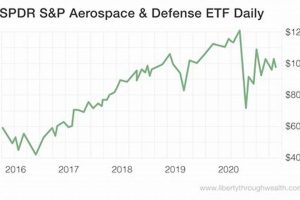
An investment vehicle focused on companies operating within the defense and aerospace sectors, offered by Fidelity Investments, pools capital from numerous investors to purchase a diversified portfolio of stocks. This portfolio typically includes entities involved in military hardware, cybersecurity, satellite technology, and commercial aviation. Investments are subject to market fluctuations and involve risk.
Such financial instruments offer investors targeted exposure to industries often driven by government spending, technological innovation, and global security concerns. Historically, performance has been influenced by geopolitical events, defense budgets, and advancements in aerospace technology. This focused investment strategy can offer diversification within a broader portfolio and access to potentially high-growth sectors.
The subsequent sections will delve into the factors influencing the performance of investments in these sectors, discuss relevant market trends, and analyze potential risks and opportunities associated with concentrated holdings in defense and aerospace.
Investment Considerations
The following points offer guidance when considering investments within the specific sector.
Tip 1: Understand Sector Dynamics: Defense and aerospace are heavily influenced by government policy, international relations, and technological advancements. Comprehensive knowledge of these factors is crucial. For example, changes in defense spending priorities by key nations can significantly impact company revenues.
Tip 2: Evaluate Company Fundamentals: Analyze the financial health of individual companies within the portfolio, examining metrics like revenue growth, profitability, and debt levels. A company with a strong backlog of orders and a history of efficient project management is often a sounder investment.
Tip 3: Monitor Geopolitical Risk: Global events, such as conflicts and trade disputes, can have a direct and often immediate impact on the defense and aerospace industries. Staying informed about these events is essential for managing risk.
Tip 4: Consider Diversification: While specializing within defense and aerospace can offer potential gains, diversification across various sub-sectors (e.g., cybersecurity, commercial aviation, space technology) can mitigate risks associated with any single area.
Tip 5: Assess Technological Innovation: The pace of technological change in these sectors is rapid. Companies that invest heavily in research and development and demonstrate a capacity for innovation are better positioned for long-term success.
Tip 6: Review Expense Ratios: Understand the fund’s expense ratio and other fees. Higher fees can erode returns over time, so consider cost-effectiveness.
Tip 7: Long-Term Perspective: Due to the cyclical nature of defense spending and the long lead times for aerospace projects, a long-term investment horizon is generally recommended.
Careful consideration of these points can improve investment decisions. Understanding the specific features allows for better risk management and potentially improved returns.
The subsequent analysis provides additional context and data points to inform a comprehensive understanding of investments within the specific segment.
1. Sector Allocation
Sector allocation represents a critical element within the investment strategy of a defense and aerospace mutual fund. It determines the fund’s distribution of assets across various sub-sectors within the defense and aerospace industries. This allocation directly influences the fund’s performance and risk profile. For example, a fund heavily weighted towards defense contractors specializing in missile defense systems may experience growth during periods of heightened geopolitical tensions but could underperform during times of peace or reduced military spending. Conversely, a fund with a significant allocation towards commercial aerospace companies might benefit from increased air travel demand but face challenges during economic downturns that affect consumer spending.
The strategic allocation of assets requires careful consideration of macroeconomic trends, technological advancements, and government policies. Investment managers analyze factors such as defense budgets, technological innovation cycles, and geopolitical risks to make informed decisions about sector weighting. The funds sector allocation directly affects its potential return and level of risk. For example, shifting allocation from traditional military hardware towards cybersecurity firms could signal a strategic adaptation to changing threats and technological landscapes. This shift also impacts a portfolio’s overall risk profile and return potential, based on the differing performance characteristics of each sector.
In summary, sector allocation is not merely a passive element but a dynamic investment decision that directly affects the risk and return profile. Effective management of sector allocation within such a fund requires ongoing analysis of global events, industry trends, and technological developments. A well-considered sector allocation is crucial to maximize investment returns while mitigating sector-specific risks, thus playing a pivotal role in the overall success of the fund.
2. Expense Ratio
The expense ratio represents the annual cost to operate a mutual fund, expressed as a percentage of the fund’s average net assets. For investors considering an investment, this ratio is a crucial factor. It directly impacts the fund’s net returns because it’s deducted from the fund’s assets. For example, if a fund has an expense ratio of 0.75%, $7.50 out of every $1,000 invested is used to cover the fund’s operating expenses annually. These expenses include management fees, administrative costs, and other operational expenses. A lower expense ratio is generally more favorable because it means more of the fund’s returns are passed on to investors.
In the specific context of a defense and aerospace investment, the expense ratio can be a decisive factor in its overall investment attractiveness. If two such funds have similar investment strategies and holdings, the fund with the lower expense ratio will typically provide better returns over time. This principle is especially pertinent given that defense and aerospace often involve substantial research and development expenses, which might inherently lead to higher management fees. Therefore, a fund that manages to maintain a lower expense ratio while providing access to this sector represents a more cost-effective option for investors. The investor needs to evaluate other parameters before taking any decision.
Understanding the expense ratio is essential for accurately assessing the potential performance. While past performance is not indicative of future results, it can still provide valuable context. The expense ratio provides transparency into the true cost of investing in a fund. A careful assessment of this ratio, in conjunction with other factors like investment strategy and historical performance, enables informed investment decisions.
3. Investment Strategy
Investment strategy is the central framework guiding the security selection and asset allocation decisions within a fund focused on the defense and aerospace sectors. It directly shapes the fund’s risk profile, potential returns, and overall suitability for investors seeking targeted exposure to these industries. The chosen approach dictates how the fund will navigate market dynamics, technological advancements, and geopolitical influences to achieve its stated objectives.
- Active vs. Passive Management
An actively managed fund entails a portfolio manager making discretionary decisions to outperform a benchmark index. This approach involves in-depth research, stock picking, and market timing. Conversely, a passively managed fund aims to replicate the performance of a specific index, typically with lower fees. For the defense and aerospace sectors, active management may seek to capitalize on emerging technologies or anticipate shifts in government spending, while passive management offers broad market exposure.
- Value vs. Growth Investing
A value investment strategy focuses on identifying undervalued companies with solid fundamentals but trading below their intrinsic worth. A growth investment strategy targets companies expected to experience above-average earnings growth, even if they trade at higher valuations. In the defense and aerospace industries, a value approach may target established defense contractors, whereas a growth approach may focus on innovative aerospace or cybersecurity firms.
- Sector Focus and Diversification
An investment strategy must define the scope of its sector focus, whether it concentrates solely on defense contractors, aerospace manufacturers, or includes related industries like cybersecurity and satellite technology. Diversification across various sub-sectors within defense and aerospace can mitigate risks associated with any single segment. A diversified portfolio might include suppliers, manufacturers, and technology providers across both defense and aerospace sectors.
- ESG Considerations
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors are increasingly incorporated into investment strategies. For defense and aerospace, ESG considerations might involve evaluating a company’s environmental impact, ethical conduct, and labor practices. Some funds may exclude companies involved in controversial weapons or those with poor safety records, aligning investments with specific ethical or sustainability criteria.
These strategic elements collectively define how an investment fund navigates the specific challenges and opportunities. Understanding the investment strategy is critical for investors seeking targeted exposure to the defense and aerospace sectors, as it directly influences the fund’s risk-adjusted returns and alignment with their investment objectives. The interplay between these diverse facets determines the investment’s overall success.
4. Historical Performance
Historical performance analysis provides critical context for evaluating an investment within the defense and aerospace sectors. While past results are not predictive of future returns, an examination of performance data can reveal trends, assess risk-adjusted returns, and provide insight into the fund’s sensitivity to market conditions and geopolitical events.
- Long-Term Growth Trends
An analysis of long-term performance reveals the fund’s ability to generate returns over extended periods. This involves assessing average annual returns over 5, 10, or 15-year periods. For example, comparing its long-term growth trend to relevant market indices, such as the S&P Aerospace & Defense Select Industry Index, can highlight periods of outperformance or underperformance and provide insights into the fund’s investment acumen and sector expertise.
- Performance During Market Cycles
Reviewing performance during different market cycles (bull markets, bear markets, and periods of economic uncertainty) demonstrates the fund’s resilience and ability to navigate varying economic conditions. For instance, assessing performance during recessionary periods can illustrate its downside risk management capabilities, while performance during expansionary phases reveals its ability to capitalize on growth opportunities.
- Risk-Adjusted Returns
Evaluating risk-adjusted return metrics, such as Sharpe Ratio and Sortino Ratio, provides a more comprehensive picture of a fund’s efficiency in generating returns relative to its level of risk. For instance, a fund with a high Sharpe Ratio has historically generated higher returns per unit of risk compared to its peers. This analysis helps investors assess whether the returns justify the level of volatility associated with the investment.
- Peer Group Comparison
Comparing historical performance against similar funds within the defense and aerospace sector allows for benchmarking and relative performance assessment. For example, if the fund consistently outperforms its peer group over various time horizons, it may indicate superior stock selection or risk management strategies. Conversely, underperformance relative to peers may raise concerns about the fund’s investment approach.
By analyzing historical performance across multiple dimensions, investors can gain a more nuanced understanding of the investment’s strengths, weaknesses, and potential risks. This information, combined with an assessment of current market conditions and future outlook, enables informed investment decisions aligned with individual risk tolerance and financial goals. This analysis is crucial for those considering allocating capital to a defense and aerospace mutual fund.
5. Risk Factors
Investments concentrated within the defense and aerospace sectors inherently involve specific risk factors that prospective investors in investment vehicles focused on these industries must carefully consider. These risks arise from the unique dynamics of these sectors, including governmental influence, technological disruptions, and geopolitical uncertainties, each with the potential to significantly impact investment returns. Understanding these risk factors is critical for making informed investment decisions and managing portfolio exposure effectively.
- Governmental and Regulatory Risks
The defense and aerospace industries are heavily reliant on government contracts and regulatory approvals. Changes in government spending priorities, defense budgets, or regulatory policies can substantially affect the financial performance of companies within these sectors. For example, a reduction in defense spending following a shift in geopolitical strategy could lead to decreased revenues for defense contractors. Similarly, stricter export controls or regulatory hurdles could hinder the international expansion of aerospace companies.
- Technological Obsolescence
Rapid technological advancements create a risk of obsolescence for existing products and services. Companies failing to innovate and adapt to emerging technologies face a competitive disadvantage. For instance, the development of drone technology and autonomous systems could disrupt traditional defense systems, while advancements in sustainable aviation fuels and electric aircraft could challenge conventional jet engine manufacturers.
- Geopolitical Instability
The defense and aerospace sectors are highly sensitive to geopolitical events and international conflicts. Escalations in geopolitical tensions, armed conflicts, or trade wars can lead to increased demand for defense products and services, positively impacting company revenues. Conversely, periods of peace or de-escalation could result in decreased demand and financial challenges. For example, a major international conflict could significantly boost the revenues of defense contractors, while a diplomatic resolution could lead to reduced military spending.
- Supply Chain Vulnerabilities
The defense and aerospace industries rely on complex global supply chains, which are vulnerable to disruptions caused by geopolitical events, natural disasters, or economic instability. Disruptions in the supply chain can lead to production delays, increased costs, and reduced profitability. For example, a shortage of critical components, such as semiconductors or rare earth minerals, could significantly impact the production of defense systems and aerospace equipment.
In conclusion, a comprehensive awareness of governmental and regulatory risks, technological obsolescence, geopolitical instability, and supply chain vulnerabilities is essential for investors considering a focus on defense and aerospace. These factors underscore the need for careful due diligence, ongoing monitoring of industry trends, and a diversified investment approach to mitigate potential risks. These risks are intrinsic characteristics of investing in this specific sector and contribute significantly to the overall risk-return profile for related instruments.
6. Portfolio Holdings
The portfolio holdings represent the specific securities and assets held within the fund. Examination of these holdings provides insight into the fund’s investment strategy, risk exposure, and potential for generating returns, offering a transparent view into where capital is allocated.
- Top Holdings Concentration
The concentration of the fund’s assets among its top holdings directly influences its performance. A fund heavily weighted towards a few key companies can experience significant volatility if those holdings underperform. For example, if a substantial portion of assets is invested in a single large defense contractor, any adverse news or contract loss affecting that company could negatively impact the fund’s overall value. Conversely, strong performance from top holdings can drive significant gains. Understanding the concentration ratio provides investors with an assessment of potential risk and reward dynamics.
- Sector Diversification Within Defense and Aerospace
While the investment is concentrated within specific sectors, the portfolio holdings illustrate how it is diversified across various sub-sectors. These sub-sectors includes military hardware, commercial aerospace, cybersecurity, and satellite technology. A fund with holdings spread across these areas can mitigate sector-specific risks. For example, a fund with exposure to both defense contractors and commercial aerospace companies may offset potential declines in defense spending with gains in the commercial aviation sector. This diversification provides a degree of stability and resilience during periods of economic or geopolitical uncertainty.
- Geographic Exposure
The geographical distribution of the companies within the holdings reveals the fund’s exposure to various regional economies and geopolitical risks. A portfolio with a large proportion of holdings in U.S.-based companies may be less affected by economic downturns in other regions but more sensitive to changes in U.S. government policies. Conversely, holdings diversified across multiple countries could provide resilience against localized economic or political instability. Understanding the geographic footprint informs an assessment of global risk factors influencing the fund’s performance.
- Overlap with Other Investments
Investors should assess the degree of overlap between the fund’s holdings and their existing investment portfolio. Significant overlap reduces diversification benefits and increases exposure to specific companies or sectors. If an investor already holds shares in a major defense contractor, adding this investment may not provide the desired diversification. Analyzing overlap helps ensure a well-balanced and diversified portfolio aligned with individual risk tolerance and investment goals.
An understanding of the portfolio’s composition facilitates better decision-making. Analyzing top holdings concentration, sector diversification, geographic exposure, and overlap with other investments allows for a comprehensive risk assessment and enables investors to determine its suitability within their overall financial strategy. The specific securities provides a level of transparency.
7. Fund Management
Fund management represents a critical determinant of the performance of financial investments, particularly those concentrated in specialized sectors such as defense and aerospace. The expertise, strategies, and decision-making processes of the fund managers directly influence the fund’s ability to navigate the unique challenges and opportunities presented by these industries. Effective fund management within this area involves a deep understanding of governmental policies, technological advancements, and geopolitical dynamics that shape the sector. Consequently, the skill and acumen of the management team are directly linked to the potential for success.
A practical example illustrating the significance of proficient stewardship is observed in evaluating a manager’s historical track record during periods of geopolitical instability. A fund manager adept at anticipating and responding to these events may reallocate portfolio assets to capitalize on increased defense spending or mitigate risks associated with market volatility. Furthermore, understanding fund management’s role in technological innovation is crucial. Managers must assess emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence or cybersecurity, and strategically position the fund to benefit from evolving trends. The absence of this strategic foresight could lead to underperformance as other investments quickly grow. This requires careful consideration of where to capitalize in a field where developments occur fast.
In conclusion, the quality of fund management is inextricably linked to the overall success of specialized investment vehicles. While external factors such as market conditions and geopolitical events undoubtedly play a role, the expertise and strategic decisions of the fund managers are paramount. A comprehensive understanding of fund management principles, coupled with diligent analysis of manager track records, is essential for investors seeking to make informed choices regarding investments. A detailed understanding of the people involved and their qualifications will ultimately decide success.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following section addresses common inquiries regarding investments focused on the defense and aerospace industries. These responses are intended to provide clarity and facilitate informed decision-making.
Question 1: What distinguishes sector-specific investments from diversified portfolios?
Sector-specific investments concentrate capital within a particular industry, offering the potential for targeted growth but also exposing investors to heightened risk relative to diversified portfolios.
Question 2: How do governmental policies impact the performance of defense and aerospace investments?
Governmental policies, including defense spending budgets, regulatory changes, and international trade agreements, exert significant influence over the revenue and profitability of companies within these sectors.
Question 3: What role does technological innovation play in defense and aerospace?
Technological innovation drives competitive advantage and shapes future growth prospects within the defense and aerospace industries. Companies investing in research and development are better positioned for long-term success.
Question 4: How can an investor assess the risk profile of sector-specific investments?
Risk assessment involves evaluating factors such as market volatility, geopolitical instability, and concentration of holdings within the investment portfolio. Metrics like beta and standard deviation provide quantitative measures of risk.
Question 5: What are key considerations when comparing expense ratios across different investment options?
Expense ratios represent the annual cost of operating a fund, expressed as a percentage of assets. Lower expense ratios generally result in higher net returns for investors, assuming all other factors remain constant.
Question 6: How can historical performance data inform investment decisions?
Historical performance provides insight into a fund’s ability to generate returns over various time horizons. However, past results are not indicative of future performance, and should be considered in conjunction with other factors, such as current market conditions and investment strategy.
In summary, informed investment decisions require a thorough understanding of the factors influencing performance, as well as careful consideration of risk tolerance and financial objectives. Sector-specific investments can offer targeted exposure but demand heightened due diligence.
The subsequent section will delve into considerations for choosing between active and passive management strategies.
Conclusion
This analysis provides a detailed examination of investments concentrated within defense and aerospace, particularly referencing fidelity defense and aerospace mutual fund. The exploration encompassed sector dynamics, expense ratios, investment strategies, historical performance, risk factors, portfolio holdings, and fund management principles. Each of these aspects contributes to the overall assessment of the fund’s potential and suitability for investors.
The information presented serves as a foundation for further due diligence and informed decision-making. Prospective investors are encouraged to consult with qualified financial advisors, conduct independent research, and carefully consider their individual risk tolerance and investment objectives before allocating capital to any specific instrument. Continued awareness of market trends and geopolitical developments remains crucial for navigating this specialized sector.