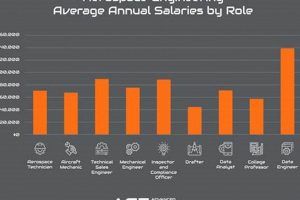
Positions within the aeronautics and astronautics sector that offer the greatest monetary compensation constitute a select group. These roles typically require advanced education, specialized skills, and considerable experience. Examples include executive leadership, specialized engineering, and highly technical scientific positions.
The pursuit of such careers can lead to substantial financial rewards, reflecting the high demand for specialized expertise in this critical field. Historically, national defense and space exploration initiatives have driven the creation and evolution of these high-paying positions, underlining their significance to technological advancement and economic growth.
The subsequent sections will examine specific roles that exemplify this level of compensation, detailing the requisite qualifications, typical responsibilities, and factors contributing to their earning potential.
Attaining roles with significant remuneration within the aeronautics and astronautics field necessitates strategic planning and consistent professional development. The following recommendations provide a framework for individuals seeking to maximize their earning potential in this competitive industry.
Tip 1: Acquire Advanced Education: Possessing a master’s degree or doctorate in a specialized area such as aerospace engineering, materials science, or a related discipline is often a prerequisite for high-paying positions. Advanced coursework deepens expertise and enhances research capabilities.
Tip 2: Cultivate Specialized Skills: Develop proficiency in niche areas such as computational fluid dynamics, advanced propulsion systems, or satellite technology. Expertise in high-demand areas distinguishes candidates and increases their value to employers.
Tip 3: Gain Relevant Experience: Seek internships, co-op programs, or entry-level positions that offer exposure to complex projects and cutting-edge technologies. Practical experience validates theoretical knowledge and demonstrates problem-solving abilities.
Tip 4: Obtain Professional Certifications: Pursue industry-recognized certifications such as those offered by professional organizations like AIAA or ASME. Certifications demonstrate competence and commitment to professional standards.
Tip 5: Network Strategically: Attend industry conferences, join professional societies, and cultivate relationships with established professionals. Networking provides access to job opportunities, mentorship, and industry insights.
Tip 6: Develop Leadership Abilities: Cultivate skills in project management, team leadership, and communication. Leadership experience is highly valued in senior-level positions and demonstrates the ability to guide teams and achieve organizational goals.
Tip 7: Stay Abreast of Technological Advancements: Continuously update knowledge of emerging technologies and industry trends. Maintaining a current understanding of the latest developments ensures relevance and adaptability in a rapidly evolving field.
Adhering to these guidelines can significantly enhance an individual’s prospects for securing roles characterized by superior financial compensation in the aeronautics and astronautics arena. Diligence and focused effort are paramount to achieving long-term career success and financial stability.
The subsequent section will provide a concluding overview of the key considerations for individuals aspiring to reach the zenith of professional accomplishment within the aerospace domain.
1. Executive Leadership
Executive leadership roles within the aeronautics and astronautics sector are consistently ranked among the positions offering the greatest financial compensation. These positions entail a high degree of responsibility and influence, directly impacting the strategic direction and financial performance of organizations operating in this technically demanding field.
- Strategic Vision and Direction
Executive leaders are responsible for formulating and implementing the long-term strategic vision of aerospace companies. This includes identifying new market opportunities, overseeing technological innovation, and ensuring the organization remains competitive. A company’s success, directly attributable to executive decisions, justifies substantial remuneration.
- Financial Oversight and Accountability
Executives manage significant financial resources, overseeing budgets, investments, and financial performance. Their decisions directly impact profitability, shareholder value, and the overall financial health of the organization. The scale of financial accountability is a key determinant of compensation.
- Risk Management and Regulatory Compliance
The aerospace industry is heavily regulated and subject to considerable risk. Executive leaders are responsible for ensuring compliance with stringent regulations and mitigating potential risks, including those related to safety, security, and environmental impact. Effective risk mitigation safeguards company assets and reputation.
- Stakeholder Management and External Relations
Executives interact with a diverse range of stakeholders, including government agencies, investors, customers, and the public. They represent the organization’s interests and cultivate positive relationships, which are crucial for securing funding, contracts, and regulatory approvals. Successful stakeholder engagement directly contributes to company growth and stability.
The combination of strategic influence, financial accountability, risk management oversight, and stakeholder engagement responsibilities inherent in executive leadership roles explains their position at the upper echelon of the aeronautics and astronautics compensation spectrum. The ability to navigate complex challenges and drive organizational success in this demanding sector is highly valued and rewarded.
2. Specialized Engineering
Specialized engineering directly correlates with elevated compensation within the aeronautics and astronautics sector. As technology advances, demand escalates for professionals possessing expertise in niche areas, creating a competitive environment that drives up salaries. Highly specific skill sets often translate to increased efficiency, innovation, and problem-solving capabilities, assets for which organizations are willing to pay a premium. The link is causal: specialized knowledge fills critical gaps, allowing companies to pursue sophisticated projects and maintain competitive advantages. Without individuals specializing in fields like hypersonics, advanced materials, or quantum computing applications for aerospace, many advanced projects would be impossible.
Real-world illustrations underscore this connection. Consider the development of new generation jet engines. Engineers specializing in advanced thermodynamics and computational fluid dynamics are vital for optimizing engine performance and efficiency. Their specialized knowledge translates directly into fuel savings, reduced emissions, and enhanced engine reliability, factors that yield substantial financial benefits for airlines and manufacturers alike. Or consider space exploration: engineers specializing in areas like radiation shielding or closed-loop life support systems are indispensable to the success and safety of long-duration missions, commanding high salaries due to the critical nature and limited availability of their expertise. These examples highlight the practical application and value proposition of specialized knowledge.
In summary, specialized engineering is not merely a desirable attribute but a foundational element contributing to superior earnings in the aerospace field. The demand for focused expertise drives competition for talent, subsequently inflating salaries. Understanding this dynamic is critical for both aspiring engineers seeking to maximize their earning potential and for organizations seeking to attract and retain top talent. Furthermore, this recognition underscores the importance of continuous learning and skill development for professionals seeking to maintain a competitive edge in an ever-evolving technological landscape.
3. Research and Development
The nexus between research and development (R&D) and elevated compensation in the aeronautics and astronautics sector is characterized by a direct correlation. R&D efforts drive innovation, and individuals leading or significantly contributing to these endeavors are commensurately rewarded. A primary factor is the inherent risk associated with R&D; projects often involve substantial investment with uncertain outcomes. Professionals who can navigate this uncertainty, generating tangible advancements, are highly valued. Their expertise reduces the risk of failure, contributing directly to long-term profitability and competitive advantage. Real-life examples, such as the development of fuel-efficient aircraft engines or advanced composite materials for spacecraft, illustrate this. The engineers and scientists spearheading these projects are not only advancing the state-of-the-art but are also directly impacting the financial bottom line of their organizations.
Beyond direct financial impact, R&D fosters intellectual property, a key driver of value within the aerospace industry. Patents, trade secrets, and proprietary technologies developed through R&D create barriers to entry for competitors, ensuring long-term market dominance. Professionals involved in this process, particularly those with expertise in intellectual property law or technology transfer, command high salaries. Their ability to protect and monetize innovations is essential for maximizing return on investment in R&D activities. For instance, companies heavily invested in developing next-generation propulsion systems rely on R&D teams and legal experts to secure patents and safeguard their technological lead.
In conclusion, the link between R&D and high compensation stems from the inherent value creation within the aerospace sector. Innovation drives revenue, secures market position, and fosters long-term growth. Professionals skilled in navigating the complexities of R&D, from initial concept to commercialization, are crucial assets. While challenges exist, including long development cycles and the risk of obsolescence, the rewards for successful innovation remain substantial, solidifying R&D as a key pathway to positions offering superior remuneration.
4. Advanced Skillsets
The acquisition and mastery of advanced skillsets serve as a primary determinant in accessing roles with considerable compensation within the aeronautics and astronautics sector. These competencies, extending beyond fundamental engineering principles, represent specialized knowledge and proficiency in areas critical to industry advancement. A causal relationship exists: the demand for individuals with such expertise outstrips supply, driving up remuneration. Highly sought-after advanced skillsets might include proficiency in computational fluid dynamics (CFD), expertise in advanced materials science, a deep understanding of aerospace systems engineering, or specialized knowledge of autonomous systems and robotics within aerospace applications. The capacity to apply these skills to solve complex technical challenges directly translates into higher earning potential.
Real-world examples underscore this connection. Engineers specializing in the design and optimization of hypersonic vehicles, a nascent area of aerospace development, command premium salaries due to the scarcity of professionals with the requisite expertise in high-speed aerodynamics, thermal management, and advanced propulsion systems. Similarly, experts in cybersecurity for aerospace systems are increasingly valuable, given the growing reliance on interconnected digital infrastructure within the industry. These individuals are tasked with protecting critical systems from cyber threats, a responsibility that demands specialized knowledge of cybersecurity protocols, threat detection methodologies, and incident response strategies. The ability to safeguard sensitive data and prevent system disruptions is deemed essential, justifying significant financial investment in talent with these advanced skills.
In summary, the pursuit of roles characterized by superior financial compensation within the aeronautics and astronautics field necessitates a strategic focus on developing advanced skillsets in high-demand areas. While foundational knowledge is essential, the ability to apply specialized expertise to solve complex, industry-specific challenges is the defining characteristic of those earning at the upper end of the compensation spectrum. Continuous learning and professional development are, therefore, not merely advisable but crucial for professionals aspiring to maximize their earning potential within this technologically dynamic sector.
5. Strategic Roles
Strategic roles within the aeronautics and astronautics sector represent positions where decision-making has a significant impact on an organization’s overall direction and performance. Such roles command substantial compensation due to the high level of responsibility and the specialized knowledge required to navigate the complexities of the industry.
- Chief Technology Officer (CTO)
The CTO is responsible for charting the technological vision of an aerospace company. This involves identifying emerging technologies, overseeing research and development efforts, and ensuring that technological investments align with strategic business objectives. For instance, a CTO might spearhead the development of a new generation of fuel-efficient aircraft or lead the adoption of advanced manufacturing techniques. The ability to anticipate technological trends and drive innovation directly impacts a company’s competitive advantage, justifying significant remuneration.
- Vice President of Business Development
This role focuses on identifying and pursuing new business opportunities for an aerospace company. This involves cultivating relationships with key clients, negotiating contracts, and expanding the company’s market presence. For example, a VP of Business Development might secure a multi-billion dollar contract to supply aircraft components to a major airline or negotiate a partnership with a space exploration company. The ability to generate revenue and expand market share is a direct driver of compensation.
- Program Manager (Large-Scale Projects)
Program managers oversee large-scale aerospace projects, such as the development of a new satellite system or the construction of a new aircraft manufacturing facility. This involves managing budgets, coordinating teams, and ensuring that projects are completed on time and within budget. Effective program management is critical for controlling costs and delivering high-quality products, leading to significant cost savings and increased profitability.
- Chief Engineer
The Chief Engineer is responsible for the technical integrity of an aerospace company’s products and services. This involves overseeing engineering design, ensuring compliance with safety standards, and resolving complex technical issues. For example, a Chief Engineer might lead the investigation into a safety incident involving an aircraft or oversee the implementation of design changes to improve product reliability. Their experience mitigates risks, upholding the operational integrity of the company.
These strategic roles all share a common thread: they require individuals who can make informed decisions that have a far-reaching impact on an organization’s success. The combination of technical expertise, leadership skills, and business acumen necessary to excel in these positions makes them highly sought after, resulting in compensation packages that reflect their critical importance to the aeronautics and astronautics sector.
6. Industry Experience
Accumulated practical knowledge and demonstrated competence within the aeronautics and astronautics sector exert a significant influence on earning potential. Individuals possessing extensive, relevant experience are demonstrably more likely to secure positions offering superior financial compensation. This correlation is attributable to the value placed on proven abilities and contextual understanding in a high-stakes, technically complex environment.
- Depth of Knowledge
Prolonged engagement within the industry allows professionals to cultivate a comprehensive understanding of its intricacies. This encompasses not only technical principles but also regulatory frameworks, market dynamics, and operational challenges. Executives and senior engineers with decades of experience possess a depth of knowledge that enables them to make informed decisions, anticipate potential problems, and develop effective solutions. This accumulated wisdom translates directly into increased value and, consequently, higher compensation.
- Established Networks
Years of working within the sector facilitates the formation of extensive professional networks. These networks provide access to valuable information, facilitate collaboration, and open doors to new opportunities. Individuals with strong industry connections are better positioned to identify promising projects, secure funding, and attract top talent. Moreover, a well-established network enhances an individual’s reputation and credibility, further increasing their marketability and earning potential. Seasoned professionals leverage their connections to navigate complex projects and influence decision-making processes.
- Proven Track Record
Industry experience provides a tangible record of accomplishments and contributions. Professionals with a demonstrated history of success are viewed as less risky hires and are therefore more likely to be offered positions with greater responsibility and higher compensation. Employers seek candidates who can provide concrete examples of how they have successfully tackled challenges, delivered results, and added value to previous organizations. A portfolio of successful projects and positive performance evaluations serves as compelling evidence of an individual’s capabilities.
- Adaptability and Problem-Solving
The aerospace industry is characterized by rapid technological advancements and evolving market conditions. Individuals with extensive experience have demonstrated the ability to adapt to these changes and solve complex problems effectively. They have encountered a wide range of challenges throughout their careers and have developed the resilience and resourcefulness necessary to overcome obstacles. This adaptability and problem-solving proficiency are highly valued by employers, who recognize the importance of having experienced professionals capable of navigating uncertainty and driving innovation.
The aforementioned facets collectively illustrate the profound impact of industry experience on the attainment of positions characterized by significant financial remuneration within the aeronautics and astronautics domain. Employers consistently prioritize candidates who possess not only theoretical knowledge but also the practical acumen and demonstrated capabilities acquired through years of dedicated service within the field.
7. Location/Demand
Geographic location and industry demand serve as critical determinants of compensation levels within the aeronautics and astronautics sector. Concentrations of aerospace activity and areas experiencing high demand for specific skill sets exert upward pressure on salaries.
- Geographic Clusters of Aerospace Activity
Regions with a significant presence of aerospace companies, government agencies, and research institutions often offer higher salaries due to increased competition for skilled professionals. Examples include California’s Silicon Valley and Southern California, Washington State (Boeing), Texas (NASA Johnson Space Center, growing commercial space sector), and Florida (Cape Canaveral). These areas benefit from established infrastructure, a concentration of talent, and a vibrant ecosystem that fosters innovation. Companies located in these clusters are often willing to pay a premium to attract and retain top talent.
- Specialized Skill Set Demand
Demand for specific skill sets within the aerospace industry fluctuates based on technological advancements, government priorities, and market trends. For example, there is currently a high demand for engineers specializing in areas such as autonomous systems, cybersecurity for aerospace, and advanced materials. Locations where companies are actively developing these technologies experience a surge in demand for professionals with the requisite expertise, leading to increased compensation. A company involved in advanced drone technology development in Nevada, for instance, will need to pay a higher wage to attract the needed expert due to lack of supply compared to demand.
- Government Contracts and Funding
Government contracts and funding initiatives significantly impact the demand for aerospace professionals in specific locations. States or regions that receive substantial government investment in aerospace projects often experience an increase in job opportunities and higher salaries. For example, a region that secures a contract to develop a new generation of military aircraft will likely see a surge in demand for aerospace engineers, project managers, and technicians. The location of major government contractors or research facilities therefore becomes a focal point for career opportunities and elevated compensation.
- Emerging Spaceports and Commercial Space Activity
The growth of commercial space activities and the establishment of new spaceports is creating new centers of aerospace employment and driving demand for skilled professionals. Locations such as Florida (with existing infrastructure), Texas, and certain regions in the Southwest are experiencing an influx of investment and job creation related to space launch, satellite manufacturing, and space tourism. This growth is leading to increased competition for talent and higher salaries in these areas. As the commercial space sector matures, the geographic distribution of opportunities and compensation levels will continue to evolve.
In summary, the interplay between geographic location and industry demand is a crucial factor influencing compensation within the aeronautics and astronautics sector. Areas with a high concentration of aerospace activity, a strong presence of government contracts, and a growing commercial space sector tend to offer higher salaries. Professionals seeking to maximize their earning potential should carefully consider these factors when making career decisions. Furthermore, continuous monitoring of industry trends and geographic shifts in demand is essential for long-term career success.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries concerning roles within the aeronautics and astronautics sector that offer considerable financial compensation. The objective is to provide clarity and accurate information for individuals exploring career options in this field.
Question 1: What educational qualifications are typically required to attain roles with the highest compensation in the aerospace industry?
Advanced degrees, such as a Master’s or Doctorate in Aerospace Engineering, Mechanical Engineering, Electrical Engineering, or a related field, are generally required. Specialized knowledge and research experience are often essential for positions in research and development or leadership roles.
Question 2: Beyond formal education, what specific skills or certifications enhance an individual’s earning potential in aerospace?
Proficiency in areas such as computational fluid dynamics (CFD), finite element analysis (FEA), systems engineering, and project management can significantly increase marketability. Professional certifications from organizations like AIAA or ASME demonstrate competence and commitment.
Question 3: Which specific job titles generally command the highest salaries within the aerospace sector?
Executive leadership positions (e.g., Chief Technology Officer, Vice President of Engineering), specialized engineering roles (e.g., Propulsion Engineer, Avionics Engineer), and program management roles for large-scale projects typically offer the highest levels of compensation.
Question 4: How does industry experience impact salary levels in aerospace?
Industry experience is a significant factor. Individuals with a proven track record of accomplishments and a deep understanding of aerospace systems and operations are highly valued and command higher salaries.
Question 5: Does geographic location influence earning potential in the aerospace field?
Yes. Areas with a high concentration of aerospace companies, government agencies, and research institutions tend to offer higher salaries due to increased competition for skilled professionals. Examples include California, Washington State, and Florida.
Question 6: What are some emerging trends in the aerospace industry that could lead to new high-paying job opportunities?
Emerging trends such as commercial space exploration, autonomous systems, advanced materials, and cybersecurity for aerospace are creating new opportunities for skilled professionals and driving demand for specialized expertise.
In summary, positions characterized by superior financial compensation in aeronautics and astronautics typically require advanced education, specialized skills, extensive experience, and a willingness to adapt to emerging industry trends. Strategic career planning and continuous professional development are essential for maximizing earning potential.
The following concluding section will provide an overview of the key considerations for individuals pursuing advanced careers within the aerospace domain.
Highest Paying Jobs in Aerospace
This exploration of the aeronautics and astronautics sector has illuminated the roles offering the most significant financial remuneration. Advanced education, specialized skillsets, relevant experience, and strategic positioning within high-demand geographic locations have been identified as critical determinants. Successful navigation of this landscape requires a commitment to continuous learning and adaptation to emerging technological trends.
The pursuit of these career paths demands diligence and strategic planning. The future of aeronautics and astronautics promises continued innovation and growth, creating both opportunities and challenges. A proactive approach to professional development and a clear understanding of industry dynamics are essential for sustained success and maximizing earning potential within this dynamic domain.