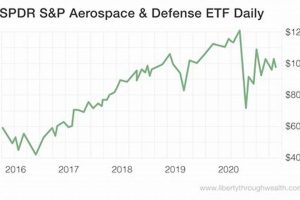
This investment benchmark serves as a representation of the performance of companies within the aerospace and defense industries located in Developed Markets countries within the European Monetary Union (EMU). It is constructed using a free-float adjusted market capitalization weighted methodology. As an example, if an investor seeks to track the overall performance of listed aerospace and defense firms specifically within the Eurozone, this benchmark provides a means to do so.
Its importance lies in its ability to provide investors with a targeted view of a specific sector within a defined geographical region. Benefits include enabling portfolio diversification, facilitating performance comparisons, and offering a tool for creating passive investment strategies. Historically, the index’s performance reflects geopolitical events, technological advancements in the aerospace sector, and government defense spending policies in the constituent EMU countries. The index is a subset of a broader market index, capturing a specific segment for focused investment.
The following analysis will delve into the factors influencing the performance of this specialized benchmark, its constituents, and its role within the broader investment landscape. Furthermore, the impact of regulatory changes and global economic trends on its valuation will be examined.
Effective investment and analysis related to the aerospace and defense sector within the European Monetary Union requires a multifaceted approach. The following points offer guidance for stakeholders seeking to understand and engage with this specific market segment.
Tip 1: Conduct Thorough Due Diligence: A comprehensive understanding of the individual companies included in the index is crucial. Analyze their financial performance, order backlogs, technological capabilities, and competitive positioning within the market.
Tip 2: Monitor Geopolitical Events: The aerospace and defense sector is highly sensitive to geopolitical developments. Closely monitor international relations, conflicts, and defense spending policies of EMU member states and their allies. These factors directly impact the demand for defense-related products and services.
Tip 3: Assess Regulatory and Policy Changes: Changes in government regulations, export controls, and defense procurement policies can significantly influence the performance of companies in this sector. Stay informed about relevant policy updates from both national governments and the European Union.
Tip 4: Track Technological Advancements: The aerospace and defense industry is characterized by rapid technological innovation. Monitor developments in areas such as unmanned aerial vehicles, cybersecurity, and advanced materials, as these advancements can create both opportunities and challenges for companies in the index.
Tip 5: Analyze Currency Fluctuations: As the index focuses on EMU countries, currency fluctuations, particularly between the Euro and other major currencies, can affect the returns for international investors. Consider hedging strategies to mitigate currency risk.
Tip 6: Evaluate Supply Chain Resilience: The aerospace and defense industry relies on complex global supply chains. Assess the resilience of these supply chains to disruptions, such as geopolitical instability, natural disasters, or trade disputes. Diversification of suppliers can mitigate risk.
Tip 7: Consider Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Factors: Increasingly, investors are incorporating ESG considerations into their investment decisions. Evaluate the ESG performance of companies in the index, paying attention to factors such as environmental impact, labor practices, and corporate governance.
Understanding the interplay of these factors is essential for making informed decisions regarding investments linked to aerospace and defense companies operating within the EMU. A holistic view that incorporates financial analysis, geopolitical awareness, and technological insight provides a strong foundation for navigating this specialized market.
The subsequent sections will explore specific companies included within this benchmark and their responses to the evolving challenges and opportunities in the global defense landscape.
1. Performance Measurement
Performance measurement is fundamental to assessing the efficacy and attractiveness of the investment benchmark. It provides quantifiable metrics that reflect the financial health and market positioning of the aerospace and defense sectors within the Eurozone. These metrics are vital for investors aiming to gauge the index’s historical returns, volatility, and risk-adjusted performance.
- Total Return Analysis
Total return analysis calculates the percentage change in the index’s value over a specific period, incorporating both capital appreciation and dividend payments from constituent companies. For example, if the index shows a 15% total return over a year, it indicates that investors tracking this benchmark would have experienced a 15% gain on their investment. This facet is critical for evaluating the historical profitability of the index.
- Volatility Assessment
Volatility assessment quantifies the degree to which the index’s value fluctuates over time, typically measured by standard deviation. A high volatility score suggests greater price swings, potentially increasing risk for investors. Conversely, lower volatility implies more stable returns. For instance, a high volatility in a period marked by geopolitical instability directly reflects the sensitivity of aerospace and defense companies to global events.
- Risk-Adjusted Return Metrics
Risk-adjusted return metrics, such as the Sharpe Ratio, assess the index’s return relative to the amount of risk taken. The Sharpe Ratio calculates the excess return earned for each unit of risk. A higher Sharpe Ratio signifies better risk-adjusted performance. This is important because it accounts for volatility, which is a major concern for an index highly dependent on geopolitical situations.
- Benchmarking and Relative Performance
Benchmarking involves comparing the index’s performance against other relevant benchmarks, such as broader market indices or other sector-specific indices. This analysis helps determine whether the aerospace and defense sector in the EMU is outperforming or underperforming relative to its peers. For instance, comparing the MSCI EMU Aerospace and Defense Index to the MSCI World Index allows investors to assess its relative strength and identify potential investment opportunities.
These interconnected metrics provide a holistic view of the financial characteristics. Monitoring each of these facets contributes to a clearer understanding of its investment merit and enables more informed decision-making.
2. Sector Representation
Sector representation is a cornerstone of the investment benchmark’s construction, directly determining its composition and performance characteristics. It ensures that the index accurately reflects the performance of companies operating within the aerospace and defense industries located in the European Monetary Union (EMU).
- Aerospace Manufacturing and Services
This facet encompasses companies involved in the design, manufacturing, and maintenance of aircraft, spacecraft, and related components. Examples include Airbus SE, a major player in commercial aircraft manufacturing, and companies providing maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO) services for aircraft fleets. Their inclusion ensures the index captures the economic performance of the civilian and commercial aerospace sectors.
- Defense Equipment and Systems
This segment represents companies that produce military equipment, weaponry, and defense systems. Thales Group, a prominent player in defense electronics and security systems, exemplifies this. The performance of these companies is strongly influenced by government defense spending and geopolitical events, making this segment a key driver of the index’s overall performance.
- Space Technology and Services
Companies engaged in the development and operation of space-related technologies and services are included. This can range from satellite manufacturers to providers of satellite communication and Earth observation services. As the space industry expands, this facet increasingly contributes to the index’s overall diversity and growth potential.
- Cybersecurity and Defense IT
With the increasing importance of cybersecurity in the modern defense landscape, companies specializing in cybersecurity solutions for the aerospace and defense sectors are represented. These firms provide critical services related to data protection, threat detection, and secure communication systems. Their inclusion underscores the growing integration of technology into the defense industry and the importance of digital security.
The interplay between these facets is critical in shaping the benchmark’s overall performance. These representative companies highlight how macroeconomic factors and innovation affect returns, leading to a comprehensive method for gauging investment performance in the EMU aerospace and defense sectors.
3. Geographic Focus
Geographic focus constitutes a defining element of this investment benchmark, directly shaping its composition and exposure. By restricting its scope to the European Monetary Union (EMU), the index provides a targeted representation of aerospace and defense companies operating within this specific economic zone. This regional concentration has significant implications for investment strategy and risk management.
- Eurozone Economic Conditions
The economic health of the Eurozone member states exerts a direct influence on the index’s performance. Factors such as GDP growth, inflation rates, and fiscal policies within the EMU impact the financial performance of constituent companies. For instance, increased government spending on defense in response to regional security concerns can boost revenues for defense contractors based in EMU countries.
- Monetary Policy of the European Central Bank (ECB)
The monetary policy decisions of the ECB, including interest rate adjustments and quantitative easing programs, affect the borrowing costs and investment climate for companies in the index. Lower interest rates can stimulate investment and economic growth, potentially benefiting aerospace and defense firms. Conversely, tighter monetary policy can dampen economic activity and negatively impact corporate earnings.
- Regulatory Environment within the EMU
The regulatory framework governing the aerospace and defense industries within the EMU, including export controls, defense procurement policies, and environmental regulations, impacts the operational environment and profitability of companies in the index. Stricter regulations can increase compliance costs, while favorable policies can create opportunities for growth and expansion. The EU’s regulatory framework for defense procurement, for example, influences the competitive landscape and market access for companies operating in the region.
- Political Stability and Geopolitical Risks
The political stability and geopolitical risks within the EMU region directly influence investor sentiment and the overall risk profile of the index. Political uncertainty, social unrest, or heightened security threats can increase market volatility and negatively impact the valuation of aerospace and defense companies. Conversely, increased political stability and regional cooperation can foster a more favorable investment environment.
These interconnected regional factors establish a risk-return profile unique to the investment benchmark. The index’s performance hinges on the interplay of economic, monetary, regulatory, and political forces within the EMU. Understanding these dynamics is essential for investors seeking to make informed decisions regarding investments linked to this specialized market segment. The effects of these conditions shape overall performance, providing information on how macro-level economic events affect returns.
4. Constituent Selection
Constituent selection is a critical process in constructing the investment benchmark, directly determining its composition and its ability to accurately represent the aerospace and defense sectors within the European Monetary Union (EMU). Rigorous criteria are employed to ensure that only eligible companies are included, maintaining the index’s integrity and relevance as a performance benchmark.
- Eligibility Criteria
To be considered for inclusion, companies must meet specific criteria related to market capitalization, liquidity, and free float. Minimum market capitalization thresholds ensure that only reasonably sized and financially stable companies are included, while liquidity requirements ensure that the index is tradable and can be efficiently tracked by investment funds. Free float requirements stipulate that a sufficient percentage of the company’s shares must be publicly available for trading, excluding shares held by insiders or controlling shareholders. These criteria ensure index tradability and representation.
- Sector Classification
Companies are classified into the aerospace and defense sectors based on their primary business activities and revenue sources. Standardized industry classification systems, such as the Global Industry Classification Standard (GICS), are used to ensure consistent and objective classification. Companies primarily engaged in the design, manufacturing, or servicing of aerospace or defense-related products are eligible for inclusion, while those with only tangential exposure to these sectors are excluded. Sector allocation ensures accurate thematic representation.
- Geographic Requirements
To be eligible, companies must be domiciled in a Developed Markets country within the European Monetary Union (EMU). This geographic restriction ensures that the index specifically represents the performance of aerospace and defense companies operating within the Eurozone. Companies based outside the EMU, even if they have significant operations in the region, are excluded from the index. Geolocation ensures focused regional assessment.
- Periodic Reviews and Adjustments
The composition of the index is periodically reviewed and adjusted to reflect changes in market conditions, corporate actions, and compliance with eligibility criteria. Rebalancing occurs at regular intervals (e.g., quarterly or semi-annually) to ensure that the index remains representative of the target market. Companies that no longer meet the eligibility criteria are removed, while new companies that qualify are added. Periodic reviews ensure continued index validity.
The careful application of these constituent selection criteria ensures that the investment benchmark accurately reflects the performance of the intended market segment. By maintaining a well-defined and transparent methodology for selecting constituents, the index provides a reliable and investable benchmark for investors seeking exposure to the aerospace and defense sectors within the EMU.
5. Weighting Methodology
Weighting methodology is a cornerstone of the MSCI EMU Aerospace and Defense Index, dictating the proportional representation of each constituent company within the benchmark. This approach directly influences the index’s performance, risk profile, and its ability to accurately reflect the dynamics of the targeted market segment.
- Market Capitalization Weighting
The MSCI EMU Aerospace and Defense Index primarily employs a market capitalization weighting scheme. This means that companies with larger market capitalizations (i.e., the total value of their outstanding shares) have a greater influence on the index’s overall performance. For example, if Airbus SE has a significantly larger market capitalization than Thales Group, its stock price movements will have a more substantial impact on the index’s value. This approach reflects the relative economic significance of each company in the sector.
- Free-Float Adjustment
To ensure that the index accurately reflects the investable universe, a free-float adjustment is applied. This adjustment excludes shares that are not readily available for trading in the public market, such as those held by controlling shareholders, governments, or other insiders. For instance, if a significant portion of a company’s shares are held by the government, the free-float adjustment reduces the company’s weight in the index to reflect the actual number of shares available to public investors. This enhancement makes the index more representative of the tradable equity base.
- Capping and Diversification Considerations
While market capitalization weighting is the primary approach, the index may incorporate capping mechanisms to limit the dominance of any single company and promote diversification. For example, a rule may be implemented to prevent any single constituent from exceeding a certain percentage of the index’s total weight. This helps to mitigate concentration risk and ensure that the index is not overly reliant on the performance of a few large companies. These rules aim to create a more balanced and diversified exposure to the aerospace and defense sectors within the EMU.
- Periodic Rebalancing
The index is periodically rebalanced to reflect changes in market capitalizations, free float, and compliance with eligibility criteria. Rebalancing involves adjusting the weights of constituent companies to maintain the desired weighting scheme. For example, if a company’s market capitalization increases significantly due to strong performance, its weight in the index will be increased during the rebalancing process. Conversely, if a company’s market capitalization declines, its weight will be reduced. This periodic adjustment ensures that the index remains representative of the target market and aligned with its intended weighting methodology. The rebalancing schedule is typically quarterly or semi-annually, aligning the index with prevailing market conditions.
The weighting methodology of the MSCI EMU Aerospace and Defense Index is a critical factor influencing its performance and risk characteristics. Through market capitalization weighting, free-float adjustments, capping mechanisms, and periodic rebalancing, the index aims to provide a reliable and investable benchmark for investors seeking exposure to the aerospace and defense sectors within the European Monetary Union. The interplay of these factors ensures accurate benchmark representation of the market.
6. Investment Diversification
The integration of the MSCI EMU Aerospace and Defense Index within a broader portfolio strategy serves as a specific instance of investment diversification. It allows investors to allocate capital to a distinct sector within a defined geographic region, potentially mitigating overall portfolio risk and enhancing return opportunities.
- Sector-Specific Exposure
The index enables investors to gain focused exposure to the aerospace and defense industries. These sectors often exhibit different performance characteristics compared to the broader market, influenced by factors such as government defense spending, technological innovation, and geopolitical events. Including this index in a portfolio can reduce the correlation with other asset classes, such as equities in different sectors or fixed-income securities. As an example, during periods of increased global security concerns, defense stocks might outperform other sectors, providing a degree of portfolio protection.
- Geographic Diversification within Equities
By focusing on companies domiciled in European Monetary Union (EMU) countries, the index provides a specific geographic diversification element within an equity portfolio. The EMU region has unique economic and political dynamics, and its aerospace and defense companies may be influenced by factors distinct from those affecting companies in North America or Asia. This geographic focus allows investors to tailor their portfolio’s exposure to specific regional trends and risks. An example would be exposure to the European Union’s defense initiatives that support local defense companies.
- Risk Mitigation Through Reduced Correlation
The aerospace and defense sectors can exhibit low correlation with other asset classes, contributing to portfolio risk mitigation. The performance drivers of these sectors often diverge from those of broader market indices, making them a potential source of stability during periods of market volatility. For instance, during economic downturns, defense spending might remain relatively stable due to long-term government contracts, providing a degree of resilience to the index’s performance.
- Enhanced Return Potential
While diversification primarily aims to reduce risk, it can also enhance long-term return potential. By allocating capital to sectors with different growth drivers, investors can potentially capture opportunities that are not available through a solely broad-based market approach. The aerospace and defense sectors are characterized by technological innovation and long-term growth trends, making them a potentially attractive source of long-term returns. For example, investment in cutting-edge defense technologies could drive future growth and outperformance.
The MSCI EMU Aerospace and Defense Index, therefore, serves as a tool for sophisticated investors seeking to refine their portfolio allocation through targeted sector and geographic diversification. It provides a means to access specific investment opportunities and manage risk within a broader portfolio context.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following questions and answers address common inquiries and considerations regarding the MSCI EMU Aerospace and Defense Index. This information aims to provide clarity and enhance understanding of this specialized investment benchmark.
Question 1: What is the objective of this index?
The primary objective is to represent the performance of companies in the aerospace and defense sectors within the Developed Markets countries of the European Monetary Union (EMU). It serves as a benchmark for investors seeking exposure to this specific market segment.
Question 2: What criteria determine a company’s inclusion in the index?
Companies must meet specific criteria related to market capitalization, liquidity, free float, sector classification (aerospace and defense), and geographic domicile (EMU). Eligibility ensures the index reflects the target market and remains tradable.
Question 3: How is the index weighted?
The index employs a market capitalization weighting methodology, adjusted for free float. This means that companies with larger market capitalizations have a greater influence on the index’s performance. Capping mechanisms may also be implemented to promote diversification.
Question 4: How often is the index rebalanced?
The index is periodically rebalanced, typically on a quarterly or semi-annual basis. Rebalancing involves adjusting the weights of constituent companies to reflect changes in market capitalizations, free float, and compliance with eligibility criteria.
Question 5: What are the key factors influencing the index’s performance?
The index’s performance is influenced by a range of factors, including geopolitical events, government defense spending, technological innovation in the aerospace and defense sectors, and the overall economic conditions of the EMU countries.
Question 6: What are the benefits of using this index in a portfolio?
The index provides sector-specific and geographic diversification within an equity portfolio. It allows investors to gain targeted exposure to the aerospace and defense sectors in the EMU, potentially mitigating portfolio risk and enhancing return opportunities.
The MSCI EMU Aerospace and Defense Index offers a valuable tool for investors seeking specialized exposure to a dynamic sector within a defined geographic region. Understanding its objectives, construction, and influencing factors is crucial for effective utilization.
The subsequent analysis will delve into the specific performance drivers and risk considerations associated with this specialized benchmark.
Conclusion
The preceding analysis has elucidated the multifaceted nature of the MSCI EMU Aerospace and Defense Index. It has explored the index’s construction, constituent selection, weighting methodology, and the key factors influencing its performance. The index serves as a specialized benchmark providing targeted exposure to a specific sector within a defined geographic region. This targeted exposure allows investors to gain a focused view of aerospace and defense firms in the Eurozone.
The index’s utility lies in its capacity to facilitate portfolio diversification and enable performance comparisons. However, investors must recognize the index’s sensitivity to geopolitical events, regulatory changes, and economic conditions within the EMU. Continued monitoring of these factors is essential for informed decision-making and effective risk management when considering investments linked to the MSCI EMU Aerospace and Defense Index.