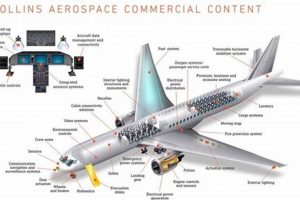
Aircraft passenger accommodations, engineered by Collins Aerospace, represent a critical component of the overall flying experience. These systems encompass a diverse range of designs, materials, and functionalities, tailored to meet the specific requirements of airlines and their passengers. Considerations in design include ergonomics, weight optimization, safety standards, and aesthetic appeal. For instance, models designated for long-haul international flights often feature enhanced recline capabilities, integrated entertainment systems, and adjustable support mechanisms for improved passenger comfort during extended periods of travel.
The availability of well-designed, comfortable, and safe installations directly influences passenger satisfaction and, consequently, an airline’s brand reputation. Furthermore, lighter designs contribute to reduced fuel consumption, offering significant economic and environmental benefits for operators. Historically, advancements in materials science and engineering have driven innovations in this sector, leading to progressively lighter, more durable, and feature-rich options. Regulatory bodies, such as the FAA and EASA, impose stringent safety standards that these products must adhere to, ensuring passenger well-being.
The subsequent sections will delve into specific aspects related to the design innovations, material advancements, and regulatory compliance relevant to modern installations. Further analysis will explore the integration of technology and connectivity within these systems, examining trends in customization and sustainability. Finally, the evolving landscape of passenger expectations and their impact on future design considerations will be addressed.
Guidance Regarding Aircraft Passenger Accommodation Systems
The following recommendations offer insights into key considerations pertaining to the selection and maintenance of aircraft passenger accommodation systems, emphasizing operational efficiency and passenger comfort.
Tip 1: Prioritize Ergonomic Design: The geometry must address anthropometric variability across the passenger population. Data from human factors studies should inform design choices to minimize discomfort and potential musculoskeletal issues.
Tip 2: Optimize Weight Reduction: Employ advanced materials and structural designs to minimize overall weight. Reduced mass translates directly into fuel savings and enhanced aircraft performance.
Tip 3: Ensure Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to all applicable safety regulations, including those pertaining to fire resistance, structural integrity, and emergency egress, is paramount. Rigorous testing and certification are essential.
Tip 4: Implement Robust Maintenance Programs: Regular inspection and maintenance schedules are critical for ensuring the continued functionality and safety. Address wear and tear promptly to prevent further degradation.
Tip 5: Select Durable Materials: Opt for materials that exhibit high resistance to abrasion, UV degradation, and chemical exposure. Longevity minimizes replacement costs and downtime.
Tip 6: Focus on Cleanability and Hygiene: Surface treatments that inhibit microbial growth and facilitate easy cleaning are vital for maintaining a healthy cabin environment.
Tip 7: Consider Modularity and Configurability: Select systems that offer flexibility in configuration to accommodate changing passenger demands and airline operational needs.
Adopting these best practices can contribute to improved passenger satisfaction, reduced operational costs, and enhanced safety within the aviation sector.
The subsequent section will address the ongoing evolution and future trends shaping the landscape of passenger accommodations in air travel.
1. Ergonomic Design
Ergonomic design is paramount in aviation, directly impacting passenger comfort, health, and overall satisfaction. Its integration into aircraft passenger accommodations, specifically within products, transcends mere aesthetics, influencing factors such as postural support, pressure distribution, and accessibility to controls and amenities.
- Lumbar Support and Spinal Alignment
Proper lumbar support is critical for maintaining spinal alignment during prolonged periods of sitting. Poor lumbar support can lead to back pain, muscle fatigue, and discomfort. Ergonomically designed systems incorporate adjustable lumbar support mechanisms, allowing passengers to customize the contour to their individual needs, thereby reducing the risk of musculoskeletal issues. This element is particularly relevant on long-haul flights where passengers spend extended periods in a seated position.
- Pressure Distribution and Cushioning
Effective pressure distribution is essential for minimizing discomfort and preventing pressure sores, especially during long flights. Ergonomic models utilize advanced cushioning materials and contoured surfaces to evenly distribute weight across the seating area. This reduces pressure points and promotes blood circulation, enhancing comfort and reducing the risk of deep vein thrombosis (DVT). The materials and construction methods employed directly contribute to the effectiveness of pressure distribution.
- Reach and Accessibility of Controls
The ease of reach and accessibility of controls for features such as entertainment systems, lighting, and recline functions are integral to ergonomic design. Controls should be intuitive to use and positioned within easy reach, regardless of passenger size or physical limitations. Poorly positioned or difficult-to-operate controls can lead to frustration and discomfort, detracting from the overall flying experience. Universal design principles are often employed to ensure accessibility for a diverse range of passengers.
- Adjustability and Customization
The ability to adjust and customize various elements, such as headrest height, armrest position, and leg rest extension, contributes significantly to ergonomic comfort. Adjustability allows passengers to tailor the seating to their individual body dimensions and preferences, optimizing support and reducing strain. The range of adjustability and the ease with which adjustments can be made are critical factors in evaluating the ergonomic effectiveness of the design.
The integration of these ergonomic facets into the design and manufacturing of passenger accommodations directly influences passenger well-being and airline brand perception. Continual refinement of ergonomic principles and materials science is essential for creating increasingly comfortable and supportive environments within aircraft cabins. This commitment to ergonomic excellence translates to enhanced passenger satisfaction and a more positive travel experience overall.
2. Weight Optimization
Weight optimization is a critical design parameter in the development of aircraft passenger accommodations. Reduced mass directly correlates to diminished fuel consumption, offering tangible economic benefits for airlines and contributing to decreased greenhouse gas emissions. The architecture of products from Collins Aerospace emphasizes the strategic application of lightweight materials and advanced structural designs to minimize the overall mass of the installation without compromising safety or structural integrity. This pursuit of weight reduction is not merely an aesthetic consideration, but a fundamental driver of operational efficiency and sustainability within the aviation industry. For example, the implementation of carbon fiber composites and high-strength aluminum alloys in frame construction demonstrably reduces weight compared to traditional steel structures, yielding substantial fuel savings over the operational lifespan of an aircraft.
The selection of materials and the engineering of structural components are inextricably linked in the weight optimization process. Finite element analysis (FEA) is routinely employed to simulate stress distribution and identify areas where material can be removed without jeopardizing structural integrity. Furthermore, design choices that consolidate functionalities or eliminate unnecessary components directly contribute to weight reduction. One practical example is the integration of In-Flight Entertainment (IFE) systems within the structure, minimizing the need for separate mounting hardware and cabling. This approach not only reduces weight but also streamlines installation and maintenance procedures. The trade-off between weight, cost, and durability is constantly evaluated to ensure the optimal balance for each specific application.
In summary, weight optimization represents a multifaceted challenge within the realm of aircraft passenger accommodations, requiring a holistic approach that encompasses material selection, structural design, and functional integration. The continued emphasis on weight reduction is driven by both economic incentives and environmental concerns, and it remains a central focus of ongoing research and development efforts within the industry. While challenges exist in balancing weight reduction with passenger comfort and safety requirements, advancements in materials science and engineering continue to pave the way for lighter, more efficient designs. This focus links directly to the broader industry trend towards sustainable aviation practices.
3. Safety Standards
Aircraft passenger accommodation systems, including those from Collins Aerospace, are subject to rigorous safety standards mandated by aviation regulatory bodies such as the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) and the European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA). These standards encompass a wide array of performance criteria, including fire resistance, structural integrity under crash-load conditions, and the absence of sharp edges or protrusions that could cause injury during normal operation or emergency situations. Compliance with these standards is not optional; it is a prerequisite for certification and operation within commercial aviation. The specific standards applicable to a particular model are determined by the type of aircraft, its operational environment, and the intended passenger capacity. Failure to meet these safety standards can result in grounding of aircraft, financial penalties for airlines, and potential legal liabilities for manufacturers.
For example, seats must withstand significant deceleration forces during simulated crash tests to prevent detachment from the aircraft floor, which could obstruct emergency egress. The materials used in construction must also meet stringent flammability requirements, limiting the spread of fire within the cabin. Furthermore, the design must incorporate features that minimize the risk of injury during turbulence or sudden maneuvers. Practical application of these standards involves meticulous engineering design, rigorous testing, and continuous monitoring throughout the product lifecycle. Airlines routinely conduct inspections and maintenance to ensure continued compliance with safety regulations, addressing wear and tear that could compromise structural integrity or fire resistance. The safety considerations extend beyond the seat itself to include adjacent components and integration with the aircraft cabin environment.
In conclusion, the connection between safety standards and aircraft passenger accommodations is critical and multifaceted. Compliance with regulatory requirements is not merely a procedural obligation but an integral aspect of ensuring passenger safety and maintaining the operational integrity of commercial aviation. The ongoing evolution of safety standards reflects advancements in materials science, engineering design, and accident investigation, driving continuous improvements in the safety performance of passenger accommodations. The challenges associated with meeting these standards include balancing safety considerations with weight optimization, passenger comfort, and aesthetic design, requiring a comprehensive and integrated approach.
4. Material Durability
Material durability represents a critical determinant in the long-term performance, safety, and economic viability of aircraft passenger accommodation systems. The selection of appropriate materials, therefore, is not merely an aesthetic consideration but a fundamental engineering requirement directly influencing the lifecycle cost and passenger well-being associated with installations from Collins Aerospace.
- Resistance to Abrasion and Wear
Aircraft interiors are subjected to constant abrasion and wear from passenger use, cleaning processes, and environmental factors. Materials used in construction must exhibit high resistance to abrasion to prevent premature degradation of surfaces, which can compromise both aesthetic appeal and structural integrity. For instance, fabrics and leathers used in upholstery are tested for abrasion resistance using standardized methods to ensure they can withstand repeated contact and cleaning without significant wear. The choice of high-performance coatings on metallic and composite components also contributes to minimizing surface degradation from abrasion.
- Resistance to Chemical Exposure
Aircraft cabins are routinely cleaned with a variety of chemicals to maintain hygiene and sanitation. Materials must demonstrate resistance to these chemicals to prevent discoloration, degradation, or weakening of structural properties. Polymers and coatings used in construction are subjected to chemical resistance testing to ensure compatibility with commonly used cleaning agents. Failure to resist chemical exposure can lead to premature replacement of components, increasing maintenance costs and aircraft downtime.
- Resistance to UV Degradation
Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation at high altitudes can degrade certain materials over time, leading to discoloration, embrittlement, and loss of structural integrity. Materials used in construction must be resistant to UV degradation to ensure long-term durability and prevent premature failure. UV stabilizers are often added to polymers and coatings to enhance their resistance to UV radiation. Testing protocols include exposure to simulated sunlight to assess the material’s resistance to UV-induced degradation.
- Resistance to Fatigue and Creep
Aircraft components are subjected to cyclic loading and sustained stresses during flight, which can lead to fatigue failure or creep deformation over time. Materials used in construction must exhibit high resistance to fatigue and creep to ensure structural integrity throughout the operational lifespan. Fatigue testing involves subjecting materials to repeated stress cycles to determine their fatigue life. Creep testing involves subjecting materials to sustained stress at elevated temperatures to assess their resistance to deformation over time. The selection of materials with high fatigue and creep resistance is critical for ensuring the long-term safety and reliability of aircraft installations.
In essence, the durability of materials employed in aircraft accommodations is paramount, influencing both the lifecycle economics and passenger safety. The stringent requirements for resistance to abrasion, chemical exposure, UV degradation, and fatigue reflect the demanding operational environment of commercial aviation. Material selection and design choices, thus, represent a critical engineering discipline that directly impacts the longevity and performance of aircraft installations.
5. Configuration Flexibility
Configuration flexibility, in the context of aircraft passenger accommodations, refers to the adaptability of seating arrangements and functionalities to meet varying operational needs and passenger demands. The inherent design of aircraft accommodations from Collins Aerospace directly influences the extent to which an airline can reconfigure its cabin to optimize revenue generation, cater to diverse passenger demographics, and adapt to evolving market conditions.
- Seat Pitch Adjustment
Seat pitch, the distance between a point on one seat and the same point on the seat in front of it, is a primary determinant of legroom and overall passenger comfort. Adjustable seat pitch allows airlines to modify cabin density, increasing the number of seats in high-demand periods or providing greater space for premium passengers. This flexibility directly impacts revenue management strategies, enabling airlines to optimize seat pricing based on passenger preference and perceived value. Systems with easily adjustable seat pitch offer a competitive advantage in responding to fluctuating market dynamics.
- Class Conversion Capabilities
Some seating systems are designed to facilitate rapid conversion between different class configurations, such as transitioning from a high-density economy configuration to a lower-density business class setup. This adaptability is particularly valuable for airlines operating routes with varying demand for premium seating. Seats with modular components and easily reconfigurable features minimize downtime associated with cabin reconfiguration, maximizing aircraft utilization and revenue generation. The engineering of these systems focuses on ease of installation and removal, enabling swift adjustments to cabin layout.
- Modular Component Design
Modular design, wherein individual seating components (armrests, headrests, IFE systems) can be easily swapped or upgraded, enhances configuration flexibility and reduces maintenance costs. Damaged or outdated components can be replaced without requiring the replacement of the entire seat, minimizing downtime and extending the lifespan of the installation. This approach also allows airlines to customize seating to specific route requirements or passenger preferences, offering tailored amenities and features. The use of standardized interfaces and quick-release mechanisms facilitates seamless component integration and replacement.
- Adaptable Stowage Solutions
The integration of adaptable stowage solutions, such as adjustable overhead bins and under-seat storage compartments, contributes to overall cabin configuration flexibility. Stowage capacity can be optimized to accommodate varying passenger baggage allowances and seasonal travel patterns. Flexible stowage options enhance passenger convenience and contribute to a more organized and comfortable cabin environment. The design of these solutions emphasizes ease of access and efficient utilization of available space.
These facets of configuration flexibility are intrinsically linked to the design and engineering of aircraft passenger accommodations. The ability to rapidly reconfigure cabin layouts, adapt to changing passenger demands, and optimize seat density provides airlines with a competitive advantage in the dynamic aviation market. The investment in systems offering enhanced configuration flexibility translates directly into improved operational efficiency, increased revenue generation, and enhanced passenger satisfaction. Continual innovation in seating technology and design is driving the development of increasingly adaptable and versatile solutions for the aviation industry.
6. IFE Integration
In-Flight Entertainment (IFE) integration represents a crucial element in the design and functionality of modern aircraft passenger accommodations, significantly impacting passenger experience and airline operational strategies. The seamless incorporation of IFE systems within products from Collins Aerospace necessitates a holistic approach, considering not only entertainment content delivery but also ergonomic design, power management, and system reliability.
- Display Technology and Integration
The selection and integration of display technology are paramount to the IFE experience. Options range from embedded seatback screens to personal electronic device (PED) integration. Seatback displays must be robust, high-resolution, and ergonomically positioned for optimal viewing angles. PED integration, conversely, requires robust power outlets and mounting solutions. The engineering considerations extend to minimizing glare, ensuring consistent brightness across viewing angles, and providing intuitive user interfaces. This facet directly affects passenger comfort and engagement with IFE content.
- Content Delivery and Management
The efficient delivery and management of IFE content demand robust network infrastructure and software solutions. Content must be stored and streamed reliably, with minimal latency, to ensure a seamless user experience. Airlines require intuitive content management systems to update programming, track usage, and personalize content offerings. The technical challenges involve managing bandwidth constraints, securing content rights, and ensuring compatibility with diverse media formats. Effective content delivery is crucial for maintaining passenger satisfaction and maximizing the value of the IFE investment.
- Power and Connectivity
IFE systems require dedicated power supplies and robust connectivity to function effectively. Power management solutions must be efficient, reliable, and compliant with aviation safety standards. Connectivity options range from wired connections to wireless networks, each with its own set of technical challenges. Wired connections offer greater bandwidth but require complex cabling infrastructure. Wireless networks provide greater flexibility but may be susceptible to interference. The design must consider power consumption, heat dissipation, and electromagnetic compatibility to ensure system reliability and passenger safety.
- Ergonomics and Accessibility
The ergonomic integration of IFE controls and interfaces is essential for passenger comfort and usability. Controls must be intuitively positioned and easily accessible, regardless of passenger size or physical limitations. Touchscreen interfaces must be responsive and user-friendly. Remote controls must be ergonomically designed and feature tactile feedback. Universal design principles are often employed to ensure accessibility for passengers with disabilities. Effective ergonomics enhance the overall passenger experience and promote greater engagement with IFE content.
These integrated facets highlight the intricate relationship between IFE systems and aircraft passenger accommodations. Successful integration requires a multidisciplinary approach, considering technical performance, ergonomic design, and passenger experience. Further advancements in IFE technology, such as personalized content recommendations and interactive gaming, are expected to drive further innovation in aircraft seating design and functionality. This trend will likely result in increasingly sophisticated and integrated IFE solutions that enhance passenger satisfaction and differentiate airline offerings.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following questions address common inquiries concerning aircraft passenger accommodation systems, specifically focusing on design, safety, and operational considerations. These responses are intended to provide clear and concise information based on established industry practices and regulatory guidelines.
Question 1: What primary factors influence the design of aircraft passenger accommodations?
Design considerations encompass a multifaceted approach, prioritizing passenger comfort, safety regulations compliance, weight optimization for fuel efficiency, and integration of In-Flight Entertainment (IFE) systems. Ergonomic principles and material selection are also key determinants in ensuring both passenger well-being and the longevity of the installation.
Question 2: How are safety standards enforced for passenger seating in commercial aircraft?
Safety standards are rigorously enforced by aviation regulatory bodies, such as the FAA and EASA, through mandatory testing and certification processes. These regulations address fire resistance, structural integrity during crash-load scenarios, and the minimization of potential hazards to passengers during normal operation and emergency egress.
Question 3: What are the advantages of utilizing lightweight materials in aircraft construction?
Employing lightweight materials, such as carbon fiber composites and high-strength aluminum alloys, contributes to reduced overall aircraft weight, leading to decreased fuel consumption and lower emissions. These materials also offer favorable strength-to-weight ratios, enhancing structural performance without compromising safety.
Question 4: How does configuration flexibility benefit airlines and passengers?
Configuration flexibility allows airlines to adapt cabin layouts to meet varying demand levels, optimize revenue generation, and cater to diverse passenger demographics. Adjustable seat pitch, class conversion capabilities, and modular component designs contribute to this adaptability, enhancing both operational efficiency and passenger comfort.
Question 5: What role does In-Flight Entertainment (IFE) integration play in modern aircraft seating?
Seamless IFE integration enhances the passenger experience by providing access to entertainment content, connectivity options, and personalized services. Ergonomic design, power management, and system reliability are critical considerations in ensuring a positive and engaging IFE experience.
Question 6: How are material durability and longevity addressed in the design of aircraft passenger accommodations?
Material selection prioritizes resistance to abrasion, chemical exposure, UV degradation, and fatigue to ensure long-term performance and minimize maintenance costs. Rigorous testing and quality control measures are implemented to verify material durability and compliance with aviation industry standards.
These FAQs serve as a summary of critical aspects relevant to understanding the design, safety, and operational characteristics of aircraft passenger accommodation systems. These considerations play a crucial role in ensuring a safe, comfortable, and efficient flying experience.
The subsequent section will explore emerging trends and future innovations shaping the development of aircraft passenger accommodations, including advancements in materials, technology, and passenger comfort.
Concluding Remarks
This analysis has explored the multifaceted aspects of Collins Aerospace seating, encompassing ergonomic design, weight optimization, safety standards, material durability, configuration flexibility, and IFE integration. Each element contributes to the overall passenger experience and operational efficiency within the aviation industry. The design choices, material selections, and engineering principles employed directly impact passenger comfort, aircraft performance, and compliance with stringent regulatory requirements.
Continued advancements in materials science, engineering design, and technological integration are essential for maintaining and enhancing the safety, comfort, and efficiency of air travel. The ongoing commitment to innovation and adherence to rigorous standards will remain paramount in shaping the future of passenger accommodations and ensuring a positive flying experience for all.



![Collins Aerospace Wisconsin: [Benefits/Innovations] & More Innovating the Future of Flight with Reliable Aviation Solutions Collins Aerospace Wisconsin: [Benefits/Innovations] & More | Innovating the Future of Flight with Reliable Aviation Solutions](https://mixaerospace.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/th-878-300x200.jpg)