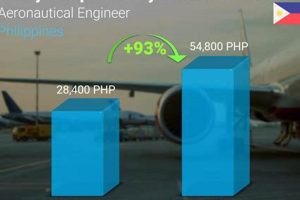
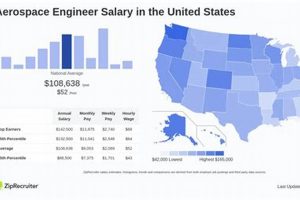
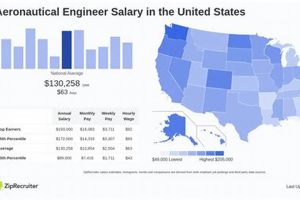
The compensation received by individuals completing their academic training in the design, development, and testing of aircraft and spacecraft is a key factor in career decisions. It reflects the demand for skilled professionals in this technologically advanced field and provides an indicator of the economic value placed on their expertise. For instance, a newly qualified engineer entering the workforce after completing a bachelor’s degree in this discipline can expect a starting remuneration package that varies based on location, specific skill set, and the employer’s size and industry sector.
This income level is important not only for personal financial planning but also as a benchmark for evaluating the return on investment in higher education. A competitive offering attracts talented individuals to the field, ensuring a continuous pipeline of innovation and expertise within the aerospace sector. Historically, this field has offered relatively strong financial incentives due to the complexities and specialized knowledge required, as well as the significant impact of advancements in air and space travel on national security and economic development.
The following sections will delve into the factors influencing entry-level compensation, geographical variations, and potential career progression pathways that contribute to salary growth within this profession.
Maximizing Compensation Potential
Strategies to enhance earnings upon entering the aerospace engineering field are crucial for securing a favorable financial future. Proactive planning and skill development significantly impact initial offers and long-term earning capacity.
Tip 1: Specialize in High-Demand Areas: Focus on areas like avionics, propulsion systems, or advanced materials. Expertise in these domains is often rewarded with higher starting salaries due to the critical role they play in aerospace advancements. For instance, knowledge of autonomous flight control systems can be particularly lucrative.
Tip 2: Acquire Relevant Certifications: Obtain certifications relevant to the desired specialization. Certifications such as those from professional engineering organizations demonstrate competence and enhance credibility, leading to improved compensation negotiations.
Tip 3: Gain Internship Experience: Completing internships with reputable aerospace companies provides invaluable practical experience. Internships showcase an ability to apply theoretical knowledge in a real-world setting, making candidates more attractive to potential employers and influencing salary expectations.
Tip 4: Develop Strong Programming Skills: Proficiency in programming languages commonly used in aerospace, such as MATLAB, Python, or C++, is highly valuable. These skills are essential for modeling, simulation, and data analysis, which are increasingly important in modern aerospace engineering.
Tip 5: Network Actively: Attend industry conferences and career fairs to network with professionals in the field. Networking can lead to job opportunities and provide insights into current salary trends and negotiation strategies.
Tip 6: Research Salary Benchmarks: Thoroughly research industry salary surveys and compensation data for similar roles in different locations. This information provides a realistic understanding of expected compensation and strengthens negotiation positions. Resources such as the Bureau of Labor Statistics or professional engineering societies are useful for this purpose.
Tip 7: Highlight Project Experience: Showcase successful projects undertaken during academic studies or internships. Quantify accomplishments and emphasize the impact of contributions to demonstrate tangible skills and problem-solving abilities. Specific examples of successful projects are often more compelling than a general statement of skills.
By proactively implementing these strategies, individuals entering the aerospace engineering profession can significantly improve their earning potential and secure a more financially rewarding career path.
These insights provide a foundation for understanding the dynamics of the compensation landscape within the aerospace engineering sector. The subsequent sections will explore strategies for long-term career advancement and salary growth.
1. Location's Cost of Living
The cost of living in a specific geographic area exerts a substantial influence on the compensation packages offered to aerospace engineering graduates. This factor serves as a critical determinant in salary negotiations and overall financial well-being for professionals entering the field.
- Housing Costs and Salary Adjustment
The price of housing, whether renting or purchasing, constitutes a major component of cost of living. Areas with high housing costs, such as major metropolitan centers or technology hubs, typically offer correspondingly higher salaries to offset the increased expense. For instance, an aerospace engineer accepting a position in Los Angeles, CA, may receive a significantly higher salary compared to an identical role in Huntsville, AL, due to the disparity in housing affordability. The higher salary is designed to maintain a comparable standard of living despite the increased housing expenditure.
- Tax Implications and Disposable Income
State and local tax rates directly impact disposable income, thereby influencing salary expectations. Locations with higher tax burdens may necessitate higher salaries to ensure that aerospace engineering graduates retain sufficient income after taxes to cover living expenses. For example, a state with no income tax may allow for a lower gross salary while still providing a similar net income compared to a state with a substantial income tax.
- Transportation Costs and Commuting Patterns
Transportation costs, including vehicle ownership, public transportation fares, and fuel expenses, contribute significantly to cost of living. Areas with limited public transportation options or long commute times often result in higher transportation-related expenses, prompting employers to factor this into compensation considerations. In densely populated areas with high commuting costs, aerospace firms may offer higher salaries or transportation subsidies to attract and retain talent.
- Goods and Services Pricing
The cost of everyday goods and services, such as groceries, utilities, and healthcare, varies considerably across different locations. Regions with higher prices for these essentials typically offer higher salaries to compensate for the increased cost of basic necessities. Aerospace engineering graduates moving to a high-cost region may find that their nominal salary increase is partially offset by the higher cost of these everyday goods and services.
The interplay between location’s cost of living and the compensation of aerospace engineering graduates highlights the need for careful consideration of financial factors when evaluating job offers. Understanding these dynamics allows graduates to make informed decisions and negotiate effectively to achieve financial stability and career satisfaction. Salary comparison tools that incorporate cost-of-living adjustments provide valuable insights for comparing offers across different geographic areas.
2. Company Size Impact
The size of the employing organization represents a significant determinant in the compensation structure for aerospace engineering graduates. Varied resources, project scope, and operational scales influence the financial packages offered to entry-level professionals.
- Resource Allocation and Compensation Budgets
Larger aerospace corporations typically possess greater financial resources, enabling them to allocate more substantial budgets for employee compensation. This translates to potentially higher starting salaries, comprehensive benefits packages, and opportunities for performance-based bonuses. In contrast, smaller companies or startups, while potentially offering unique growth opportunities, may operate with more constrained financial resources, potentially leading to lower initial compensation. For example, a graduate joining a multinational aerospace firm may receive a higher initial salary than a peer joining a smaller, specialized engineering consultancy.
- Project Scale and Complexity
The scale and complexity of projects undertaken by different sized companies often correlate with the compensation offered to aerospace engineering graduates. Larger firms are typically involved in large-scale, complex projects such as the development of commercial aircraft or space exploration vehicles. These projects require specialized skills and expertise, justifying higher compensation levels. Smaller companies may focus on niche areas or component-level development, which may not command the same level of financial reward. As project complexity increases, there is a higher demand for individuals with a complex understanding.
- Career Advancement and Compensation Growth
Larger organizations frequently offer structured career advancement programs and formalized compensation growth trajectories. This provides aerospace engineering graduates with a clear path for salary increases and promotions over time. Smaller companies may offer more rapid career advancement due to flatter organizational structures, but the potential for significant salary growth may be limited by the company’s overall financial performance. An employee at a large organization may expect regular increments based on years of service.
- Benefits Packages and Ancillary Compensation
The scope and value of benefits packages offered by aerospace companies vary significantly based on their size. Larger corporations typically provide more comprehensive benefits, including health insurance, retirement plans, paid time off, and employee assistance programs. These benefits contribute substantially to an employee’s overall compensation and financial well-being. Smaller companies may offer fewer benefits or require employees to contribute a larger portion of the cost. These additions provide a financial advantage.
In summary, the company size exerts a multifaceted influence on the starting compensation for aerospace engineering graduates. The interplay between resource allocation, project scale, career advancement opportunities, and benefits packages shapes the financial landscape for entry-level professionals. These considerations warrant careful evaluation when assessing employment opportunities in the aerospace sector.
The concept of specialized skill premium directly affects the remuneration commanded by aerospace engineering graduates. The demand for specific, highly technical abilities in the aerospace sector creates a competitive market, driving up the salaries offered to individuals possessing those skills. For instance, expertise in areas such as hypersonic flight, advanced propulsion systems, or autonomous aircraft control is considered highly valuable due to the limited number of engineers proficient in these domains. This scarcity, combined with the critical nature of these skills to ongoing projects, translates into a significant increase in earning potential.
One practical example is the burgeoning field of space exploration and satellite technology. Graduates with demonstrable experience in orbital mechanics, satellite communications, or radiation hardening of electronic components are often sought after by private space companies and government agencies alike. These organizations are willing to offer premium compensation packages to secure the services of engineers who can contribute to these highly specialized and complex projects. Similarly, within the aviation sector, expertise in composite materials, aerodynamic design, or flight simulation software also attracts higher salary offers. This premium reflects the impact of these specializations on aircraft performance, safety, and efficiency.
In conclusion, the acquisition and demonstration of specialized skills represents a crucial strategy for aerospace engineering graduates seeking to maximize their earning potential. By focusing on high-demand areas and developing a deep understanding of specific aerospace technologies, graduates can significantly increase their value in the job market. This understanding is critical for both individual career planning and for organizations seeking to attract and retain top talent within the aerospace industry.
4. Degree level influence
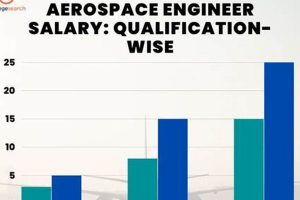
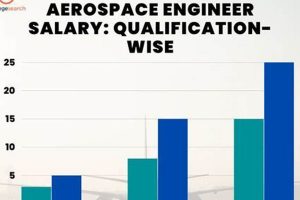
The attainment of advanced academic qualifications within aerospace engineering significantly impacts subsequent remuneration. A direct correlation exists between the level of educational achievement and the expected compensation. This relationship stems from the increased depth of knowledge, research experience, and specialized skills acquired during postgraduate studies. For instance, a graduate holding a Master of Science degree often possesses a more comprehensive understanding of advanced aerospace concepts and analytical techniques compared to a Bachelor’s degree holder. This enhanced expertise translates into a higher starting salary and improved prospects for career advancement.
Furthermore, doctoral-level graduates typically command even greater compensation due to their extensive research experience and demonstrated ability to conduct independent, original work. The specialized knowledge and problem-solving skills honed during a Ph.D. program are highly valued in research-intensive roles and leadership positions within the aerospace industry. Consider the example of an aerospace engineer tasked with designing a novel propulsion system. A Ph.D. holder, having likely conducted extensive research in propulsion technologies, would be better equipped to address the complex engineering challenges associated with this task, thereby justifying a higher salary.
In conclusion, the level of academic attainment exerts a demonstrable influence on the earning potential of aerospace engineering graduates. Higher degrees signify specialized knowledge and advanced skills that are highly sought after in the aerospace sector. Understanding this connection allows individuals to make informed decisions regarding their educational path and career trajectory, ultimately impacting their long-term financial prospects. This understanding serves as a reminder to consider the potential future earnings versus investment in education.
5. Industry sector variances
The sector of employment significantly influences the compensation offered to aerospace engineering graduates. A demonstrable disparity exists between the salaries available across distinct segments of the industry, arising from factors such as project funding, profit margins, and the strategic value placed on engineering talent. For example, graduates entering the defense sector might experience a different compensation structure compared to those joining commercial aviation or space exploration companies.
Within the defense industry, projects are often characterized by long-term contracts and substantial government funding, which can translate to stable employment and competitive salaries, especially for roles requiring security clearances or specialized expertise in military aircraft or missile systems. Conversely, the commercial aviation sector is subject to market fluctuations and airline profitability, potentially impacting salary levels and job security. Space exploration, particularly with the rise of private companies, presents a dynamic landscape. Some companies, backed by substantial venture capital, may offer attractive compensation packages to attract top talent focused on innovative technologies like reusable rockets or space-based manufacturing. However, these roles can also carry a higher degree of risk due to the volatile nature of startup funding and project timelines.
In conclusion, aerospace engineering graduates should carefully consider the financial implications associated with different industry sectors when evaluating job offers. Understanding these variances allows for informed decision-making, aligning career aspirations with realistic salary expectations. The choice of sector represents a critical factor shaping long-term earning potential and career trajectory in the aerospace field.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following questions address common inquiries regarding the compensation of aerospace engineering graduates, providing clarity on factors influencing earning potential and career progression.
Question 1: What starting remuneration can a recent aerospace engineering graduate realistically expect?
The anticipated starting compensation is influenced by geographic location, the specific industry sector, the size of the employing organization, and the graduate’s academic qualifications. Generally, new graduates can anticipate a range informed by industry surveys and cost-of-living adjustments for the relevant location.
Question 2: How significantly does a Master’s degree impact entry-level compensation compared to a Bachelor’s degree in the same field?
A Master’s degree typically correlates with a higher starting salary due to the advanced knowledge and specialized skills acquired during postgraduate studies. Employers often recognize the value of this advanced training, offering commensurate compensation.
Question 3: Are there specific specializations within aerospace engineering that command a higher premium in terms of salary?
Yes, specializations in high-demand areas such as avionics, propulsion systems, autonomous flight control, and advanced materials often attract higher salaries. Expertise in these domains is particularly valuable to employers.
Question 4: How does the size of the aerospace company affect the compensation package offered to graduates?
Larger aerospace corporations generally possess greater financial resources, enabling them to offer more competitive salaries and comprehensive benefits packages. Smaller companies may offer different advantages, such as equity or faster career progression, but may not match the starting salaries of larger firms.
Question 5: What role does geographic location play in determining aerospace engineering graduate salaries?
Geographic location is a significant factor, with salaries often adjusted to reflect the cost of living in a particular region. Metropolitan areas and locations with high demand for aerospace engineers typically offer higher compensation to offset increased living expenses.
Question 6: Are there any effective negotiation strategies that can be employed to maximize starting remuneration?
Thorough research of industry salary benchmarks, demonstrating relevant skills and experience through internships and projects, and actively networking within the aerospace community can strengthen negotiation positions and potentially lead to improved compensation.
These frequently asked questions provide insights into the dynamics of compensation within the aerospace engineering profession. Understanding these factors enables graduates to make informed decisions and pursue financially rewarding career paths.
The next section will delve into resources for researching compensation data and career planning within the aerospace engineering field.
Conclusion
The preceding analysis has explored the multifaceted factors influencing compensation for those entering the aerospace engineering field. Location’s cost of living, company size, specialized skill premiums, academic degree level, and sector variances all contribute to the complex determination of initial earnings. Recognizing these elements is crucial for informed career planning and financial expectations.
A realistic understanding of aerospace engineering graduate salary prospects empowers individuals to strategically position themselves for success. Diligent research, targeted skill development, and thoughtful consideration of diverse career paths are essential to maximizing long-term earning potential in this demanding yet rewarding profession. The future of aerospace relies on skilled professionals; a well-informed approach to compensation ensures a sustainable talent pipeline.


![Your Aerospace Engineering Salary in San Diego [Guide] Safem Fabrication - Precision Engineering & Custom Manufacturing Solutions Your Aerospace Engineering Salary in San Diego [Guide] | Safem Fabrication - Precision Engineering & Custom Manufacturing Solutions](https://mixaerospace.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/th-4364-300x200.jpg)