The integration of two major players in the aerospace and defense industries, namely Raytheon and Collins Aerospace (formerly a part of Rockwell Collins), represents a significant consolidation within the sector. This combination creates a larger, more diversified entity with expanded capabilities across a wider range of products and services. One consequence of such a combination is a more comprehensive offering to both government and commercial customers.
This type of business transaction can yield several potential advantages, including enhanced research and development capabilities, streamlined operations through synergy, and improved negotiating power with suppliers and customers. Historically, such unions have aimed to reduce costs, increase market share, and foster innovation by combining the distinct expertise and technologies of the constituent companies. This consolidation can also lead to increased efficiency and a stronger competitive position in the global market.
Subsequent sections will delve into the specific impacts of this integration on areas such as technological advancement, market dynamics, and the competitive landscape within the aerospace and defense industries. Further analysis will examine the resulting organization’s strategy and its implications for stakeholders, including employees, customers, and shareholders.
Considerations Regarding the Integration of Raytheon and Collins Aerospace
The following points offer observations regarding the implications of the integration of Raytheon and Collins Aerospace for various stakeholders.
Tip 1: Assess Product Portfolio Overlap: Analyze the combined product offerings to identify potential redundancies and opportunities for rationalization. Streamlining the product portfolio can lead to cost savings and a more focused market approach.
Tip 2: Evaluate Supply Chain Synergies: Investigate potential efficiencies in the supply chain. Combining the procurement processes of both organizations can result in improved pricing and reduced lead times.
Tip 3: Understand Technology Integration Challenges: Examine the difficulties associated with integrating disparate technological platforms. A comprehensive integration strategy is critical for realizing the full potential of combined research and development efforts.
Tip 4: Monitor Market Share Shifts: Track changes in market share resulting from the merger. The combined entity’s increased size may lead to new competitive dynamics and regulatory scrutiny.
Tip 5: Analyze Customer Impact: Evaluate the effects on existing customers of both Raytheon and Collins Aerospace. Clear communication and a commitment to maintaining service levels are essential for customer retention.
Tip 6: Address Talent Management Considerations: Develop a strategy for retaining key talent from both organizations. Uncertainty surrounding the merger can lead to employee attrition if not managed proactively.
Tip 7: Assess Regulatory Compliance: Ensure ongoing compliance with all applicable regulations. Mergers of this scale often require scrutiny from antitrust authorities and other regulatory bodies.
These considerations highlight critical aspects of the merger’s impact on operations, market position, and stakeholder relationships. A thorough evaluation of these areas is essential for understanding the long-term implications of the integration.
The following sections will explore the strategic implications of this consolidation in greater detail.
1. Market Consolidation
The integration of Raytheon and Collins Aerospace demonstrably contributes to market consolidation within the aerospace and defense sectors. This consolidation arises from the combination of two significant industry participants, leading to a larger, more dominant entity. This reduces the number of independent competitors capable of offering similar breadth of capabilities and comprehensive solutions. The immediate effect is a shift in market power, with the combined organization holding a greater share of existing contracts and a stronger position to compete for future opportunities. For example, the combined entity controls a significant portion of avionics and defense electronics, affecting competition for government contracts and commercial aircraft components. This process is inherent to the nature of mergers and acquisitions; when independent companies unite, the market becomes less fragmented.
One practical manifestation of this market consolidation is an enhanced ability to dictate pricing and terms, albeit constrained by regulatory oversight. Furthermore, innovation may be impacted, either positively through increased R&D investment, or negatively through reduced competitive pressure. The acquisition of smaller companies by the newly formed larger one may also result in further industry concentration. Examining past mergers within the defense industry reveals similar trends, indicating that consolidation is a recurring phenomenon driven by factors such as economies of scale and a desire for increased market influence. The historical precedent provides context for understanding the likely long-term implications.
In summary, the combination of Raytheon and Collins Aerospace exemplifies market consolidation by creating a larger and more influential entity. This market dynamic necessitates vigilant regulatory oversight, awareness among competing businesses, and a clear understanding of the potential impact on innovation. The merging of companies and associated industry landscape alteration underscore the critical need for strategic planning and adaptability from all stakeholders.
2. Technological Synergy
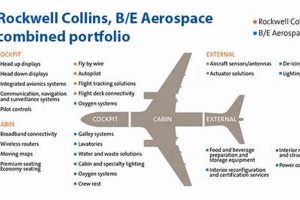
The integration of Raytheon and Collins Aerospace holds the potential for significant technological synergy. This arises from the complementary nature of their respective expertise and product portfolios, offering opportunities to develop integrated solutions and enhance existing capabilities. Realizing this synergy, however, requires careful planning and execution to overcome technical and organizational challenges.
- Enhanced Sensor and Communication Integration
Raytheon’s proficiency in radar, sensors, and missile defense systems can be integrated with Collins Aerospace’s expertise in communication, navigation, and avionics. This combination allows for the development of advanced sensing and communication systems tailored for both military and commercial applications. For instance, combining Raytheon’s radar technology with Collins Aerospace’s communication systems could lead to more efficient and reliable air traffic control systems. The implication is the creation of more sophisticated and integrated defense and aerospace solutions.
- Advanced Avionics and Flight Control Systems
Collins Aerospace possesses a strong position in the avionics market, providing flight control systems, displays, and other critical components for commercial and military aircraft. Pairing these capabilities with Raytheon’s advanced software and systems integration expertise could lead to the development of next-generation avionics platforms with enhanced safety features and improved performance. A practical example is the integration of advanced pilot assistance systems, improving flight safety and reducing pilot workload. This signifies a leap in aviation technology by combining control system experience.
- Cybersecurity Integration for Aerospace Systems
With increasing reliance on digital systems in aerospace, cybersecurity has become paramount. Raytheon’s established cybersecurity capabilities can be leveraged to enhance the security of Collins Aerospace’s avionics and other aircraft systems. This integration is crucial to protect against cyber threats and ensure the integrity of critical flight systems. An instance of this would be reinforcing avionics systems against cyberattacks and to comply with emerging aviation cybersecurity requirements. Cybersecurity is becoming a mandatory element, especially since air travel is increasing and more reliant on software and data.
- Research and Development Collaboration
The merger creates opportunities for joint research and development initiatives. Combining the R&D resources and expertise of both companies can accelerate the development of new technologies and innovative solutions. This could lead to breakthroughs in areas such as autonomous flight, advanced materials, and next-generation propulsion systems. As a consequence, this may contribute to new opportunities and innovations in air and space travel.
Ultimately, the successful realization of technological synergy hinges on effective collaboration and knowledge sharing between the two organizations. By carefully integrating their respective strengths, the merged entity can achieve a competitive advantage and drive innovation across the aerospace and defense industries. This collaborative integration should enable the merged entity to bring new and powerful technologies to the aerospace sector.
3. Operational Efficiency
The integration of Raytheon and Collins Aerospace presents a significant opportunity to achieve enhanced operational efficiency. This efficiency improvement stems from streamlining processes, eliminating redundancies, and leveraging economies of scale, all contributing to a more optimized and cost-effective operation. The successful realization of these efficiencies is crucial for the merged entity to achieve its financial objectives and maintain competitiveness in the aerospace and defense sectors.
- Supply Chain Optimization
Combining the supply chains of Raytheon and Collins Aerospace allows for improved negotiation power with suppliers, resulting in lower procurement costs. Streamlining the logistics and distribution networks also reduces transportation expenses and improves delivery times. This entails consolidating supplier contracts, standardizing procurement processes, and implementing advanced supply chain management technologies. For example, negotiating bulk discounts with raw material providers can lead to substantial cost savings. Improved supply chain coordination reduces lead times and minimizes inventory holding costs.
- Manufacturing Process Integration
Integrating manufacturing processes enables the adoption of best practices from both organizations, leading to improved production efficiency and reduced waste. This involves standardizing manufacturing processes, consolidating production facilities, and implementing lean manufacturing principles. An instance is adopting advanced automation technologies from one company to improve the production throughput of the other. Reduced defect rates and improved quality control are direct outcomes of integrated manufacturing processes.
- Administrative and Overhead Cost Reduction
Consolidating administrative functions, such as human resources, finance, and information technology, reduces overhead costs. This involves eliminating duplicate positions, streamlining administrative processes, and leveraging shared service centers. A practical illustration is consolidating IT infrastructure and support services, leading to significant cost savings. Reduced administrative overhead contributes directly to improved profitability.
- Research and Development Efficiencies
Integrating research and development efforts allows for the elimination of redundant projects and the sharing of knowledge and expertise. This fosters innovation and accelerates the development of new technologies. An example is combining research teams working on similar technologies, leading to more focused and productive R&D efforts. Streamlined R&D processes reduce development costs and accelerate time-to-market for new products.
The operational efficiencies achieved through the integration of Raytheon and Collins Aerospace are essential for maximizing the value of the merger. By carefully planning and executing the integration process, the merged entity can realize significant cost savings, improve productivity, and enhance its competitiveness in the global marketplace. This focus on operational effectiveness is an ongoing process, with continuous improvements being necessary to maintain a competitive edge.
4. Financial Performance
The financial performance following the Raytheon and Collins Aerospace merger is a critical indicator of the combination’s success. Positive financial results, such as increased revenue, improved profit margins, and enhanced shareholder value, validate the strategic rationale behind the merger. Conversely, lackluster or declining financial performance raises questions about the integration process, potential market synergies, and overall management effectiveness. The financial outcomes directly reflect the realization of projected cost savings, revenue enhancements, and operational efficiencies that were foundational to justifying the considerable investment and restructuring efforts associated with the merger. For instance, if the merged entity fails to achieve anticipated reductions in operating expenses or fails to capitalize on cross-selling opportunities within its expanded customer base, the financial performance will suffer, ultimately impacting investor confidence and long-term viability.
Key metrics to evaluate financial performance include revenue growth, operating income, earnings per share, and return on invested capital. Examining these metrics provides insight into the merger’s impact on the company’s overall profitability and efficiency. Tracking these figures over subsequent fiscal periods after the merger is essential for gauging the actual performance against initial projections. As an example, the merged entitys success in winning large defense contracts or securing significant commercial aerospace orders, and then efficiently executing them will translate directly into revenue and profitability improvements. Moreover, a decline in these metrics could indicate integration challenges, unforeseen market conditions, or increased competitive pressures, necessitating a reassessment of strategic objectives and operational strategies. The resulting financial data provide tangible evidence of the integration’s effectiveness and highlight areas requiring further attention.
In conclusion, financial performance serves as a vital feedback mechanism for assessing the effectiveness of the Raytheon and Collins Aerospace merger. It quantifies the realization of anticipated benefits and reveals any unforeseen challenges. Consistently monitoring and analyzing financial metrics, benchmarked against pre-merger performance and industry peers, offers crucial insights into the long-term sustainability and value creation potential of the combined entity. Positive financial performance provides validation of the strategic decision, while negative trends necessitate corrective actions to ensure the merger achieves its intended objectives. The financial outcomes, therefore, are not merely a retrospective report but also a vital tool for steering the organization toward future success.
5. Regulatory Oversight
Regulatory oversight plays a crucial role in mergers and acquisitions, particularly in industries as sensitive as aerospace and defense. The combination of Raytheon and Collins Aerospace, therefore, underwent intense scrutiny by various regulatory bodies to ensure compliance with antitrust laws, national security concerns, and other relevant regulations. This oversight aimed to safeguard competition, protect national interests, and maintain fair market practices.
- Antitrust Review
Antitrust agencies, such as the Department of Justice (DOJ) in the United States and the European Commission, examined the merger’s potential impact on competition. Their review focused on whether the merger would create a monopoly or significantly reduce competition in specific product markets, leading to higher prices or reduced innovation. As an example, regulators may have analyzed whether the combined entity would dominate markets for specific types of avionics equipment or defense systems. The implications of an unfavorable review could include required divestitures or conditions on the merger’s approval to mitigate anticompetitive effects.
- National Security Considerations
Given the involvement of Raytheon and Collins Aerospace in defense-related activities, national security agencies assessed the merger’s potential impact on sensitive technologies and defense capabilities. The review considered whether the merger would create vulnerabilities in the supply chain, compromise classified information, or give foreign entities undue access to critical technologies. An instance of this oversight involves scrutiny of the merged entity’s dealings with foreign governments or its handling of classified defense contracts. Any security concerns identified could result in restrictions on technology transfer or other measures to protect national interests.
- Export Control Compliance
Both Raytheon and Collins Aerospace are subject to export control regulations, such as the International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) in the United States. The merger required careful attention to ensure continued compliance with these regulations, preventing the unauthorized export of controlled technologies and defense articles. This involved reviewing the merged entity’s export control procedures, training employees on compliance requirements, and implementing measures to prevent violations. A compliance failure could result in substantial fines, penalties, and restrictions on export privileges.
- Contractual Obligations
The merger also triggered a review of existing contracts with government agencies and commercial customers. These contracts often contain provisions addressing mergers and acquisitions, requiring notification, consent, or other actions. Failure to comply with these contractual obligations could result in breaches of contract or termination of agreements. An example would be a government contract requiring prior approval of any change in ownership or control of the contractor. Contract reviews were necessary to ensure a smooth transition and avoid any disruptions in ongoing programs.
The regulatory oversight surrounding the Raytheon and Collins Aerospace merger demonstrates the complexities and sensitivities involved in consolidating major players within the aerospace and defense sectors. The scrutiny aimed to balance the potential benefits of the merger, such as increased efficiency and innovation, with the need to protect competition, national security, and compliance with applicable regulations. Successful navigation of this regulatory landscape was essential for the merger to proceed and for the merged entity to operate effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following addresses common inquiries concerning the integration of Raytheon and Collins Aerospace, providing concise and objective responses.
Question 1: What was the primary rationale behind the Raytheon and Collins Aerospace merger?
The core justification centered on achieving greater scale and diversification in the aerospace and defense industries. The combination was projected to yield cost synergies, enhance technological capabilities, and improve competitiveness in a global market.
Question 2: How did the merger affect the competitive landscape within the aerospace and defense sectors?
The merger resulted in increased market consolidation, with the combined entity possessing a larger market share and greater influence. This consolidation reduced the number of independent competitors capable of offering comprehensive solutions, thereby altering the competitive dynamics within the industry.
Question 3: What were the major regulatory hurdles encountered during the merger process?
Regulatory agencies conducted thorough antitrust reviews to assess the potential impact on competition. These reviews focused on potential monopolies or undue market dominance. Export control regulations and national security concerns also necessitated careful compliance and scrutiny.
Question 4: What steps were taken to integrate the technologies and operations of Raytheon and Collins Aerospace?
Integration efforts involved streamlining supply chains, standardizing manufacturing processes, and consolidating administrative functions. Technological integration focused on combining complementary capabilities in areas such as avionics, sensors, and cybersecurity.
Question 5: How was the financial performance of the merged entity evaluated following the integration?
Financial performance was assessed through key metrics such as revenue growth, operating income, earnings per share, and return on invested capital. These metrics were compared against pre-merger performance and industry benchmarks to gauge the success of the integration.
Question 6: What was the impact of the merger on employees of both Raytheon and Collins Aerospace?
The merger involved workforce adjustments, including consolidation of roles and potential layoffs. Efforts were made to retain key talent and provide employees with opportunities within the combined organization.
In summary, the integration of Raytheon and Collins Aerospace represents a complex undertaking with far-reaching implications for the aerospace and defense industries. The merger’s success hinges on effective integration, adherence to regulatory requirements, and sustained financial performance.
The following section will provide concluding remarks on the combined entity and its future outlook.
Conclusion
The preceding analysis has presented a multifaceted examination of the combination of Raytheon and Collins Aerospace. Key points discussed include the market consolidation resulting from the union, the potential for technological synergy between the two entities, and the challenges of achieving operational efficiency through integration. Also crucial were the consideration of financial performance metrics and the navigation of regulatory oversight.
The long-term implications of the Raytheon and Collins Aerospace merger remain to be fully realized. Continued observation and analysis are warranted to assess the true impact on the aerospace and defense landscape. Stakeholders must remain cognizant of evolving market dynamics, technological advancements, and regulatory changes to effectively adapt to the new industry environment and foster future success.


![U.S. Hubs: Collins Aerospace US Locations Guide [2024] Innovating the Future of Flight with Reliable Aviation Solutions U.S. Hubs: Collins Aerospace US Locations Guide [2024] | Innovating the Future of Flight with Reliable Aviation Solutions](https://mixaerospace.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/03/th-97-300x200.jpg)

![Collins Aerospace Holiday Schedule: [Year] Dates & Guide Innovating the Future of Flight with Reliable Aviation Solutions Collins Aerospace Holiday Schedule: [Year] Dates & Guide | Innovating the Future of Flight with Reliable Aviation Solutions](https://mixaerospace.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/03/th-71-300x200.jpg)

