The determination of nations offering optimal environments for the pursuit and practice of aeronautical and astronautical engineering involves assessing factors such as educational infrastructure, research opportunities, industry presence, and governmental support. These nations often boast leading universities with specialized curricula, significant investment in aerospace research and development, and established aerospace industries providing employment opportunities.
Focusing on nations exhibiting strengths in these areas is vital for individuals seeking advanced education, research collaborations, or professional careers. The benefits extend beyond individual advancement to encompass national technological progress, economic growth, and contributions to scientific discovery. Historically, nations investing heavily in aerospace have seen substantial returns in technological innovation and global competitiveness.
An examination of countries providing strong academic programs, research and development funding, and ample employment opportunities in the aeronautics and astronautics fields follows. This will shed light on the nations positioned to be leading centers for this demanding but exciting area of engineering.
Strategic Considerations for Aspiring Aerospace Engineers
Individuals contemplating a career in aeronautical or astronautical engineering should consider several strategic points to maximize their potential for success, particularly when evaluating international opportunities. These points are essential for long-term professional development and maximizing contributions to the field.
Tip 1: Research Academic Institutions Thoroughly: Prioritize institutions with robust research programs, specialized laboratories, and strong industry partnerships. Investigate faculty expertise and research focus to align with individual interests.
Tip 2: Evaluate Funding Opportunities: Investigate national and international scholarship programs, research grants, and industrial sponsorships. Secure adequate financial support to facilitate uninterrupted academic progress and research endeavors.
Tip 3: Consider Industry Presence: Target countries with established aerospace industries and a high demand for skilled engineers. Examine employment statistics and projected growth rates in relevant sub-disciplines.
Tip 4: Assess Visa and Immigration Policies: Understand the immigration regulations and visa requirements for international students and workers. Investigate potential pathways to long-term residency or citizenship.
Tip 5: Develop Language Proficiency: Acquire a strong command of the local language to facilitate communication, collaboration, and integration into the professional environment. Language skills enhance both professional opportunities and personal well-being.
Tip 6: Build a Strong Network: Actively participate in professional organizations, attend conferences, and cultivate relationships with industry professionals and academic researchers. Networking expands career prospects and fosters collaboration.
Tip 7: Focus on Specialization: Identifying and developing a niche expertise within aerospace engineering can greatly enhance career prospects. Areas such as propulsion systems, avionics, or space mission design offer specialized opportunities.
Adhering to these strategic considerations will optimize the opportunities available to aerospace engineers, positioning them for success in contributing to aerospace advancement.
Moving forward, this analysis prepares us for a more in-depth look at specific nations prominent in the aerospace engineering domain.
1. Academic Excellence
Academic excellence forms a cornerstone of nations recognized as leaders in aeronautical and astronautical engineering. This encompasses the quality and breadth of educational institutions, the rigor of their curricula, and the caliber of their faculty. Countries demonstrating a strong commitment to academic excellence attract and cultivate top talent, fostering an environment conducive to innovation and advancement within the field. The presence of highly-ranked universities with specialized aerospace programs directly contributes to a nation’s ability to conduct groundbreaking research and develop cutting-edge technologies. For instance, the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) and Stanford University in the United States consistently produce highly skilled engineers and researchers who contribute significantly to the nation’s aerospace industry.
The link between academic excellence and a nation’s standing in aerospace is evident in the correlation between the ranking of its universities and its contributions to major aerospace projects. Nations with reputable aerospace engineering programs are often involved in international collaborations, such as the International Space Station or the development of advanced aircraft technologies. The quality of education directly impacts the workforce available to aerospace companies and research institutions, influencing their ability to compete globally. Moreover, the emphasis on theoretical understanding coupled with practical application, often found in these academically strong programs, ensures graduates are well-prepared to tackle the complex challenges inherent in the design, development, and operation of aerospace systems.
In conclusion, academic excellence is not merely a desirable attribute but a crucial determinant for nations aspiring to be leaders in aerospace engineering. The investment in top-tier universities, rigorous curricula, and experienced faculty directly translates into a highly skilled workforce, driving innovation and ensuring sustained success in the competitive global aerospace landscape. Without a strong foundation in academic excellence, nations will struggle to attract talent, generate groundbreaking research, and maintain a competitive edge in this technologically advanced field.
2. Research Funding
The availability and allocation of research funding are intrinsically linked to the identification of leading nations in aerospace engineering. Substantial investment in research and development (R&D) directly correlates with a nation’s capacity to innovate, develop advanced technologies, and attract top talent in the field. Without sufficient financial resources, groundbreaking research is severely limited, hindering a country’s ability to remain competitive. The relationship is causative: increased funding leads to more research, which, in turn, drives technological progress and enhances a nation’s standing. For example, the United States and Germany allocate significant portions of their GDP to aerospace R&D, resulting in pioneering advancements in areas such as propulsion systems, materials science, and autonomous flight.
The importance of sustained research funding extends beyond individual projects and impacts the broader ecosystem. It supports the development of state-of-the-art research facilities, the education and training of future engineers and scientists, and the fostering of collaborations between universities, government agencies, and private sector companies. The European Union’s “Horizon Europe” program, for instance, provides substantial funding for aerospace research, promoting international cooperation and facilitating the development of innovative technologies. Such coordinated efforts contribute to the overall competitiveness of European nations in the global aerospace market. The practical significance of this understanding lies in recognizing that strategic investment in research is not merely an expenditure but a crucial factor in long-term economic growth, technological advancement, and national security.
In summary, research funding is an indispensable component of a successful aerospace engineering landscape. Nations prioritizing and allocating sufficient resources to R&D create an environment conducive to innovation, attract top talent, and maintain a competitive edge in the global aerospace market. This understanding underscores the critical need for policymakers and stakeholders to recognize the vital role of research funding in shaping the future of aerospace engineering and ensuring national prosperity. Challenges remain in effectively allocating resources and fostering collaboration, but sustained investment is essential for long-term success.
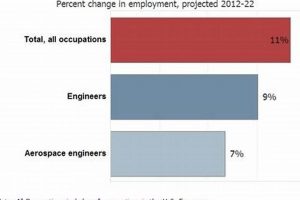
3. Industry Opportunities
The presence and breadth of industry opportunities are decisive factors when evaluating the superiority of nations in aerospace engineering. These opportunities offer crucial pathways for engineers to apply their knowledge, develop practical skills, and contribute to technological advancement. The depth and diversity of these prospects directly impact a country’s ability to attract and retain talent, fostering a thriving aerospace sector.
- Manufacturing and Production
The manufacturing and production of aircraft, spacecraft, and related components form a core aspect of industry opportunities. Nations with established manufacturing sectors, such as the United States with Boeing and Lockheed Martin, or France with Airbus, provide extensive employment and development opportunities for aerospace engineers. These roles encompass design, fabrication, assembly, testing, and quality control, contributing significantly to national economic prosperity and technological advancement.
- Research and Development (R&D)
Robust R&D initiatives drive innovation and technological progress within the aerospace sector. Nations that invest heavily in R&D, through government agencies, universities, and private companies, offer engineers the chance to push the boundaries of knowledge and develop cutting-edge technologies. Examples include NASA in the United States or the German Aerospace Center (DLR), which provide platforms for groundbreaking research in areas such as propulsion, materials science, and autonomous systems.
- Engineering Services and Consulting
A range of engineering services and consulting firms support the aerospace industry, providing specialized expertise in areas such as design, analysis, testing, and certification. Companies like Jacobs Engineering Group or Atkins offer diverse career paths for aerospace engineers, working on a variety of projects across different sectors. The presence of these firms indicates a mature and multifaceted aerospace ecosystem, providing opportunities for both specialized and broad-based engineering careers.
- Space Exploration and Satellite Technology
Nations actively involved in space exploration and satellite technology offer unique and compelling industry opportunities. Programs such as the European Space Agency (ESA) or the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) provide opportunities for engineers to contribute to the design, development, launch, and operation of satellites and space missions. These roles often involve collaboration with international partners and exposure to the most advanced technologies, contributing to scientific discovery and expanding human knowledge.
These multifaceted industry prospects, ranging from manufacturing to space exploration, collectively define the attractiveness of nations for aerospace engineering professionals. Countries exhibiting robust and diverse industry opportunities provide fertile ground for career advancement, technological innovation, and economic prosperity, underscoring their position as prominent hubs within the global aerospace landscape. Further, the density of the industrial landscape allows for symbiotic relationships between academic institutions and industry, allowing for an infusion of ideas and talent.
4. Government Support
Government support is a pivotal determinant in identifying leading nations in aerospace engineering. Its significance extends beyond direct funding, encompassing policy frameworks, regulatory environments, and strategic initiatives that foster a thriving aerospace ecosystem. This support directly affects a country’s capacity for innovation, technological advancement, and global competitiveness in the aerospace sector. For example, the United States’ Department of Defense and NASA provide substantial research grants, contracts, and infrastructure, which directly support aerospace innovation. This, in turn, leads to the development of cutting-edge technologies and a strong aerospace industrial base. The causal effect is clear: increased government assistance translates into enhanced technological capabilities and industry growth.
The practical implications of this support are multifaceted. Favorable government policies can attract foreign investment, encourage private sector participation, and create a stable environment for long-term research and development. Tax incentives, regulatory streamlining, and intellectual property protection are examples of government actions that stimulate aerospace innovation. France, with its strong government support for Airbus and the Centre National d’tudes Spatiales (CNES), demonstrates the effectiveness of strategic government investment in creating a world-leading aerospace industry. Moreover, government-funded research programs often serve as catalysts for technological breakthroughs, which then find applications in both the civilian and military sectors.
In summary, government support is not merely a beneficial factor but an essential prerequisite for nations aspiring to excel in aerospace engineering. Its impact on research funding, policy frameworks, and industry development is profound. The strategic allocation of resources, coupled with conducive regulatory environments, enables nations to foster innovation, attract talent, and maintain a competitive edge in the global aerospace market. Nations that recognize and prioritize government support within their aerospace strategies are positioned to achieve sustained success and contribute significantly to the future of aerospace technology. While challenges exist in aligning policy with technological advancements and balancing competing interests, the crucial role of government support remains undeniable.
5. Technological Advancement
Technological advancement is a central pillar supporting the standing of nations recognized as leaders in aerospace engineering. It is the relentless pursuit of innovation and application of cutting-edge technologies that enables progress in this complex field, shaping capabilities in both aeronautics and astronautics. The pace of this advancement directly influences a nation’s competitiveness and capacity to contribute meaningfully to global aerospace endeavors.
- Advanced Materials and Manufacturing
The development and implementation of advanced materials, such as composites and alloys with superior strength-to-weight ratios, are critical for enhancing aircraft and spacecraft performance. Advanced manufacturing techniques, like additive manufacturing (3D printing), enable the creation of complex geometries and customized components. Countries investing heavily in these areas, such as the United States and Germany, possess a distinct advantage in designing and producing next-generation aerospace systems. Examples include the development of lightweight aircraft structures using carbon fiber composites and the production of rocket engine components using additive manufacturing, both resulting in improved efficiency and reduced costs.
- Propulsion Systems Innovation
Advancements in propulsion systems are essential for increasing flight speed, range, and payload capacity. Hypersonic propulsion, electric propulsion, and advanced rocket engine designs are areas of intense research and development. Nations at the forefront of propulsion technology, such as Russia with its scramjet research and the United States with its ongoing development of advanced rocket engines, are well-positioned to dominate future aerospace missions. These advancements are enabling faster and more efficient air travel, as well as enabling the exploration of more distant destinations in space.
- Autonomy and Artificial Intelligence
The integration of autonomy and artificial intelligence (AI) into aerospace systems is revolutionizing flight control, navigation, and mission planning. Autonomous aircraft, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), and AI-powered satellite systems are increasingly prevalent. Countries investing in AI research and development, such as China and the United States, are leading the way in developing autonomous flight control systems, intelligent sensor networks, and AI-driven mission optimization. This facilitates more efficient airspace management, enhances safety, and allows for the execution of complex missions in challenging environments.
- Communication and Navigation Systems
Sophisticated communication and navigation systems are indispensable for modern aerospace operations. Advanced radar systems, satellite communication networks, and precision navigation technologies are essential for ensuring safe and reliable air travel and space missions. Countries with robust communication infrastructure and advanced navigation capabilities, such as the United States with its GPS system and Europe with its Galileo system, maintain a significant advantage in managing air traffic, tracking satellites, and conducting precision navigation for both civilian and military applications. These systems ensure accurate positioning and communication, enabling seamless global connectivity and safe navigation in all weather conditions.
These facets of technological advancement are intertwined and mutually reinforcing. A nation’s ability to integrate and leverage these technologies determines its standing in the global aerospace arena. Nations that prioritize investment in these areas are not only better positioned to develop cutting-edge aerospace systems, but they also foster a culture of innovation that attracts top talent and stimulates economic growth. Furthermore, the technologies developed for aerospace applications often find applications in other sectors, further enhancing a nation’s overall technological competitiveness. The examples cited demonstrate that leadership in aerospace engineering is inseparable from a commitment to continuous technological improvement.
6. Global Collaboration
Global collaboration is an indispensable element in the landscape of aerospace engineering, particularly for nations aspiring to leadership. The complexity and scale of contemporary aerospace projects necessitate international cooperation, pooling resources, expertise, and infrastructure to achieve common objectives. This collaborative environment fosters innovation, distributes risk, and accelerates technological progress.
- Joint Research and Development Programs
Collaborative research and development programs allow countries to share knowledge and resources, resulting in faster and more efficient advancements. Projects such as the International Space Station (ISS) exemplify this, involving contributions from the United States, Russia, Europe, Canada, and Japan. The ISS fosters international cooperation in space exploration and research, providing a shared platform for scientific experimentation and technological development. Countries participating in such programs gain access to advanced technologies and expertise that might otherwise be unavailable, enhancing their aerospace capabilities.
- International Standards and Regulations
Global collaboration is essential for establishing common standards and regulations in the aerospace industry, ensuring safety, interoperability, and harmonization of practices. Organizations like the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) play a crucial role in setting global standards for air navigation, aircraft design, and operational procedures. Countries that actively participate in these efforts contribute to a safer and more efficient global aerospace system, facilitating international trade and travel. Adherence to these standards also enhances a nation’s credibility and standing within the international aerospace community.
- Technology Transfer and Knowledge Sharing
Collaborative ventures often facilitate technology transfer and knowledge sharing between nations, enabling countries to acquire and develop new capabilities. Through joint projects, licensing agreements, and educational exchanges, nations can access advanced technologies and expertise from other countries. This is particularly beneficial for developing nations seeking to build their aerospace industries. For example, collaborative agreements between established aerospace companies and emerging aerospace nations can accelerate technology transfer and promote local innovation.
- Multinational Aerospace Projects
Complex aerospace projects, such as the development of new aircraft or spacecraft, often involve multinational consortia, pooling resources and expertise from multiple countries. Airbus, for example, is a European consortium involving companies from France, Germany, Spain, and the United Kingdom, demonstrating the benefits of international collaboration in developing competitive products. Such ventures foster innovation, share risk, and enable the creation of advanced aerospace systems that would be difficult or impossible for a single nation to develop independently.
These facets of global collaboration underscore its vital role in shaping the aerospace engineering landscape. Nations that actively engage in international partnerships, adhere to global standards, and facilitate technology transfer are better positioned to foster innovation, enhance their technological capabilities, and achieve sustained success in the competitive aerospace sector. Global collaboration is not merely a matter of choice but an essential strategy for nations aiming to achieve prominence in aerospace engineering.
7. Innovation Ecosystem
An environment conducive to innovation is an inextricable component of nations identified as the foremost in aerospace engineering. This ecosystem comprises interconnected elements including research institutions, industry partnerships, venture capital availability, entrepreneurial culture, and supportive government policies. The presence of a robust innovation ecosystem exerts a causal effect, fostering rapid technological advancement and attracting skilled personnel, thereby solidifying a nation’s position in the aerospace sector. A deficiency in any of these elements can impede progress, regardless of investment in other areas. Silicon Valley, for example, though not exclusively aerospace-focused, illustrates how a concentration of venture capital, research universities like Stanford, and a risk-accepting entrepreneurial culture has fostered innovation in various technology sectors, with spillover effects benefiting aerospace startups and established companies alike.
Successful integration within a thriving innovation ecosystem enables aerospace firms to leverage the collective knowledge and resources available, leading to accelerated product development cycles and enhanced competitiveness. The existence of incubators, accelerators, and technology transfer offices facilitates the translation of research findings into marketable products and services. Countries such as Israel, despite their relatively small size, demonstrate how targeted government support and academic-industry collaborations can create a vibrant innovation ecosystem, fostering advancements in areas like unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and satellite technologies. The practical application of this understanding lies in recognizing that nations aspiring to lead in aerospace engineering must actively cultivate and sustain a comprehensive innovation ecosystem, rather than solely focusing on isolated investments in research or infrastructure.
The construction and maintenance of a strong innovation ecosystem present significant challenges. These include fostering effective communication between academia and industry, securing adequate funding for early-stage ventures, and mitigating regulatory barriers to innovation. Overcoming these obstacles requires a concerted effort from governments, universities, and private sector stakeholders. In conclusion, a nation’s aerospace engineering prowess is inextricably linked to the strength and dynamism of its innovation ecosystem. A comprehensive strategy encompassing research funding, entrepreneurial support, and supportive policies is crucial for establishing and sustaining a leading position in the global aerospace landscape. The recognition of this interconnection, and sustained commitment to ecosystem cultivation, is the key.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following section addresses common inquiries regarding the optimal nations for pursuing aerospace engineering studies or careers. These questions are intended to provide clarity on factors influencing this determination.
Question 1: What metrics are used to assess the “best countries for aerospace engineering”?
Evaluations typically consider the strength of academic programs, levels of research funding, the abundance of industry employment opportunities, and the extent of government support for the aerospace sector. The presence of established aerospace companies and the technological advancement within the nation are also key indicators.
Question 2: How significantly does a nation’s investment in research and development impact its standing in aerospace engineering?
Substantial investment in research and development is critical. It fuels innovation, attracts top talent, and enables the development of advanced technologies necessary to maintain a competitive edge in the aerospace industry. Countries with robust R&D funding often lead in groundbreaking discoveries and technological advancements.
Question 3: Are career prospects more favorable in countries with established aerospace industries?
Generally, yes. Nations with established aerospace industries offer more employment opportunities for engineers, as well as chances for professional growth and specialization. The presence of major aerospace companies creates a demand for skilled engineers in various roles, from design and manufacturing to research and development.
Question 4: What role does government policy play in fostering a strong aerospace engineering sector?
Government policies play a crucial role through financial support, regulatory frameworks, and strategic initiatives. These policies can encourage private sector investment, streamline regulations, and protect intellectual property, creating a stable environment for innovation and growth in the aerospace industry.
Question 5: Is international collaboration a significant factor for success in aerospace engineering?
Yes, international collaboration is increasingly important. Aerospace projects are becoming more complex and costly, often necessitating partnerships between nations to share resources and expertise. Countries that actively participate in international collaborations gain access to advanced technologies and knowledge, enhancing their capabilities.
Question 6: How can aspiring aerospace engineers best position themselves for success in a globally competitive field?
Aspiring engineers should focus on obtaining a strong academic foundation, actively seek research opportunities, develop specialized skills, and cultivate professional networks. Proficiency in multiple languages and a willingness to work in international environments can also significantly enhance career prospects.
In summary, numerous factors contribute to a nation’s prominence in the field of aerospace engineering. Academic rigor, R&D investment, industry presence, government policy, and global collaboration all play vital roles.
Following this overview, the next section provides specific examples of nations that consistently excel in aerospace engineering and details their particular strengths.
Best Countries for Aerospace Engineering
This analysis has explored factors defining nations as leaders in aeronautical and astronautical engineering. Academic infrastructure, research funding, industry opportunities, government backing, technological progress, international partnerships, and an innovative atmosphere are all critical. Each elements presence and synergistic interaction influence a nation’s aerospace sector’s competitive standing and innovative capabilities. Nations displaying high levels of all attributes often provide an environment favorable for both career development and overall industry growth.
As technological frontiers continue to expand, nations prioritizing these key elements and fostering an environment conducive to advancement will likely lead the future of aerospace engineering. Aspiring engineers and stakeholders should leverage this understanding when selecting opportunities, developing policies, and directing investment towards maximizing both individual and national potential within the global aerospace arena.