Positions within the aeronautics and astronautics industry, located in a specific North Texas city, constitute a significant segment of the regional economy. These roles encompass a wide array of specializations, ranging from engineering and manufacturing to research and development, all contributing to the design, production, and maintenance of aircraft and related technologies. For example, a structural engineer designing wing components for a new fighter jet at a local defense contractor would fall under this category.
The availability of such roles contributes significantly to the economic prosperity of the area. They provide high-skill, high-paying opportunities, attracting a talented workforce and fostering innovation. Historically, the presence of major aerospace companies in the region has driven technological advancement and spurred growth in related industries, creating a positive feedback loop of economic development.
The following sections will delve into the specific types of opportunities available, the key employers in the region, the qualifications typically required for these positions, and the overall outlook for the sector in the near future.
Tips for Securing Aerospace Positions in Fort Worth
Navigating the landscape of opportunities in the aeronautical and astronautical sector requires a strategic approach. The following guidance provides key considerations for those seeking employment in the specified geographic location.
Tip 1: Research Key Employers: Identify prominent companies actively engaged in aerospace activities within the city. Understanding their specializations, projects, and corporate culture allows for targeted application strategies. Examples include major defense contractors and companies specializing in aviation maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO).
Tip 2: Tailor Resumes and Cover Letters: Generic applications are unlikely to succeed. Customize application materials to align with specific job descriptions, highlighting relevant skills and experience. Emphasis should be placed on demonstrating how individual qualifications directly address the employer’s needs.
Tip 3: Focus on Relevant Education and Certifications: Prioritize educational attainment and professional certifications that are highly valued in the field. Degrees in aerospace engineering, mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, and related disciplines are typically essential. Relevant certifications, such as FAA Airframe and Powerplant licenses, can also be advantageous.
Tip 4: Network Strategically: Attend industry events, conferences, and career fairs to connect with professionals and recruiters. Building relationships can provide valuable insights into available positions and increase visibility within the sector. Utilize professional networking platforms to connect with individuals working in relevant roles and companies.
Tip 5: Develop Technical Skills: Demonstrate proficiency in relevant software, tools, and technologies. Familiarity with CAD/CAM software, simulation tools, and industry-specific programming languages can enhance candidacy. Participating in relevant training programs or online courses can bolster these skills.
Tip 6: Highlight Security Clearance Eligibility: Many opportunities within this sector require security clearances. If eligible, clearly indicate this on the resume. If not, understand the requirements for obtaining a clearance and begin the process, if possible.
Tip 7: Prepare for Technical Interviews: Technical interviews are a standard component of the hiring process. Practice answering common technical questions and be prepared to discuss specific projects and technical challenges. Demonstrate a thorough understanding of aerospace principles and engineering concepts.
Adhering to these recommendations will significantly improve the probability of successfully obtaining positions related to aeronautics and astronautics in the designated area.
The subsequent section will explore the long-term prospects and future trends within the regional aerospace industry.
1. Engineering Expertise
Engineering expertise is a cornerstone of the aeronautics and astronautics sector in the specified North Texas city. It drives innovation, ensures product safety and reliability, and underpins the region’s competitiveness in the global aerospace market. Without a highly skilled engineering workforce, sustained growth in related employment opportunities would be impossible.
- Design and Development
Engineering professionals are responsible for the design, development, and testing of aircraft, spacecraft, and related systems. This encompasses a wide range of disciplines, including aerospace, mechanical, electrical, and software engineering. For example, engineers develop new aerodynamic designs for fuel efficiency or create advanced control systems for autonomous flight. These activities directly create positions for designers, analysts, and test engineers.
- Manufacturing and Production
Engineering expertise is critical in the manufacturing and production phases of aerospace projects. Manufacturing engineers optimize production processes, develop tooling and fixtures, and ensure quality control throughout the manufacturing cycle. For instance, they may implement advanced manufacturing techniques such as additive manufacturing (3D printing) to create complex aerospace components. This requires process engineers, quality assurance specialists, and production managers.
- Research and Development
Aerospace engineering research and development (R&D) drives future innovation and competitiveness. Engineers conduct research on new materials, propulsion systems, and avionics technologies. For example, researchers may investigate the use of composite materials to reduce aircraft weight or develop more efficient jet engines. This generates opportunities for research scientists, engineers, and technicians.
- Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul (MRO)
The MRO sector relies heavily on engineering expertise to ensure the continued airworthiness of aircraft. Engineers develop maintenance procedures, troubleshoot technical issues, and oversee repairs and modifications. For instance, they may design structural repairs for damaged aircraft components or upgrade avionics systems. This creates a demand for maintenance engineers, avionics technicians, and structural repair specialists.
The synergy between these facets underscores the fundamental role of engineering expertise. Companies in the North Texas city depend on a continuous supply of qualified engineers to remain at the forefront of the industry, thus sustaining and expanding aerospace jobs. Furthermore, the presence of strong engineering programs at local universities and colleges helps to create a pipeline of talent that fuels the sector’s growth, making aerospace jobs fort worth appealing.
2. Defense Contracts
Defense contracts are a critical driver of employment within the aeronautics and astronautics sector in Fort Worth. These contracts, awarded by the Department of Defense (DoD) and related agencies, provide funding for the design, development, production, and maintenance of military aircraft, weapons systems, and related technologies. The substantial financial investments associated with defense contracts directly translate into job creation across various engineering, manufacturing, and support roles. For instance, a contract awarded to a local company to produce new fighter jets necessitates hiring engineers to design the aircraft, manufacturing personnel to assemble it, and quality control specialists to ensure it meets stringent military specifications. The presence of large defense contractors in the area is a primary reason for the concentration of aerospace jobs in Fort Worth. A reduction in defense spending or a failure to secure key contracts can lead to workforce reductions, illustrating the direct link between these agreements and local employment levels.
The nature of defense contracts also shapes the types of jobs available. These contracts often require specialized skills and expertise related to military technologies, such as avionics, radar systems, and cybersecurity. Consequently, individuals seeking employment in this sector may benefit from acquiring relevant training and certifications that align with the demands of defense-related work. Furthermore, many defense contracts require employees to possess security clearances, adding another layer of qualification to the hiring process. The long-term stability of many defense contracts can provide a degree of job security that is less common in other sectors, making these positions particularly attractive to job seekers. An example of this can be seen with Lockheed Martin’s F-35 program, which has generated thousands of jobs in the area and is projected to continue to do so for decades to come.
In summary, defense contracts represent a significant source of funding and employment opportunities for the aeronautics and astronautics industry in the Fort Worth area. The ability of local companies to secure and fulfill these contracts is a key factor in the region’s economic prosperity and its status as a hub for aerospace jobs. Understanding the dynamics of defense spending, the requirements associated with defense work, and the specific needs of major defense contractors is essential for individuals seeking to enter or advance within this sector. A challenge faced by the industry is adapting to evolving defense priorities and technological advancements to maintain competitiveness and secure future contracts.
3. Manufacturing Hub
The designation of a geographic area as a “Manufacturing Hub” directly correlates with the availability and nature of aeronautics and astronautics-related employment opportunities in that location. This is particularly pertinent to positions in a specific North Texas city, where a robust manufacturing infrastructure supports a significant segment of the aerospace sector.
- Component Production and Assembly
A core function of the manufacturing hub involves the fabrication of individual components and their subsequent assembly into larger aerospace systems. This includes the production of airframe structures, engine parts, avionics modules, and interior components. For example, local facilities may specialize in the precision machining of turbine blades for jet engines or the automated assembly of circuit boards for flight control systems. These activities generate demand for machinists, assemblers, quality control inspectors, and manufacturing engineers.
- Advanced Materials Processing
The aerospace industry increasingly relies on advanced materials such as composites, titanium alloys, and high-strength aluminum alloys. A manufacturing hub must possess the capabilities to process these materials into usable forms, including forging, casting, extrusion, and machining. For instance, facilities may employ advanced composite layup techniques to create lightweight aircraft structures or utilize plasma spraying to apply wear-resistant coatings to engine components. This creates opportunities for materials scientists, metallurgists, and skilled technicians.
- Specialized Manufacturing Services
Beyond component production, a manufacturing hub often provides specialized services that support the aerospace industry. These may include heat treating, surface finishing, non-destructive testing, and calibration services. For example, facilities may offer specialized heat treatments to improve the strength and durability of metal components or perform ultrasonic testing to detect flaws in aircraft structures. This creates a need for technicians, engineers, and inspectors with expertise in these specialized processes.
- Supply Chain Integration
A well-developed manufacturing hub integrates a network of suppliers and subcontractors that provide raw materials, components, and services to aerospace manufacturers. This integration streamlines the production process and reduces lead times. For instance, local suppliers may provide specialized fasteners, wiring harnesses, or hydraulic components to aerospace manufacturers. This creates opportunities for logistics personnel, procurement specialists, and supply chain managers.
The interconnectedness of these aspects underscores the crucial role of a manufacturing hub in supporting and expanding the scope of local aeronautics and astronautics-related jobs. Investment in manufacturing infrastructure, workforce training, and technological innovation is essential to maintaining a competitive edge and attracting aerospace companies to the area, which, in turn, bolster positions in a specific North Texas city. The presence of a strong manufacturing base not only provides direct employment opportunities but also fosters a supportive ecosystem for innovation and entrepreneurship within the aerospace sector.
4. Skilled Workforce
A highly skilled workforce is a foundational requirement for a thriving aeronautics and astronautics sector in any geographic location. The presence, or absence, of qualified personnel directly influences the ability of companies to innovate, manufacture, and maintain complex aerospace systems, ultimately impacting the availability and quality of related employment opportunities in a specific North Texas city.
- Engineering Talent Pool
The availability of qualified engineers, encompassing disciplines such as aerospace, mechanical, electrical, and software engineering, is paramount. These engineers are responsible for designing, developing, and testing aircraft, spacecraft, and related systems. For instance, engineers with expertise in aerodynamics, structural analysis, or control systems are essential for developing more efficient and safer aircraft. Companies establish or expand operations in locations where they can readily access a pool of talented engineers, contributing to the number and quality of aerospace positions in that area.
- Technical Trade Expertise
Skilled technicians, including machinists, welders, avionics technicians, and aircraft mechanics, are crucial for manufacturing, assembling, and maintaining aerospace systems. Their expertise ensures that components are produced to exacting specifications and that aircraft are properly maintained and repaired. For example, skilled machinists are needed to manufacture precision parts for jet engines, while avionics technicians are required to install and troubleshoot complex electronic systems. A shortage of skilled tradespeople can hinder production and maintenance activities, limiting the growth of the industry and the availability of related jobs.
- Specialized Training and Certifications
The aerospace industry demands specialized training and certifications to ensure that personnel possess the knowledge and skills required to perform their jobs safely and effectively. Examples include FAA certifications for aircraft mechanics, welding certifications for aerospace welders, and specialized training in composite materials processing. Companies often seek employees who have completed relevant training programs or hold industry-recognized certifications, giving them a competitive edge in the job market. Access to high-quality training programs and certification opportunities is essential for maintaining a skilled workforce and attracting aerospace companies to a region.
- Continuous Learning and Adaptation
The aerospace industry is constantly evolving, with new technologies and materials emerging regularly. Therefore, a skilled workforce must be committed to continuous learning and adaptation to stay current with the latest advancements. Companies invest in training programs to help employees develop new skills and knowledge, while individuals may pursue continuing education opportunities on their own. For instance, engineers may need to learn new software tools for simulation and analysis, while technicians may need to become proficient in working with new composite materials. A culture of continuous learning is essential for ensuring that the workforce remains competitive and can adapt to the changing needs of the aerospace industry, thereby supporting the long-term growth of related jobs.
In conclusion, a skilled workforce is not merely a desirable attribute but a fundamental prerequisite for a thriving aeronautics and astronautics sector. The availability of qualified engineers, skilled technicians, and personnel with specialized training and certifications directly impacts the ability of companies to innovate, manufacture, and maintain complex aerospace systems in any location including a specific North Texas City. Continuous investment in education, training, and workforce development is essential for ensuring the long-term competitiveness and prosperity of related job opportunities.
5. Economic Impact
The aeronautics and astronautics sector centered in Fort Worth generates substantial economic impact at the local, regional, and even national levels. This impact is directly linked to the presence and activity of aerospace companies, which, in turn, are sustained by the availability of qualified personnel. A significant number of high-paying positions in this sector, spanning engineering, manufacturing, research and development, and support services, contribute directly to household incomes and consumer spending. For instance, the presence of major defense contractors such as Lockheed Martin creates thousands of direct jobs, and each of those positions supports additional indirect jobs in related industries and service sectors. The wages earned by aerospace employees are typically higher than the average for other industries, leading to increased tax revenues for local governments, which can then be reinvested in infrastructure, education, and other public services. These jobs contribute significantly to property values, retail sales, and overall economic stability.
Furthermore, the economic impact extends beyond direct employment. The aerospace industry fosters innovation and technological advancements that can spill over into other sectors of the economy. Research and development activities related to aircraft design, materials science, and avionics can lead to new products, processes, and technologies that benefit other industries, such as automotive, energy, and healthcare. These innovations drive further economic growth and job creation. The presence of a strong aerospace industry also attracts other businesses and investment to the region, creating a positive feedback loop of economic development. Educational institutions, in particular, benefit from close collaboration with aerospace companies, allowing them to tailor their curricula to meet the evolving needs of the industry and produce graduates with the skills and knowledge demanded by employers. This alignment between education and industry ensures a steady supply of qualified personnel to sustain future growth.
In summary, the economic impact of the aeronautics and astronautics sector in Fort Worth is multifaceted and far-reaching. It encompasses direct and indirect job creation, increased tax revenues, technological innovation, and the attraction of investment and talent to the region. The presence of a robust and thriving aerospace industry is a key driver of economic prosperity and a significant contributor to the quality of life for residents of the area. Challenges include maintaining competitiveness in the global market, adapting to changing defense priorities, and addressing workforce shortages, but the long-term outlook remains positive due to ongoing investment in research and development and the region’s strong commitment to supporting the aerospace sector.
6. Technological Advancements
Technological advancements serve as a primary catalyst for the evolution and expansion of aerospace roles in the Fort Worth area. The ongoing development and implementation of new technologies directly influence the types of skills and expertise demanded by employers, as well as the overall volume of opportunities available. For example, the integration of advanced composite materials in aircraft design requires engineers and technicians with specialized knowledge of their properties, manufacturing processes, and repair techniques. Similarly, the increasing reliance on autonomous systems and artificial intelligence in aviation necessitates professionals skilled in software development, data analytics, and robotics. The continuous pursuit of greater efficiency, safety, and performance in aerospace necessitates a workforce capable of adapting to and implementing these innovations.
The practical implications of this connection are multifaceted. Companies actively engaged in developing and deploying cutting-edge technologies, such as hypersonic flight systems, electric propulsion, or advanced sensor technologies, are more likely to create high-skill, high-paying employment opportunities. Furthermore, the ability of local educational institutions to provide relevant training and educational programs that align with these technological advancements is crucial for ensuring a steady supply of qualified personnel. Consider the impact of 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, on the aerospace industry. It allows for the creation of complex parts with reduced material waste and shorter lead times. Companies adopting this technology require skilled designers, materials scientists, and manufacturing technicians trained in additive manufacturing processes, directly impacting the demand for specific skills.
In summary, technological advancements are not merely a backdrop to the aerospace sector in Fort Worth, but rather a fundamental driver of its growth and evolution. Understanding the specific technologies that are shaping the industry and proactively developing the skills needed to support their implementation is essential for both job seekers and the long-term prosperity of the region. A challenge lies in anticipating future technological trends and adapting workforce development initiatives accordingly. Investment in research and development, coupled with close collaboration between industry, academia, and government, is crucial for ensuring that the Fort Worth area remains at the forefront of aerospace innovation and continues to generate high-quality employment opportunities.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following addresses common inquiries regarding career opportunities within the aeronautics and astronautics sector in a specific North Texas city.
Question 1: What educational qualifications are generally required for aerospace jobs fort worth?
Typically, a bachelor’s degree in a relevant engineering discipline (e.g., aerospace, mechanical, electrical) is the minimum requirement. Certain positions may necessitate advanced degrees (master’s or doctoral) or specialized certifications.
Question 2: Which companies are the primary employers for aerospace jobs fort worth?
Key employers include major defense contractors, aerospace manufacturers, and aviation maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO) providers. Specific company names can be identified through online job boards and industry directories.
Question 3: Are security clearances typically required for aerospace jobs fort worth?
Many positions, particularly those related to defense contracts, mandate security clearances. The level of clearance required depends on the specific role and the nature of the work involved.
Question 4: What are the most in-demand skills for aerospace jobs fort worth?
In-demand skills include expertise in CAD/CAM software, finite element analysis, composite materials, avionics systems, and cybersecurity, reflecting current industry trends and technological advancements.
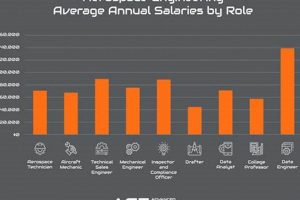
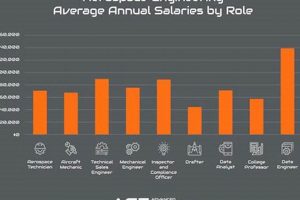
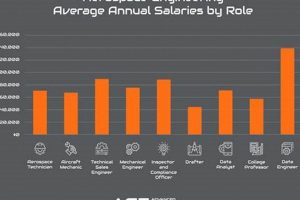
Question 5: What is the typical salary range for aerospace jobs fort worth?
Salary ranges vary depending on the position, experience level, and the specific employer. However, aerospace jobs generally offer competitive compensation packages that reflect the technical expertise and skills required.
Question 6: How can job seekers improve their chances of securing aerospace jobs fort worth?
Networking with industry professionals, tailoring resumes and cover letters to specific job descriptions, obtaining relevant certifications, and highlighting security clearance eligibility can significantly improve a candidate’s prospects.
These answers provide a foundation for understanding the employment landscape. Further research and targeted preparation are essential for a successful job search.
The subsequent section will offer additional resources for job seekers and those seeking to learn more about the aerospace industry in the region.
Aerospace Employment in Fort Worth
This exploration has illuminated key facets of “aerospace jobs fort worth,” highlighting the sector’s reliance on engineering expertise, defense contracts, a strong manufacturing base, a skilled workforce, significant economic impact, and continuous technological advancements. These elements are inextricably linked, forming a complex ecosystem that drives employment opportunities within the region.
Sustained investment in education, workforce development, and research and development is crucial for ensuring the long-term competitiveness of the area’s aeronautics and astronautics sector. The challenges of adapting to evolving technological landscapes and global market pressures must be addressed proactively to maintain the region’s position as a hub for high-quality “aerospace jobs fort worth.”