Positions requiring a doctoral degree in aerospace engineering, or a closely related field, typically involve advanced research, development, and design roles within the aerospace industry. These specialized opportunities often demand a high level of technical expertise and innovative thinking. An example would be a research scientist position at a NASA center focusing on advanced propulsion systems.
The pursuit of such roles offers significant benefits, including opportunities to contribute to cutting-edge technological advancements, lead complex projects, and potentially shape the future of air and space travel. Historically, individuals with this level of education have been instrumental in driving innovation in areas such as aircraft design, spacecraft engineering, and space exploration.
The subsequent sections will delve into specific career paths available to individuals holding this advanced qualification, required skills and qualifications, and strategies for a successful job search. These topics will provide a detailed understanding of the landscape for doctoral-level professionals in the aerospace sector.
The acquisition of a doctoral degree in aerospace engineering represents a significant achievement, opening doors to specialized and demanding career paths. The following tips offer guidance to individuals seeking employment leveraging this advanced qualification.
Tip 1: Cultivate a Strong Publication Record. Publication of research in peer-reviewed journals and presentations at conferences demonstrates expertise and enhances credibility within the aerospace community. For instance, publishing research on novel composite materials for aircraft structures can attract the attention of potential employers.
Tip 2: Target Specific Industry Sectors. Focus job search efforts on sectors aligning with research interests and skill sets. This could include commercial aviation, space exploration, defense, or government research laboratories. Identifying key companies in these sectors is crucial.
Tip 3: Network Strategically. Attend industry conferences and workshops to connect with professionals and potential employers. Active participation in professional organizations such as the American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics (AIAA) can expand professional network.
Tip 4: Tailor Applications to Specific Job Requirements. Customize resumes and cover letters to highlight relevant skills and experiences for each position. Emphasize achievements and quantifiable results whenever possible. For example, quantify the impact of research contributions on project outcomes.
Tip 5: Demonstrate Practical Skills. Highlight proficiency in relevant software tools (e.g., CAD, CFD) and hardware platforms used in aerospace engineering. Specific examples of projects where these tools were employed should be included.
Tip 6: Prepare for Technical Interviews. Technical interviews often involve solving complex engineering problems and demonstrating in-depth knowledge of aerospace principles. Practicing common interview questions and reviewing fundamental concepts is essential.
Tip 7: Consider Postdoctoral Research Opportunities. Postdoctoral positions provide valuable experience and can lead to tenure-track faculty positions or research roles in industry. A postdoctoral appointment can further refine research skills and build a stronger publication record.
The strategic implementation of these guidelines can significantly enhance the prospects of securing a desirable position following the completion of a doctorate in aerospace engineering. Diligence and a focused approach are paramount.
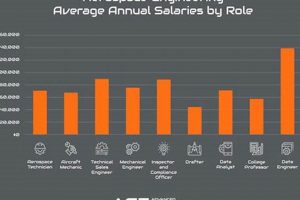
The subsequent section will provide information on the salary expectations for positions related to aerospace engineering.
1. Research-focused roles
Research-focused roles constitute a significant segment within the landscape of opportunities available to individuals possessing a doctoral degree in aerospace engineering. These positions are fundamentally centered on advancing the knowledge base and technological capabilities within the field. The attainment of a doctorate inherently signifies a capability for independent, original research, making graduates uniquely qualified for such roles. This connection is not merely correlational but causal; the skills honed during doctoral studies directly enable success in research-intensive employment. These positions typically involve designing, conducting, and analyzing experiments, developing theoretical models, and contributing to scholarly publications. The importance of research roles is paramount, as they drive innovation, inform policy decisions, and ultimately shape the future of the aerospace industry. As an example, an aerospace engineer with a PhD might lead a research team investigating novel propulsion systems to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions in commercial aircraft.
Further exemplification can be seen in the development of advanced materials for spacecraft. These materials must withstand extreme temperatures, radiation, and micrometeoroid impacts. Doctoral-level engineers employed in research roles design and test new alloys, composites, and coatings to meet these demanding requirements. Another practical application lies in the field of computational fluid dynamics (CFD). Research-focused engineers develop and validate sophisticated CFD models to simulate airflow around aircraft and spacecraft, optimizing aerodynamic performance and stability. The outputs from this research may then be used in real-world design of commercial aircraft and spacecraft.
In summary, research-focused roles are both a natural extension of, and a critical component of, the career paths for individuals with doctorates in aerospace engineering. These roles leverage the expertise and skills acquired during doctoral studies to drive innovation and address complex challenges within the industry. Understanding the importance and potential impact of research-focused positions is crucial for anyone pursuing advanced studies in aerospace engineering and considering a career in the field. The advancement of the entire industry depends on this research.
2. Advanced technical proficiency
Advanced technical proficiency serves as a foundational requirement for securing doctoral-level employment within the aerospace sector. These positions invariably necessitate a mastery of complex engineering principles, specialized software tools, and experimental techniques beyond the scope of undergraduate or master’s level education. The causal link between advanced proficiency and employability at this level is undeniable: employers seek individuals capable of independent problem-solving and innovation in areas such as aerodynamics, propulsion, structures, and control systems. The failure to demonstrate such capabilities during the application and interview process significantly diminishes an applicant’s prospects.
Practical application of advanced technical skills can be seen in the design and analysis of complex aerospace systems. For example, a doctoral-level engineer might be tasked with optimizing the aerodynamic performance of a novel aircraft wing configuration. This requires proficiency in computational fluid dynamics (CFD) software, a deep understanding of boundary layer theory, and the ability to interpret and validate simulation results. Another instance involves the development of advanced control algorithms for autonomous spacecraft navigation. This demands expertise in control theory, optimization techniques, and real-time embedded systems programming. The specific skills required will vary depending on the particular role and industry sector, but a consistently high level of technical competence is paramount.
In summary, advanced technical proficiency is not merely a desirable attribute, but a core prerequisite for positions requiring a doctorate in aerospace engineering. The capacity to apply sophisticated knowledge to complex problems is the defining characteristic of these roles, and successful candidates must demonstrate a clear and comprehensive understanding of relevant engineering principles and tools. The continuing evolution of aerospace technology necessitates a commitment to lifelong learning and the ongoing refinement of technical skills. Without a firm foundation of advanced technical proficiency, an aerospace phd jobs is an unrealistic expectation.
3. Industry specializations
A doctoral degree in aerospace engineering provides a strong foundation, but specializing within a specific industry segment is crucial for career advancement. The aerospace sector encompasses diverse areas, each with unique technical demands and skill requirements. Focusing on a niche allows candidates to develop deep expertise and become highly sought-after by employers. Neglecting industry specializations results in a generalized skillset that may not align with specific employer needs, reducing the likelihood of securing relevant employment. For example, an individual specializing in hypersonic propulsion will be more competitive for roles at companies developing next-generation missiles or space launch vehicles. The industry specializations often dictate the skill sets and specific knowledge needed in the aerospace field.
Examples of industry specializations include: unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), commercial aviation, space exploration, defense aerospace, and satellite technology. Each specialization demands a different combination of skills. A UAV specialist requires expertise in control systems, autonomy, and sensor integration. Commercial aviation engineers need a strong understanding of aerodynamics, structural integrity, and safety regulations. Space exploration specialists focus on propulsion systems, orbital mechanics, and materials science. The ability to demonstrate knowledge of these specific specializations is a significant differentiator in the job market. For example, it is not uncommon for an aerospace engineer with specialize skills of mechanical and robotics to work on the creation of a commercial airbus model in the aviation company.
In summary, pursuing an industry specialization is a strategic approach for doctoral graduates in aerospace engineering. It demonstrates a commitment to focused expertise, aligning skills with specific employer demands. Individuals who tailor their education, research, and professional experience to a particular industry segment significantly enhance their career prospects. Focusing on specializations and using them to address industry-specific problems gives applicants edge in the selection process.
4. Competitive compensation
Competitive compensation is intrinsically linked to positions requiring a doctoral degree in aerospace engineering due to the advanced skill sets, specialized knowledge, and extensive education demanded of candidates. The pursuit of a PhD represents a significant investment in time and resources, and individuals holding this qualification typically expect remuneration commensurate with their expertise. The scarcity of qualified professionals in certain niche areas of aerospace engineering, such as hypersonic propulsion or advanced materials, further contributes to the competitive compensation packages offered.
The level of remuneration reflects the critical role these individuals play in driving innovation and technological advancement within the industry. For instance, a lead research scientist at a major aerospace corporation, responsible for developing novel aircraft engine designs, commands a significantly higher salary than an entry-level engineer with a bachelor’s degree. Similarly, a professor at a top-tier university, conducting cutting-edge research in space exploration and mentoring future aerospace engineers, receives competitive compensation, considering the impact on the next generation of professionals.
In conclusion, competitive compensation is a fundamental component of “aerospace phd jobs”, serving as a critical factor in attracting and retaining top talent within the field. It acknowledges the advanced skills, specialized knowledge, and substantial contributions of these individuals to the ongoing development of aerospace technology. The expectation of adequate compensation is also critical and must be satisfied in order to get talented people into the field and maintain the progression of the industry.
5. Leadership opportunities
The acquisition of a doctorate in aerospace engineering often serves as a gateway to leadership positions within the industry, government, and academic sectors. This advanced degree signifies not only technical expertise but also the capacity for strategic thinking, complex problem-solving, and effective communication, all essential attributes for successful leadership.
- Research Team Leadership
Doctoral-level engineers frequently lead research teams focused on cutting-edge projects, such as developing new propulsion systems or designing advanced spacecraft. They guide the direction of research, manage resources, and mentor junior engineers, fostering a collaborative environment conducive to innovation. This role requires both technical proficiency and interpersonal skills to motivate and direct team members towards shared goals.
- Project Management in Complex Programs
Large-scale aerospace projects, such as the development of a new commercial aircraft or the deployment of a satellite constellation, demand skilled project managers with a deep understanding of engineering principles. Doctoral graduates are well-suited for these roles, possessing the technical knowledge to oversee all aspects of the project lifecycle, from conceptual design to testing and deployment. Successful project management ensures projects are completed on time, within budget, and to the required performance specifications.
- Technical Consulting and Advisory Roles
Government agencies and private companies often seek technical consultants with doctoral-level expertise to provide guidance on critical engineering decisions. These advisors may assess the feasibility of new technologies, evaluate the performance of existing systems, or provide expert testimony in legal proceedings. This role requires a broad understanding of aerospace engineering principles and the ability to communicate complex technical information to non-technical audiences.
- Academic Leadership Positions
Doctoral graduates often pursue careers in academia, where they can lead research programs, mentor graduate students, and shape the future of aerospace engineering education. Academic leaders play a crucial role in setting research agendas, securing funding, and fostering a culture of innovation within their departments. They also contribute to the broader scientific community through publications, conferences, and professional societies.
These diverse leadership opportunities underscore the value of a doctoral degree in aerospace engineering. The combination of advanced technical knowledge, research experience, and communication skills equips graduates with the tools necessary to excel in positions of influence and contribute meaningfully to the advancement of the aerospace sector. Individuals aspiring to leadership roles should strategically cultivate these skills throughout their academic and professional careers.
6. Innovation potential
The intersection of doctoral-level expertise in aerospace engineering and the inherent capacity for innovation represents a cornerstone of progress within the field. Positions demanding a PhD in aerospace engineering are frequently predicated on the individual’s ability to conceive, develop, and implement novel solutions to complex challenges.
- Novel Propulsion Systems Development
Doctoral-level engineers are at the forefront of developing advanced propulsion technologies, such as hypersonic engines, electric propulsion systems, and fusion-based rockets. Their research directly impacts the feasibility of future space exploration missions and high-speed air travel. This requires expertise in thermodynamics, fluid dynamics, and materials science, along with the ability to translate theoretical concepts into tangible engineering solutions.
- Advanced Materials and Structures Design
The development of lightweight, high-strength materials is crucial for improving aircraft and spacecraft performance. Engineers with PhDs are involved in designing and characterizing novel composites, alloys, and coatings that can withstand extreme temperatures and stresses. This work requires a deep understanding of materials science, mechanics, and manufacturing processes. These developments will shape aircraft designs of the future by enhancing speed and fuel economy.
- Autonomous Systems and Control Algorithms
The increasing reliance on autonomous systems in aerospace applications, such as unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and autonomous spacecraft, requires the development of sophisticated control algorithms and sensor integration techniques. Doctoral-level engineers play a key role in designing these systems, incorporating artificial intelligence and machine learning to improve performance and reliability. The designs for control systems and autonomous functions within aircrafts and spacecrafts is the direct result of PhD-level researchers.
- Sustainable Aerospace Technologies
Addressing the environmental impact of air travel and space exploration is a growing concern. Engineers with PhDs are developing sustainable aerospace technologies, such as biofuels, electric aircraft, and reusable launch systems, to reduce emissions and minimize resource consumption. This research requires a multidisciplinary approach, combining engineering principles with environmental science and policy considerations.
The common thread linking these facets is the demand for original thought and a capacity to push the boundaries of existing knowledge. Positions that require doctoral-level engineers are tasked with this type of innovation and improvement. “Aerospace phd jobs” are those that are meant to solve the industry’s current problems and innovate the future.
7. Global Impact
Positions requiring a doctorate in aerospace engineering inherently possess the potential for widespread global impact. The advancements and innovations stemming from these roles often transcend national boundaries, influencing areas such as transportation, communication, and scientific exploration on a global scale.
- Advancements in Air Transportation
Doctoral-level engineers contribute to the development of more efficient and sustainable aircraft, leading to reduced fuel consumption, lower emissions, and improved air travel accessibility for populations worldwide. This includes optimization of designs for aerodynamics, reduction of noise pollution, and creation of more fuel-efficient engines. These improvements result in better air travel worldwide.
- Satellite Technology and Global Connectivity
Aerospace engineers with advanced degrees are instrumental in designing and deploying satellite systems that provide global communication, navigation, and Earth observation capabilities. These technologies support critical infrastructure, disaster response efforts, and scientific research, benefiting communities across the globe. Satellite imagery and data also allows for weather tracking and helps to prevent the loss of human lives.
- Space Exploration and Scientific Discovery
Individuals holding doctorates in aerospace engineering play a pivotal role in planning and executing space exploration missions, expanding our understanding of the universe and searching for extraterrestrial life. These endeavors often lead to technological spin-offs with applications in diverse fields, benefiting society as a whole. Discoveries of minerals, gases, and potentially new life forms on other planets could change the course of human existence.
- Global Security and Defense
Aerospace engineers contribute to the development of defense technologies that ensure global security and stability. This includes designing advanced surveillance systems, missile defense systems, and unmanned aerial vehicles for reconnaissance and peacekeeping operations. These systems not only help to secure the world but assist with the quick resolution of global conflicts.
In conclusion, the pursuit of “aerospace phd jobs” offers individuals the opportunity to make significant contributions with global implications. The work undertaken by these professionals directly impacts various aspects of human life, from improving transportation and communication to expanding scientific knowledge and enhancing global security. Those who pursue the job positions and education required, make a global impact on the population of planet Earth.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Aerospace PhD Jobs
The following section addresses common inquiries pertaining to career paths and opportunities for individuals holding a doctoral degree in aerospace engineering. These questions aim to provide clarity on expectations, requirements, and prospects within the field.
Question 1: What are the primary differences between a research scientist role and a faculty position for aerospace PhD graduates?
Research scientist roles typically involve conducting focused research within government laboratories or industrial settings, often with specific project objectives and deliverables. Faculty positions, conversely, entail a broader range of responsibilities, including teaching, mentoring students, securing research funding, and contributing to the academic community.
Question 2: To what extent does prior industry experience impact the prospects of securing a desirable “aerospace phd jobs” following graduation?
Prior industry experience is generally viewed favorably by employers, as it demonstrates practical application of theoretical knowledge and familiarity with industry practices. However, a strong publication record, relevant research experience, and demonstrated technical proficiency can often compensate for a lack of extensive industry experience.
Question 3: What are the essential software skills and tools required for success in an “aerospace phd jobs”?
Proficiency in computational fluid dynamics (CFD) software (e.g., ANSYS Fluent, OpenFOAM), finite element analysis (FEA) software (e.g., ABAQUS, Nastran), CAD software (e.g., CATIA, SolidWorks), and programming languages (e.g., MATLAB, Python) is highly valued by employers. The specific software requirements may vary depending on the specific role and industry sector.
Question 4: What strategies can be employed to effectively network with professionals in the aerospace industry?
Attending industry conferences, participating in professional organizations (e.g., AIAA), engaging with online communities, and reaching out to alumni from one’s academic institution are effective networking strategies. Networking should be approached as a means of building relationships and exchanging knowledge, rather than solely as a job-seeking activity.
Question 5: How crucial is a strong publication record in securing competitive “aerospace phd jobs”?
A strong publication record is highly important, particularly for research-oriented positions and academic appointments. Publications in peer-reviewed journals and presentations at conferences demonstrate research capabilities, technical expertise, and contribution to the scientific community.
Question 6: What are some common misconceptions regarding “aerospace phd jobs”?
One common misconception is that “aerospace phd jobs” are exclusively confined to research and development roles. In reality, doctoral graduates also find employment in areas such as project management, consulting, and policy-making. Another misconception is that a PhD guarantees immediate employment; diligent job searching and strategic career planning remain essential.
These FAQs offer a foundational understanding of key considerations for individuals seeking “aerospace phd jobs”. Proactive career planning and the development of relevant skills are paramount for success in this competitive field.
The subsequent section will provide resources and links for people seeking “aerospace phd jobs”.
Aerospace PhD Jobs
This exploration has illuminated the multifaceted landscape of “aerospace phd jobs”, underscoring the advanced skills, specialized knowledge, and significant contributions expected of individuals pursuing these career paths. The analysis encompassed research-focused roles, technical proficiency demands, industry specializations, competitive compensation structures, leadership opportunities, the potential for innovation, and the capacity to exert global impact.
The aerospace sector stands at the cusp of significant technological advancements. Individuals possessing a doctoral degree in aerospace engineering are uniquely positioned to drive these innovations and shape the future of air and space travel. A commitment to continuous learning, strategic networking, and a proactive approach to career development will be essential for navigating this dynamic and demanding field. The challenges and opportunities are significant, and the contributions of qualified professionals are vital for continued progress.