Compensation for professionals in the field of flight vehicle and spacecraft design, development, and testing, specifically those employed within the Lone Star State, represents the economic value placed upon their specialized skills and contributions. This remuneration reflects factors such as experience level, educational attainment, specific job responsibilities, and the employing company’s size and location. For instance, an entry-level engineer might receive a different compensation package than a seasoned specialist with advanced certifications.
The financial aspect of this profession is crucial for attracting and retaining talent within the state, which boasts a significant aerospace industry presence. Competitive pay scales ensure continued innovation and excellence within this sector, driving economic growth and maintaining the state’s prominence in space exploration and aeronautics. The history of this industry in Texas, particularly around major hubs like Houston, has shaped the demand for skilled professionals and, consequently, the financial rewards they receive.
Therefore, a comprehensive understanding of the various factors influencing earnings for these engineers is vital for both prospective professionals and established members of the field. The following sections will delve into the specifics of salary ranges, influencing factors, and regional variations in compensation for aerospace engineers throughout Texas.
The information surrounding appropriate earnings levels for professionals in the aerospace engineering field within Texas requires careful consideration. The following points provide guidance in understanding and managing compensation expectations:
Tip 1: Research Regional Cost of Living: The cost of living varies significantly across Texas cities. Salaries in metropolitan areas like Houston or Dallas may be higher to compensate for increased expenses related to housing, transportation, and general living costs. Thorough research into the cost of living in a specific location is essential when evaluating a potential compensation package.
Tip 2: Assess Educational Qualifications: Advanced degrees, such as a Master’s or Doctorate in aerospace engineering or a related field, can significantly impact earning potential. Quantify the potential return on investment for advanced education when considering career advancement and salary negotiations.
Tip 3: Analyze Experience Level: Entry-level positions will naturally command lower salaries than those requiring extensive experience. Understanding the typical salary range for specific experience brackets (e.g., 0-3 years, 5-10 years, 10+ years) is crucial for setting realistic expectations and negotiating effectively.
Tip 4: Evaluate Specific Skill Sets: Specialized skills in high-demand areas, such as computational fluid dynamics (CFD), systems engineering, or specific software proficiency, can command a premium. Highlight these specialized skills during the application and negotiation processes to justify a higher salary.
Tip 5: Compare Company Size and Type: Larger aerospace corporations or those involved in government contracts often offer more competitive salaries and benefits packages compared to smaller companies or startups. Research the typical compensation structures of various employers to gauge industry standards.
Tip 6: Consider Benefits Packages: The total compensation package extends beyond base salary. Health insurance, retirement plans (401k), paid time off, and other benefits should be factored into the overall value of an employment offer. Assign a monetary value to these benefits to facilitate a comprehensive comparison of different offers.
Tip 7: Negotiate Strategically: Salary negotiation is a critical component of accepting a job offer. Be prepared to justify desired salary expectations with concrete examples of accomplishments, skills, and contributions. Research industry averages and be confident in articulating one’s value to the organization.
Understanding and proactively managing expectations surrounding earnings is essential for a successful career trajectory in aerospace engineering. Careful research, realistic self-assessment, and strategic negotiation will contribute to securing a compensation package commensurate with one’s skills and contributions.
The following sections will further analyze compensation trends, future outlooks, and strategies for maximizing earning potential within the aerospace engineering sector in Texas.
1. Experience Level
The correlation between experience level and compensation for aerospace engineers in Texas is direct and significant. As engineers accumulate practical experience, their value to employers increases, leading to higher earnings. Entry-level positions, typically requiring a bachelor’s degree and minimal prior experience, offer the lowest salaries. This initial compensation reflects the time required for new graduates to develop proficiency and contribute meaningfully to complex projects. For example, a recent graduate might assist in design tasks under the supervision of a senior engineer, requiring further on-the-job training and mentorship. Therefore, the early career phase provides essential foundational knowledge and skills, laying the groundwork for subsequent career progression and increased earning potential.
Mid-career professionals, generally with five to ten years of experience, demonstrate a higher level of technical expertise and project management capabilities. These engineers typically handle more complex assignments, potentially leading project teams or specializing in a specific area of aerospace engineering, such as propulsion systems or avionics. The increased responsibility and demonstrated competence translate into substantial salary increases. A mid-career engineer, for instance, might lead the design and testing of a new aircraft component, requiring independent decision-making and problem-solving skills. This level of expertise directly impacts the project’s success, justifying higher compensation.
Senior-level engineers, possessing over ten years of experience, represent the pinnacle of technical expertise and leadership within their organizations. These individuals often hold management positions, oversee large-scale projects, and mentor junior engineers. Senior engineers are expected to make critical technical decisions, provide strategic guidance, and contribute to the company’s overall success. For example, a senior engineer might manage the development of an entire satellite system, requiring extensive knowledge of various engineering disciplines and the ability to coordinate cross-functional teams. This level of responsibility and expertise commands the highest salaries within the profession. The understanding of this correlation allows engineers to strategically plan their career development, focusing on acquiring the skills and experience necessary to progress to higher-paying roles. The relationship emphasizes the continuous need for professional development and skill enhancement to remain competitive in the aerospace engineering job market in Texas.
2. Education Attainment
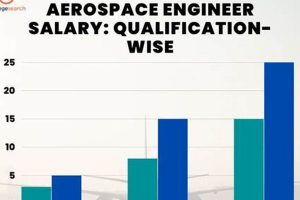
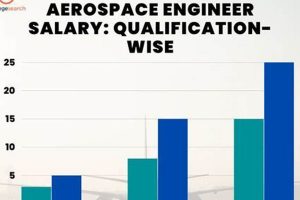
Educational qualifications serve as a fundamental determinant of compensation levels for aerospace engineers within Texas. The level of academic achievement attained directly correlates with the specialized knowledge, analytical abilities, and problem-solving skills an engineer possesses, thereby influencing their market value and earning potential.
- Bachelor’s Degree
A Bachelor’s degree in Aerospace Engineering, or a closely related field such as Mechanical Engineering or Electrical Engineering, represents the entry-level educational requirement for most positions. This foundational degree equips engineers with the core principles of aerodynamics, propulsion, structures, and control systems. However, possessing only a Bachelor’s degree typically results in a lower starting salary compared to candidates with advanced degrees, as the depth and breadth of knowledge are comparatively limited. Entry-level roles may involve assisting senior engineers in design and analysis tasks.
- Master’s Degree
Pursuing a Master’s degree allows for specialized knowledge acquisition in a specific area of aerospace engineering, such as computational fluid dynamics, spacecraft design, or advanced materials. This advanced knowledge enhances problem-solving capabilities and positions engineers for more complex and challenging projects. Employers often recognize this enhanced expertise by offering higher salaries and opportunities for career advancement. For example, an engineer with a Master’s degree specializing in propulsion systems might be involved in the design and testing of rocket engines, a role typically requiring a deeper understanding of thermodynamics and fluid mechanics than a Bachelor’s degree holder would possess.
- Doctoral Degree (Ph.D.)
A doctoral degree signifies the highest level of academic achievement and represents a commitment to research and innovation. Ph.D. holders typically engage in cutting-edge research, develop new technologies, and contribute to the advancement of aerospace engineering knowledge. These individuals are highly sought after by research institutions, government agencies, and aerospace companies engaged in advanced development programs. A Ph.D. degree commands the highest salaries and offers opportunities for leadership roles in research and development. An engineer with a Ph.D., for instance, might lead a research team focused on developing new materials for hypersonic vehicles, pushing the boundaries of aerospace technology.
- Specialized Certifications and Training
Beyond formal degrees, specialized certifications and training courses can also impact earning potential. Certifications in areas such as project management, systems engineering, or specific software tools demonstrate a commitment to professional development and enhance an engineer’s skillset. These certifications can differentiate candidates in the job market and justify higher salary expectations. An aerospace engineer certified in systems engineering, for example, is more likely to be involved in the integration of complex aerospace systems, a role that demands a broad understanding of various engineering disciplines and effective communication skills.
In conclusion, the level of education attainment significantly influences the earnings of aerospace engineers in Texas. Advanced degrees and specialized certifications demonstrate a deeper understanding of aerospace principles and enhance problem-solving abilities, leading to higher salaries and opportunities for career advancement. The decision to pursue higher education or specialized training should be carefully considered, taking into account career goals and the potential return on investment in terms of increased earning potential and professional opportunities within the aerospace engineering field in Texas.
3. Company Size
The size of an aerospace company operating within Texas constitutes a significant factor influencing the compensation packages offered to its engineering staff. Larger organizations, characterized by extensive resources and broader project portfolios, tend to provide more competitive salaries and benefits compared to smaller firms or startups. This disparity arises from a confluence of factors, including revenue generation, project complexity, and overall financial stability.
- Resource Availability
Larger aerospace corporations typically possess greater financial resources, enabling them to offer more attractive salaries and benefits packages to attract and retain top talent. These resources allow for investment in employee training, advanced software and hardware, and comprehensive health insurance plans, all contributing to a more desirable employment proposition. For example, a multinational aerospace company might offer a more robust retirement plan and tuition reimbursement program than a smaller company focused on niche engineering services.
- Project Complexity and Scale
Larger companies often undertake more complex and large-scale projects, demanding a wider range of specialized engineering skills. These projects, such as the development of commercial aircraft or space exploration vehicles, require teams of engineers with diverse expertise, justifying higher compensation levels to secure individuals with specialized knowledge. Smaller companies, often specializing in specific areas like drone technology or component manufacturing, may offer less complex projects, resulting in comparatively lower salary structures.
- Revenue Generation and Profit Margins
Greater revenue generation and higher profit margins allow larger aerospace companies to allocate more resources towards employee compensation. A company with substantial government contracts or a strong market share in commercial aviation can afford to offer more competitive salaries to remain attractive to top engineering talent. Smaller companies, with potentially lower revenue streams and narrower profit margins, might face constraints in matching the compensation packages offered by larger competitors.
- Branding and Prestige
Established aerospace companies with strong brand recognition and a reputation for innovation often attract a larger pool of qualified candidates. This increased competition for positions allows these companies to be more selective in their hiring process and potentially offer lower salaries while still attracting top talent due to the perceived prestige of working for a renowned organization. Smaller companies, lacking the same brand recognition, may need to offer more competitive salaries to attract qualified engineers.
In summary, the size of an aerospace company in Texas plays a crucial role in determining the salary levels of its engineers. Larger companies, with their superior resources, complex projects, and higher revenue generation, tend to offer more competitive compensation packages. However, factors such as company branding and specialization can also influence salary levels, emphasizing the importance of considering a holistic view when evaluating potential employment opportunities within the aerospace engineering field in Texas.
4. Geographic Location
The geographic location within Texas exerts a notable influence on compensation levels for aerospace engineers. This relationship stems from varying cost-of-living indices, concentration of aerospace industry activity, and local demand for specialized skills across different regions of the state. For instance, the Houston metropolitan area, home to NASA’s Johnson Space Center and numerous aerospace contractors, often commands higher salaries due to its prominent role in space exploration and related technologies. This concentration of industry activity creates a competitive job market, driving up compensation to attract and retain qualified engineers. Conversely, regions with fewer aerospace employers or a lower cost of living may exhibit comparatively lower salary ranges. Therefore, the proximity to major aerospace hubs directly impacts the financial prospects for professionals in this field.
Furthermore, the type of aerospace activity prevalent in a specific location can also affect salary levels. Areas specializing in manufacturing and production may offer different compensation packages than those focused on research and development. For example, a city with a significant presence of aerospace component manufacturing plants might prioritize engineers with expertise in production processes and quality control, whereas a location centered around research institutions may value advanced degrees and specialized skills in areas such as computational fluid dynamics or advanced materials. Understanding these regional specializations is crucial for aerospace engineers seeking to maximize their earning potential within Texas. Practical application of this knowledge involves identifying locations that align with individual skillsets and career aspirations, considering both salary potential and professional growth opportunities.
In summary, geographic location represents a key determinant of aerospace engineering salaries in Texas, influenced by cost-of-living, industry concentration, and regional specializations. The challenge lies in balancing the desire for higher compensation with factors such as career growth opportunities, quality of life, and personal preferences regarding location. A thorough understanding of these regional variations empowers aerospace engineers to make informed decisions about their career paths and optimize their financial outcomes within the state’s dynamic aerospace industry. The interplay of geographic location and compensation extends beyond individual career choices, also affecting industry recruitment strategies and the overall competitiveness of Texas within the national aerospace landscape.
5. Specific Skills
Within the Texas aerospace engineering sector, specialized proficiencies exert a direct influence on compensation levels. The demand for particular skills, driven by evolving technological advancements and industry needs, creates a premium for engineers possessing these competencies. An evaluation of specific skills provides insights into the determinants of earnings for these professionals.
- Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) Expertise
CFD proficiency is highly valued for simulating fluid flows around aircraft and spacecraft, optimizing aerodynamic designs. Real-world applications include analyzing wing performance or predicting heat transfer in rocket engines. Engineers skilled in CFD software and analysis techniques command higher salaries due to their ability to improve design efficiency and reduce development costs.
- Systems Engineering Knowledge
Systems engineering involves managing the complexities of integrating various subsystems within aerospace vehicles. This includes requirement definition, interface control, and verification testing. Professionals with strong systems engineering backgrounds are essential for ensuring the successful operation of integrated aerospace systems and are compensated accordingly.
- Proficiency in Aerospace Software Tools
Expertise in industry-standard software packages, such as CATIA, MATLAB, or ANSYS, significantly enhances an engineer’s productivity and effectiveness. These tools are utilized for design, analysis, and simulation, streamlining the engineering process. Engineers with advanced software skills are valuable assets, contributing to efficiency and are often rewarded with higher earnings.
- Specialization in Advanced Materials
Knowledge of advanced materials, including composites, alloys, and nanomaterials, is increasingly crucial for developing lighter, stronger, and more heat-resistant aerospace structures. Engineers specializing in materials science and engineering contribute to enhancing vehicle performance and safety. Due to the specialized knowledge required and the growing importance of these materials, these engineers are well-compensated.
The remuneration of aerospace engineers in Texas is directly linked to the possession of in-demand skills. As technology advances and industry priorities shift, the value placed on specific expertise fluctuates. To maximize earning potential, engineers must continuously acquire and refine skills aligned with the evolving needs of the aerospace sector. By mastering these skills, engineers in Texas can command higher salaries and contribute significantly to the advancement of aerospace technology.
6. Industry Demand
The correlation between industry demand and aerospace engineering compensation within Texas is direct and significant. Elevated demand for aerospace engineers invariably exerts upward pressure on salary levels. This relationship arises from fundamental economic principles: when the number of available positions exceeds the supply of qualified professionals, employers compete for talent by offering more attractive compensation packages. For instance, periods of increased government spending on space exploration or military aviation initiatives demonstrably lead to a surge in demand for engineers, consequently driving up salaries across the board. Conversely, economic downturns or reductions in defense budgets can dampen demand, potentially moderating salary growth or even leading to stagnation in certain segments of the profession. The state’s geographical location, with proximity to key government and private sector installations, makes it a significant factor in these dynamics. Understanding the interplay between industry demand and compensation is therefore essential for both prospective and practicing aerospace engineers aiming to optimize their career trajectories.
Real-world examples illustrate this dynamic. The resurgence of commercial spaceflight activities, coupled with ongoing technological advancements in areas such as unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and electric propulsion, have generated a heightened demand for engineers possessing specialized skills in these domains. Companies actively recruiting in these areas often offer substantial salary premiums to attract candidates with the requisite expertise. Furthermore, the presence of major aerospace contractors in Texas, engaged in long-term development programs, ensures a relatively stable demand for engineering talent, mitigating the potential for drastic salary fluctuations experienced in regions with less diversified aerospace economies. Monitoring industry trends, including government contracts, technological advancements, and overall economic conditions, provides valuable insights into the forces shaping demand and compensation within the sector.
In conclusion, industry demand serves as a primary driver of aerospace engineering salaries in Texas. Fluctuations in government spending, technological innovation, and the overall health of the aerospace sector directly impact the demand for engineers, influencing their earning potential. A proactive understanding of these dynamics, coupled with continuous professional development to acquire in-demand skills, empowers aerospace engineers to navigate the job market effectively and secure competitive compensation packages. The challenges lie in anticipating future industry trends and adapting skillsets accordingly, ensuring continued relevance and marketability within the ever-evolving aerospace landscape.
7. Federal Contracts
Federal contracts represent a significant determinant of compensation for aerospace engineers in Texas. These contracts, awarded by agencies such as NASA, the Department of Defense, and other government entities, inject substantial funding into the aerospace industry within the state. The influx of federal dollars directly fuels research and development, design, manufacturing, and testing activities, creating a demand for skilled aerospace engineers. This increased demand, driven by specific project requirements outlined in the contracts, leads to competitive bidding among companies for qualified personnel, resulting in higher salary offerings to attract and retain talent. The direct impact is that companies with large federal contracts typically offer more lucrative compensation packages compared to firms reliant on commercial ventures or private funding alone. Examples include projects related to space exploration, defense systems, and advanced aeronautical technologies, each requiring specialized engineering expertise and contributing to elevated salary benchmarks.
The nature of federal contracts also influences the specific skills that are highly sought after and, consequently, the corresponding salary premiums. For example, contracts involving classified or sensitive projects often require engineers with security clearances and expertise in areas such as cybersecurity, secure communication systems, and advanced sensor technologies. These specialized skills command higher salaries due to the limited pool of qualified candidates and the critical importance of the work. Moreover, federal contracts often impose stringent quality control standards and rigorous testing requirements, necessitating engineers with expertise in quality assurance, reliability engineering, and systems validation. These individuals play a pivotal role in ensuring compliance with contract specifications and are accordingly compensated for their specialized knowledge and contributions. Therefore, an understanding of the specific requirements and priorities outlined in federal contracts allows engineers to strategically develop their skill sets and enhance their earning potential.
In conclusion, federal contracts exert a considerable influence on the financial landscape for aerospace engineers in Texas. The flow of federal funding stimulates demand, elevates salary levels, and shapes the demand for specialized skills. Understanding the dynamics of federal contracting, including project types, funding cycles, and required expertise, is crucial for engineers seeking to maximize their earning potential within the state’s aerospace industry. The challenge lies in staying informed about emerging trends in federal spending and proactively acquiring skills aligned with future contract opportunities, ensuring long-term career stability and financial security.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following addresses common inquiries regarding financial aspects within the aerospace engineering field in Texas, providing clarity on factors influencing earning potential.
Question 1: What is the typical earnings range for entry-level aerospace engineers in Texas?
Entry-level compensation varies, dependent upon educational background and specific employer. However, a range of $70,000 to $90,000 annually can be considered representative for individuals with a bachelor’s degree and limited prior experience.
Question 2: How significantly does a Master’s degree impact potential income in this field?
A Master’s degree generally leads to a notable increase in earning potential, potentially adding 10-20% to the base salary compared to a bachelor’s degree. This increase reflects specialized knowledge and enhanced skills acquired through advanced studies.
Question 3: Which Texas cities offer the highest salaries for aerospace engineers?
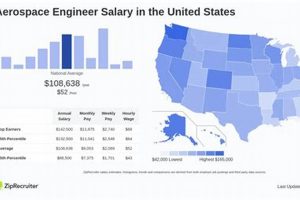
Metropolitan areas with a strong aerospace presence, such as Houston, Dallas-Fort Worth, and San Antonio, typically offer the highest compensation levels. This is due to the concentration of aerospace companies and government facilities in these regions.
Question 4: Are there specific skills or certifications that command a salary premium?
Yes. Expertise in areas like Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD), Systems Engineering, and proficiency with industry-standard software such as CATIA or ANSYS can lead to higher compensation, reflecting the demand for these specialized skills.
Question 5: How do federal government contracts affect compensation in the aerospace industry?
Federal contracts are a major driver of demand for aerospace engineers in Texas. Companies securing large government contracts often offer more competitive salaries and benefits to attract qualified personnel.
Question 6: What long-term career prospects correlate with an upward trajectory in compensation?
Long-term career advancement and increased earning potential are typically associated with acquiring specialized skills, pursuing advanced education, obtaining professional certifications, and demonstrating leadership capabilities within an organization.
Understanding these factors is essential for navigating the financial landscape within the aerospace engineering profession in Texas.
The subsequent discussion will address strategies for maximizing earning potential and career advancement.
Aerospace Engineering Salary in Texas
This exploration of aerospace engineering salary in Texas reveals the multifaceted nature of compensation within this specialized field. Factors such as experience, education, company size, geographical location, specialized skills, industry demand, and federal contracts all demonstrably impact earning potential. The interplay of these variables necessitates a strategic approach for engineers seeking to optimize their financial outcomes within the Texas aerospace sector. Consideration must be given to regional cost of living, the acquisition of in-demand skills, and the pursuit of advanced education to enhance marketability and secure competitive compensation packages. Understanding these drivers is crucial for both prospective and established professionals.
The aerospace industry in Texas continues to evolve, driven by technological advancements and fluctuating government priorities. A proactive approach to career development, coupled with a commitment to lifelong learning, will be essential for engineers seeking to navigate the changing landscape and maximize their long-term earning potential. Aspiring professionals should, therefore, conduct thorough research, seek mentorship from experienced engineers, and continuously adapt their skills to meet the emerging demands of the aerospace sector within the state.



![Your Aerospace Engineering Salary in San Diego [Guide] Safem Fabrication - Precision Engineering & Custom Manufacturing Solutions Your Aerospace Engineering Salary in San Diego [Guide] | Safem Fabrication - Precision Engineering & Custom Manufacturing Solutions](https://mixaerospace.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/th-4364-300x200.jpg)