The career opportunities available within the aerospace sector across the European continent represent a significant area of professional interest. These roles encompass a wide spectrum of activities, from the design and manufacture of aircraft and spacecraft to research and development of new aerospace technologies and management of related projects and programs. An example includes positions focusing on propulsion systems for next-generation aircraft within a multinational engineering firm headquartered in Germany.
The significance of pursuing a career in this field in Europe lies in several factors. The continent boasts a rich history of aerospace innovation and is home to leading companies and research institutions in the sector. Furthermore, the presence of international collaborations, such as those facilitated by the European Space Agency (ESA), offers exposure to diverse projects and advanced technologies. The growth of the European space program and continuous advancements in air travel contribute to the ongoing demand for skilled professionals.
Therefore, understanding the nuances of the European aerospace employment market is critical for individuals seeking entry or advancement in this domain. Subsequent discussion will explore specific job roles, required qualifications, regional variations in demand, and resources available to prospective applicants. These elements provide a more detailed view of navigating career paths within European aerospace.
The following provides focused guidance for professionals seeking roles in the European aerospace sector. Adherence to these suggestions can enhance prospects for successful entry and advancement.
Tip 1: Target Strategic Locations: Focus application efforts on regions with established aerospace hubs, such as Toulouse (France), Hamburg (Germany), and Bristol (United Kingdom). These areas host significant aerospace industries and research facilities.
Tip 2: Acquire Specialized Skills: Develop expertise in high-demand areas, including aerodynamics, computational fluid dynamics (CFD), structural analysis, or avionics. Specific software proficiency, such as CATIA or ANSYS, is often required.
Tip 3: Emphasize Relevant Experience: Highlight previous projects, internships, or research that directly relate to aerospace engineering principles. Quantifiable achievements and demonstrable problem-solving skills are particularly valuable.
Tip 4: Obtain Advanced Certifications: Pursue relevant certifications, such as those related to project management (e.g., PMP) or specific engineering software. These credentials demonstrate a commitment to professional development.
Tip 5: Cultivate Language Proficiency: Enhance language skills, particularly in languages spoken in key aerospace centers, such as French or German. Fluency broadens opportunities and facilitates collaboration.
Tip 6: Leverage Networking Opportunities: Attend industry conferences, workshops, and career fairs to connect with potential employers and learn about emerging trends. Active participation in professional organizations can also be beneficial.
Tip 7: Understand European Regulations: Familiarize with European Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) regulations and standards. Knowledge of these guidelines is essential for ensuring compliance in design, manufacturing, and operations.
In summary, securing a role in European aerospace demands a targeted approach that combines technical expertise, strategic location focus, and awareness of industry-specific requirements. These preparatory steps can significantly increase the likelihood of achieving career objectives.
Further discussion will delve into resources and strategies for successful job application and interview preparation within the European context.
1. Skills
The acquisition and demonstration of specific technical skills are directly causative to securing employment within the European aerospace sector. Employers actively seek candidates possessing expertise in areas such as aerodynamics, propulsion systems, materials science, and control systems. The absence of such skills significantly diminishes an applicant’s competitiveness in the “aerospace engineering jobs europe” market. For example, an engineer lacking proficiency in computational fluid dynamics (CFD) would be unable to contribute effectively to the design and analysis of aircraft wings, a critical function in many aerospace engineering roles.
Furthermore, the evolving nature of aerospace demands continuous skill development. Emerging fields such as autonomous flight control, electric propulsion, and sustainable materials require engineers to adapt and acquire new competencies. Practical application of these skills is paramount; theoretical knowledge alone is insufficient. Demonstrable experience through projects, internships, or prior employment showcasing the successful application of these skills is a key differentiator. For instance, a candidate with a portfolio demonstrating the design and simulation of a drone control system using Model-Based Systems Engineering (MBSE) tools would be highly valued.
In summary, the requisite skills form the foundation for accessing opportunities in European aerospace engineering. The challenges lie in identifying the specific skills demanded by employers, acquiring them through relevant education and training, and effectively showcasing their practical application. Understanding this direct relationship between demonstrable skills and employment prospects is essential for individuals pursuing a career in “aerospace engineering jobs europe.” A failure to address the skills gap will result in significant barriers to entry and advancement within the field.
2. Location
Geographic location exerts a significant influence on the availability and nature of opportunities within the European aerospace sector. The concentration of aerospace industries and research facilities in specific regions shapes career trajectories and necessitates a strategic approach to job searching.
- Aerospace Clusters
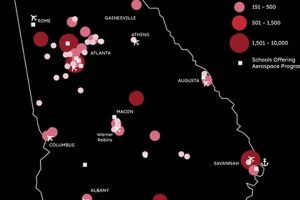
Certain regions across Europe function as prominent aerospace clusters. Examples include Toulouse in France, known for Airbus headquarters and associated supply chain companies; Hamburg in Germany, a major center for aircraft manufacturing; and the South West region of the United Kingdom, home to numerous aerospace firms and research institutions. Targeting job applications within these established clusters increases the likelihood of finding relevant positions due to the higher density of aerospace employers.
- Research and Development Centers
The presence of renowned research and development centers impacts the demand for specialized aerospace engineers. Locations with significant investment in aerospace research, such as the German Aerospace Center (DLR) sites across Germany or research hubs near universities with strong aerospace engineering programs, often offer opportunities in cutting-edge technologies and research-oriented roles. These locations attract highly skilled professionals and foster innovation.
- Government and Regulatory Agencies
The placement of government agencies and regulatory bodies, such as the European Space Agency (ESA) facilities in various countries, also influences job availability. These agencies often employ engineers in areas related to space exploration, satellite development, and regulatory compliance. Proximity to these institutions can offer unique career paths involving policy, standardization, and international collaboration.
- Supply Chain Networks
Beyond major aerospace companies, the extensive supply chain supporting the industry creates employment opportunities in various locations. Component manufacturers, suppliers of specialized materials, and providers of engineering services are often geographically dispersed across Europe. Understanding the distribution of this supply chain allows job seekers to identify potential employers in less obvious, but nonetheless relevant, regions.
In conclusion, strategic consideration of geographic location is paramount when pursuing career opportunities in European aerospace. The concentration of industries, research centers, regulatory bodies, and supporting supply chains creates specific areas of high demand. Targeting job applications within these regions maximizes the probability of securing employment and advancing a career in the aerospace sector across Europe.
3. Regulations
Regulatory frameworks exert a profound influence on the nature and availability of opportunities in European aerospace engineering. Compliance with established standards and directives is a non-negotiable aspect of the profession, directly shaping engineering practices and job requirements.
- EASA Certification Requirements
The European Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) sets rigorous certification standards for aircraft, components, and maintenance procedures. Aerospace engineers involved in design, manufacturing, and maintenance must possess a thorough understanding of EASA regulations. For example, engineers working on aircraft structural integrity must demonstrate compliance with EASA CS-25 airworthiness standards. Failure to adhere to these regulations can result in project delays, financial penalties, and legal liabilities, directly impacting job security and career progression.
- Environmental Regulations
Increasingly stringent environmental regulations, such as those aimed at reducing noise and emissions, are shaping aerospace engineering roles. Engineers are needed to develop and implement technologies that minimize the environmental impact of aircraft. This includes designing more fuel-efficient engines, developing alternative fuels, and optimizing flight paths to reduce noise pollution. Knowledge of regulations like those related to the Single European Sky ATM Research (SESAR) project is becoming increasingly important.
- Safety Standards and Procedures
Aerospace engineering inherently involves adherence to strict safety standards and procedures. Engineers are responsible for ensuring the safety of aircraft and passengers throughout the design, manufacturing, and operational phases. This requires a deep understanding of safety management systems, risk assessment methodologies, and human factors engineering. Engineers working on critical systems, such as flight controls or landing gear, must demonstrate a high level of competence in these areas.
- Export Control Regulations
The international nature of the aerospace industry necessitates compliance with export control regulations. Engineers working on technologies with potential military applications must be aware of restrictions on the transfer of technology to certain countries. Violations of these regulations can have severe legal and reputational consequences. Knowledge of regulations such as the Wassenaar Arrangement is crucial for engineers involved in international collaborations or the export of aerospace products.
In summary, a comprehensive understanding of regulations is essential for success in European aerospace engineering. These regulations impact every aspect of the profession, from design and manufacturing to operations and international collaboration. Engineers who demonstrate expertise in regulatory compliance are highly sought after and well-positioned for career advancement in “aerospace engineering jobs europe”.
4. Competition
The European aerospace job market presents a highly competitive landscape for engineering professionals. Multiple factors contribute to this dynamic, impacting both entry-level and experienced engineers seeking positions within the sector. The relatively high concentration of skilled engineers graduating from European universities, coupled with the presence of established global aerospace companies, generates a significant pool of qualified candidates vying for available roles. This heightened competition necessitates that individuals differentiate themselves through specialized skills, relevant experience, and proactive career development strategies.
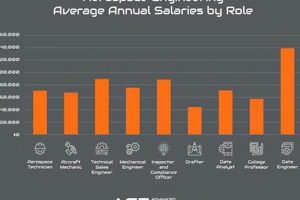
The consequences of intense competition are multifaceted. Employers often have the latitude to demand higher levels of qualification and experience from applicants. This can translate into a requirement for advanced degrees, specialized certifications, or a proven track record of success in complex aerospace projects. Furthermore, compensation packages may be influenced by the competitive environment, with companies potentially offering more attractive salaries and benefits to secure top talent. The impact extends beyond individual job seekers, potentially fostering innovation and driving continuous improvement within the aerospace industry as companies seek to attract and retain the most capable engineers. For example, a recent recruitment drive by a major European aircraft manufacturer saw hundreds of applications for each open engineering position, forcing the company to implement rigorous selection criteria including technical assessments and behavioral interviews to identify the most promising candidates.
In summary, understanding the competitive nature of the European aerospace engineering job market is crucial for aspiring professionals. Success requires a proactive approach encompassing continuous skill development, strategic networking, and a commitment to exceeding expectations. While the competition presents challenges, it also serves as a catalyst for individual growth and innovation within the industry, ultimately contributing to the advancement of aerospace technology and engineering practices across Europe. Individuals should actively seek opportunities to gain practical experience, participate in industry-related events, and tailor their skills to meet the evolving demands of the market, thereby enhancing their competitiveness and increasing their prospects for a successful career in European aerospace.
5. Innovation
The European aerospace sector is intrinsically linked to innovation, thereby significantly shaping the nature and availability of related employment opportunities. Technological advancements and the pursuit of novel solutions are central to the competitiveness and growth of the industry, creating a constant demand for engineers capable of driving innovation. These engineers are not merely implementers of existing technologies but are actively involved in research, development, and deployment of cutting-edge solutions. The presence of research institutions like the German Aerospace Center (DLR) and collaborations fostered by the European Space Agency (ESA) directly stimulate innovative projects, resulting in a higher demand for engineers with specialized skills in emerging fields such as electric propulsion, advanced materials, and autonomous flight systems. This focus on innovation has a cascading effect, influencing the skills required for “aerospace engineering jobs europe”, pushing the industry to seek professionals who can contribute to the next generation of aerospace technologies.
Real-world examples underscore the practical significance of innovation in the European aerospace job market. Consider the development of the Airbus A350, which incorporated advanced composite materials and fuel-efficient engine designs to improve performance and reduce environmental impact. Engineers involved in this project required expertise in areas such as structural analysis, aerodynamics, and systems integration, demonstrating a tangible demand for innovative skill sets. Similarly, the increasing emphasis on unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) for various applications has created a surge in demand for engineers with expertise in robotics, artificial intelligence, and sensor technologies. Companies are investing heavily in research and development related to UAVs, creating new “aerospace engineering jobs europe” focused on developing innovative solutions for autonomous flight and data analysis. These advancements in technological capabilities drive expansion of skill set requirements from the employees.
In conclusion, innovation is a critical driver of employment opportunities within the European aerospace engineering sector. The industry’s commitment to developing cutting-edge technologies creates a constant demand for skilled engineers who can contribute to advancements in areas such as sustainability, autonomy, and performance. While this focus on innovation presents challenges for aspiring engineers, it also provides exciting opportunities to work on groundbreaking projects and shape the future of aerospace. The demand for innovation also requires engineers to be adaptable, continuously learning and upgrading their skills to stay abreast of the latest technological developments. The continued investment in research and development by European aerospace companies and institutions reinforces the central role of innovation in shaping “aerospace engineering jobs europe” and securing the future of the industry.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following addresses common inquiries regarding opportunities in the European aerospace engineering sector, providing concise and factual responses.
Question 1: What are the primary skills employers seek in aerospace engineering candidates in Europe?
Employers prioritize candidates demonstrating proficiency in aerodynamics, computational fluid dynamics (CFD), structural analysis, propulsion systems, and control systems. Knowledge of relevant software, such as CATIA or ANSYS, is frequently expected.
Question 2: Which European regions offer the most abundant aerospace engineering job opportunities?
Established aerospace hubs like Toulouse (France), Hamburg (Germany), and the South West region of the United Kingdom typically present the greatest concentration of available positions.
Question 3: How important is knowledge of European Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) regulations for aerospace engineers in Europe?
Compliance with EASA regulations is paramount. A thorough understanding of these standards is essential for ensuring safety, airworthiness, and adherence to legal requirements in design, manufacturing, and maintenance activities.
Question 4: What are the key strategies for differentiating oneself in the competitive European aerospace job market?
Candidates should focus on acquiring specialized skills, obtaining relevant certifications (e.g., PMP), showcasing project experience, and cultivating language proficiency (particularly French or German).
Question 5: How significant is the role of innovation in shaping job opportunities within the European aerospace sector?
Innovation is a critical driver. The industry’s commitment to developing cutting-edge technologies creates a demand for engineers capable of contributing to advancements in areas like sustainability, autonomy, and performance.
Question 6: What is the impact of environmental regulations on the European aerospace engineering job market?
Increasingly stringent environmental regulations are creating a demand for engineers specialized in developing technologies that minimize the environmental impact of aircraft, including fuel-efficient engines and alternative fuel development.
In summary, success in securing a European aerospace engineering position necessitates a combination of technical expertise, strategic location focus, regulatory awareness, and proactive career development. Continuous learning and adaptability are also crucial attributes.
The subsequent discussion will provide specific resources for individuals seeking to further explore career options within the European aerospace engineering landscape.
Concluding Observations on European Aerospace Opportunities
This exploration of “aerospace engineering jobs europe” has elucidated the key factors influencing career prospects within the sector. These include the necessity of specialized skills, strategic location considerations, the imperative of regulatory compliance, the reality of intense competition, and the critical role of innovation. Each of these aspects presents both challenges and opportunities for individuals seeking to enter or advance within the European aerospace engineering field.
Understanding these dynamics is paramount for those contemplating a career in this domain. While the path may be demanding, the rewardscontributing to technological advancements and shaping the future of flightare considerable. Continued diligence in skill development and strategic preparation will remain essential for navigating the evolving landscape of “aerospace engineering jobs europe” and securing a fulfilling career in this vital sector.





![Aerospace Jobs: Engineer Job Growth [Trends & Outlook] Innovating the Future of Flight with Reliable Aviation Solutions Aerospace Jobs: Engineer Job Growth [Trends & Outlook] | Innovating the Future of Flight with Reliable Aviation Solutions](https://mixaerospace.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/th-861-300x200.jpg)