-solving skills required for success in both military and civilian aerospace sectors. The depth and breadth of the curriculum are specifically designed to meet the complex challenges inherent in designing, developing, and maintaining advanced aerospace systems.
- Advanced Mathematical Foundations
The program emphasizes mastery of advanced mathematical concepts, including calculus, differential equations, linear algebra, and probability theory. These principles form the foundation for understanding aerodynamic forces, structural mechanics, and control systems. For example, the accurate modeling of aircraft flight dynamics requires a deep understanding of differential equations. A failure to grasp these concepts would limit a graduate’s ability to design effective flight control algorithms.
- Specialized Engineering Disciplines
Students delve into specialized engineering disciplines, such as aerodynamics, propulsion, structures, and control systems. Each discipline is taught with an emphasis on practical application. Aerodynamics courses cover topics ranging from subsonic to hypersonic flow, providing students with the knowledge needed to design efficient and stable aircraft. Propulsion courses explore various engine types, including turbojets, turbofans, and rocket engines, equipping graduates to contribute to advancements in propulsion technology. Graduates need the knowledge of designing structures that withstand immense stresses and temperatures to develop space-worthy crafts.
- Design and Project-Based Learning
A cornerstone of the curriculum is its emphasis on design and project-based learning. Students participate in team-based design projects throughout their academic careers, culminating in a capstone design project that requires them to apply their accumulated knowledge to solve a complex engineering problem. For instance, students might design an unmanned aerial vehicle, a satellite, or a new aircraft wing. Such projects promote teamwork, problem-solving skills, and practical engineering experience, providing a smooth transition into professional practice.
- Integration of Military Training
The military academy setting integrates military training with the engineering curriculum. This integration prepares graduates for the unique challenges of serving as officers in the Air Force. Military training instills discipline, leadership skills, and a strong sense of duty, all of which are essential for success in a military engineering role. Moreover, graduates gain an understanding of military protocols and procedures, enabling them to effectively manage resources and lead teams in a military environment. The fusion of these two distinct domains provides the graduate to become a leader in various career paths.
The rigorous curriculum at the Air Force Academy provides aerospace engineering graduates with a solid foundation in engineering principles, practical experience, and the leadership skills necessary to excel in their careers. This comprehensive approach ensures that graduates are well-prepared to contribute to the advancement of aerospace technology and serve their country with distinction. The program’s commitment to excellence positions graduates as leaders in both military and civilian sectors.
4. Research Opportunities
Within the framework of aerospace engineering education at the Air Force Academy, participation in research initiatives represents a crucial component. These opportunities transcend mere academic exercises, serving as vital conduits for cadets to engage with cutting-edge technologies and contribute to advancements relevant to national security. The rigorous curriculum is complemented by avenues for cadets to explore specialized interests, fostering innovation and preparing them for leadership roles in both military and civilian sectors.
- Faculty-Led Research Programs
Faculty-led research programs offer cadets the chance to collaborate with experienced researchers on projects spanning a wide array of aerospace engineering disciplines. These projects may involve experimental investigations, computational modeling, or theoretical analyses. For example, a cadet might contribute to research on hypersonic aerodynamics, working alongside faculty to design and test innovative aircraft configurations. Such involvement provides invaluable hands-on experience and fosters a deeper understanding of the scientific method.
- Independent Research Projects
Cadets also have the option to pursue independent research projects, allowing them to delve into topics of particular interest. This option encourages self-directed learning and fosters creativity. A cadet, for instance, may choose to investigate novel propulsion systems for spacecraft, developing a theoretical model and conducting simulations to assess its feasibility. Independent research promotes critical thinking and problem-solving skills, essential for future engineers and leaders.
- Collaboration with External Organizations
The Academy facilitates collaborations with external organizations, including government agencies, aerospace companies, and research institutions. These partnerships provide cadets with opportunities to work on real-world engineering problems and gain exposure to industry practices. A cadet, for example, could participate in a research project at a NASA center, contributing to the development of advanced space exploration technologies. Such experiences broaden cadets’ perspectives and enhance their career prospects.
- Conference Presentations and Publications
Cadets are encouraged to present their research findings at conferences and publish their work in peer-reviewed journals. This process hones their communication skills and allows them to contribute to the body of scientific knowledge. A cadet might present a paper at an AIAA conference, sharing their research on innovative materials for aircraft structures. Publication and presentation of research fosters professional development and enhances the Academy’s reputation as a center of excellence in aerospace engineering.
These research opportunities, carefully integrated into the aerospace engineering curriculum, equip Air Force Academy cadets with the technical skills, critical thinking abilities, and leadership qualities necessary to excel in their careers. The experiences gained through research not only enhance their academic knowledge but also prepare them to address the complex challenges facing the aerospace industry and the nation’s defense. The knowledge generated often directly contributes to improved performance, safety, and efficiency within military aerospace operations.
5. Strategic Advantage
The confluence of advanced aerospace engineering education and rigorous military training yields a strategic advantage, a critical element in maintaining national security and technological superiority. The Air Force Academy serves as a key institution in fostering this advantage, producing graduates equipped to address complex challenges in defense and aerospace sectors.
- Technological Innovation and Superiority
Graduates possess the technical acumen to drive innovation in aerospace technologies. This includes the design and development of advanced aircraft, satellite systems, and unmanned aerial vehicles. Such advancements provide a distinct military advantage, allowing for enhanced surveillance capabilities, improved communication networks, and more effective deployment of resources. For instance, the development of hypersonic weapons systems requires engineers with specialized knowledge in aerodynamics, propulsion, and materials science, areas of focus within the academy’s curriculum.
- Adaptive and Agile Force Development
The integration of military training and engineering education cultivates adaptability and agility among graduates. They are prepared to respond effectively to evolving threats and adapt to rapidly changing technological landscapes. This adaptability is crucial in maintaining a responsive and proactive defense posture. The ability to quickly integrate new technologies and adapt existing systems to meet emerging threats provides a significant strategic edge.
- Enhanced Decision-Making Capabilities
The rigorous academic environment and leadership training foster enhanced decision-making capabilities among graduates. They are equipped to analyze complex situations, assess risks, and make informed judgments, particularly in high-pressure environments. This skillset is invaluable in military operations and strategic planning, where critical decisions can have far-reaching consequences. An officer with a strong engineering background can better assess the feasibility and impact of technological deployments.
- Attraction and Retention of Top Talent
The Air Force Academy’s reputation for academic excellence and its unique blend of engineering and military education serves as a magnet for attracting and retaining top talent. The opportunity to serve the nation while pursuing a challenging and rewarding career in aerospace engineering is appealing to many highly qualified individuals. This influx of talent contributes to the continuous improvement of the Air Force’s technical capabilities and ensures that it remains at the forefront of aerospace innovation.
These facets collectively underscore the strategic advantage derived from the unique educational environment at the Air Force Academy. By cultivating technical expertise, adaptability, and leadership skills, the institution produces graduates who are well-prepared to contribute to national security and maintain the nation’s dominance in the aerospace domain. Continued investment in and support for this institution are vital for preserving this strategic advantage in an increasingly competitive global landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following addresses common inquiries regarding specialized engineering education within a military context. These questions aim to provide clarity and detailed understanding for prospective applicants and interested parties.
Question 1: What are the eligibility requirements for pursuing this academic path at the Air Force Academy?
Applicants must meet stringent academic, physical, and character requirements as stipulated by the United States Air Force Academy. This includes a competitive high school GPA, strong performance on standardized tests (SAT/ACT), demonstrated leadership potential, and successful completion of a comprehensive medical examination.
Question 2: How does the curriculum differ from a civilian university offering a similar engineering degree?
While foundational engineering principles are consistent, the curriculum incorporates military-specific training, leadership development, and exposure to aerospace applications relevant to national defense. Furthermore, the program often includes classified research opportunities not available at civilian institutions.
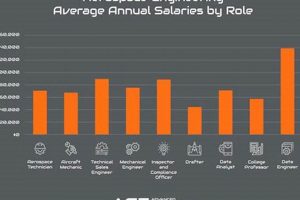
Question 3: What career paths are available to graduates following completion of the program and military service?
Graduates may pursue careers as Air Force officers in roles such as flight test engineers, program managers for aerospace systems, research scientists at Air Force Research Laboratory, or instructors at military training facilities. Following military service, opportunities exist in the civilian aerospace industry, government agencies (e.g., NASA), and consulting firms.
Question 4: Is prior military experience required for admission?
Prior military experience is not a prerequisite for admission. The Air Force Academy is designed to provide comprehensive military training alongside engineering education. However, applicants with Junior ROTC experience may be viewed favorably.
Question 5: What is the service commitment following graduation?
Graduates are obligated to fulfill a minimum service commitment as commissioned officers in the United States Air Force. The specific length of this commitment varies depending on the program and any additional training received (e.g., flight training).
Question 6: What are the opportunities for advanced study beyond the bachelor’s degree?
Graduates may pursue advanced degrees (master’s or doctoral) through Air Force-sponsored programs or at civilian universities. These programs provide opportunities for specialization in areas such as aerospace engineering, astronautical engineering, or related fields.
The answers provided offer a condensed overview. Detailed information can be obtained from the official Air Force Academy website or by contacting admissions personnel directly.
The next section will analyze real-world examples of graduates successfully utilizing their education and training to advance aerospace technology.
Conclusion
This exploration has illuminated the multifaceted nature of aerospace engineering education within the United States Air Force Academy. It is evident that the programs rigorous curriculum, coupled with military leadership training and access to advanced research opportunities, equips graduates with a unique skillset highly valued in both military and civilian sectors. The academy’s commitment to excellence cultivates professionals capable of driving technological innovation and addressing the evolving challenges facing the aerospace industry and national defense.
The confluence of technical proficiency and leadership acumen positions graduates as critical contributors to the advancement of aerospace technology and the safeguarding of national interests. Continued investment in the Air Force Academys aerospace engineering program remains vital for ensuring the United States maintains its strategic advantage in an increasingly competitive global landscape. The future demands individuals capable of navigating complex technological and geopolitical challenges; the Air Force Academy plays a pivotal role in cultivating such individuals. Therefore, continued support for and evolution of this program are essential for national security and technological progress.