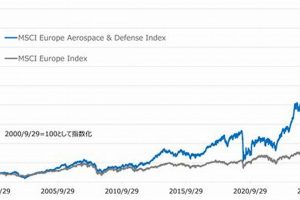
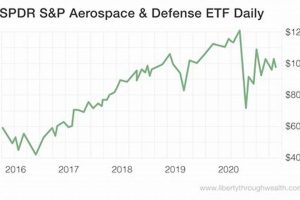
The leading entities in the global aerospace and defense sector comprise a group of corporations distinguished by their substantial revenue, technological innovation, and market share. These organizations are pivotal in developing and manufacturing a wide array of products and services, ranging from commercial aircraft and military hardware to advanced electronic systems and space exploration technologies. Rankings are typically determined by annual revenue derived from aerospace and defense-related activities.
The significance of these major players extends beyond mere economic value. They drive technological advancements in materials science, propulsion systems, and cybersecurity, which often have spillover effects into other industries. Historically, these companies have played a crucial role in national security, economic growth, and scientific exploration. Their performance is often a barometer of global geopolitical trends and investment climates.
The subsequent analysis will delve into factors influencing the standings of dominant firms within the aerospace and defense landscape, exploring key trends and strategic considerations shaping the future of the industry.
Strategic Insights from Leading Aerospace and Defense Firms
The practices of the top companies in the aerospace and defense sector offer valuable insights for businesses seeking to improve performance and maintain a competitive edge. These insights span strategic investments, operational efficiencies, and talent management.
Tip 1: Prioritize Research and Development: Sustained investment in R&D is crucial for maintaining technological superiority. Companies should allocate resources strategically to emerging technologies and disruptive innovations. Example: Developing advanced drone technology or hypersonic propulsion systems.
Tip 2: Foster Strategic Partnerships: Collaboration with other companies, research institutions, and government agencies allows for risk-sharing and access to diverse expertise. Example: Joint ventures for developing new aircraft components or cybersecurity solutions.
Tip 3: Implement Robust Supply Chain Management: Efficient and resilient supply chains are essential for mitigating disruptions and controlling costs. Diversification of suppliers and the adoption of advanced tracking technologies are key. Example: Ensuring multiple sources for critical raw materials or implementing blockchain technology for supply chain transparency.
Tip 4: Emphasize Cybersecurity: Protecting sensitive data and critical infrastructure from cyber threats is paramount. Companies must invest in cybersecurity expertise, implement stringent security protocols, and conduct regular vulnerability assessments. Example: Employing advanced threat detection systems and conducting penetration testing.
Tip 5: Cultivate a Highly Skilled Workforce: Attracting, retaining, and developing top talent is essential for driving innovation and maintaining a competitive advantage. Investment in training programs, employee development, and competitive compensation packages is crucial. Example: Establishing apprenticeship programs or offering tuition reimbursement for advanced degrees.
Tip 6: Focus on International Expansion: Expanding into new markets allows for revenue diversification and access to new opportunities. Companies should carefully assess market conditions and tailor their products and services to meet local needs. Example: Establishing manufacturing facilities or sales offices in emerging economies.
These insights highlight the importance of strategic investments, robust operational practices, and a commitment to innovation within the aerospace and defense industry.
The final section will summarize key takeaways and offer concluding thoughts on the future of these major organizations.
1. Revenue Generation
Revenue generation stands as a foundational pillar for any corporation aspiring to be recognized among the top echelon within the aerospace and defense industries. The capacity to consistently generate substantial revenue is both a consequence of, and a prerequisite for, maintaining a leading position. High revenue allows these entities to fund extensive research and development, acquire cutting-edge technologies, and expand their global footprint. A direct correlation exists: higher revenue enables further investment, which in turn fuels innovation and market penetration, leading to sustained or increased revenue streams. For example, Lockheed Martin’s consistent revenue growth, driven by substantial defense contracts, enables the company to invest heavily in developing advanced technologies like hypersonic weapons and next-generation aircraft. This investment subsequently positions them to secure further lucrative contracts, creating a self-reinforcing cycle.
The practical importance of understanding this connection lies in evaluating the long-term viability and competitive strength of these companies. Revenue diversitythe degree to which revenue streams are not solely dependent on a single product or marketis another critical consideration. Companies with diversified revenue sources are better positioned to weather economic downturns or shifts in geopolitical landscapes. Boeing’s commercial aircraft division, for instance, provides a counterweight to its defense business, mitigating risks associated with fluctuating defense budgets. Furthermore, revenue generation strategies often dictate a company’s operational focus, influencing decisions related to mergers and acquisitions, strategic partnerships, and geographic expansion.
In summary, revenue generation is not merely a financial metric; it represents a strategic imperative that shapes the trajectory of corporations within the aerospace and defense industries. Sustained revenue allows for innovation, expansion, and resilience, all essential components of maintaining a top-tier position. Monitoring and analyzing revenue streams, along with understanding their underlying drivers, provides critical insights into the long-term prospects and competitive advantages of these key players.
2. Technological Innovation
Technological innovation serves as the lifeblood of success and competitiveness for entities vying for recognition among the leading aerospace and defense corporations. These entities operate in an environment characterized by continuous technological advancements, demanding perpetual research, development, and implementation of cutting-edge solutions to maintain an advantage.
- Advanced Materials Science
The development and application of novel materials, such as lightweight composites and high-temperature alloys, is paramount for enhancing aircraft performance and durability. For instance, the utilization of carbon fiber reinforced polymers in modern aircraft structures reduces weight, thereby improving fuel efficiency and extending operational range. This has direct implications for companies like Boeing and Airbus, as they strive to create more efficient and environmentally friendly aircraft. The application extends to defense firms as well, where advanced materials enhance the survivability of military vehicles and aircraft against threats.
- Autonomous Systems and Robotics
The integration of autonomous systems and robotics is revolutionizing aerospace and defense operations. From unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) for surveillance and reconnaissance to autonomous systems for manufacturing and maintenance, these technologies enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve safety. Northrop Grumman, for example, has developed advanced UAVs for military applications, while companies like General Atomics are pioneering autonomous drone technology for various purposes, including border patrol and infrastructure inspection. The increasing reliance on autonomy necessitates robust cybersecurity measures to protect against potential threats.
- Digital Transformation and Data Analytics
The adoption of digital technologies, including artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and big data analytics, is enabling companies to optimize operations, improve decision-making, and enhance product performance. Predictive maintenance, powered by AI and ML, allows for early detection of equipment failures, minimizing downtime and reducing maintenance costs. Furthermore, data analytics enables companies to gain insights into customer needs and market trends, facilitating the development of more targeted and effective products and services. Lockheed Martin, for example, utilizes data analytics to optimize supply chain management and improve manufacturing processes.
- Next-Generation Propulsion Systems
The development of advanced propulsion systems is critical for enhancing aircraft speed, range, and efficiency. Research into hypersonic propulsion, electric propulsion, and alternative fuels is gaining momentum, with the potential to revolutionize air travel and military operations. Companies like Raytheon Technologies are investing in hypersonic technologies for missile systems, while others are exploring electric propulsion for commercial aircraft. The successful development and implementation of these technologies will provide a significant competitive advantage.
These facets collectively highlight the critical role of technological innovation in shaping the competitive landscape within the aerospace and defense industries. The ability to consistently develop and implement cutting-edge technologies is essential for maintaining a leading position, securing lucrative contracts, and driving long-term growth. By focusing on advanced materials, autonomous systems, digital transformation, and next-generation propulsion, these entities can unlock new opportunities and address emerging challenges in an ever-evolving global market.
3. Global Presence
Global presence is a defining characteristic of leading firms in the aerospace and defense sector, intrinsically linked to their status as top-tier organizations. A broad international footprint provides access to diverse markets, talent pools, and technological resources, fostering revenue diversification and mitigating risks associated with regional economic or political instability. Moreover, establishing a presence in key strategic locations enables closer collaboration with international partners, including governments and other industry stakeholders. This cooperation is crucial for securing defense contracts, participating in multinational projects, and maintaining a competitive edge in the global arena. Companies such as Boeing, Lockheed Martin, and Airbus exemplify this trend, with manufacturing facilities, research centers, and sales offices strategically positioned across multiple continents. These investments demonstrate a commitment to local markets and facilitate access to international expertise and innovation.
The expansion of global operations also presents opportunities for knowledge transfer and technology sharing between different regions, fostering innovation and efficiency improvements across the organization. For instance, a company may leverage advanced manufacturing techniques developed in one location to enhance production processes in another. Furthermore, a robust global presence enables companies to navigate complex regulatory landscapes and comply with international standards, ensuring market access and operational efficiency. This is particularly relevant in the aerospace and defense industries, where strict regulatory requirements and compliance standards govern product development, manufacturing, and export controls. Companies like BAE Systems have successfully navigated these challenges by establishing strong relationships with local authorities and adapting their operations to meet specific regional requirements.
In summary, global presence is not merely a geographical expansion but a strategic imperative for leading aerospace and defense firms. It enables revenue diversification, access to talent and technology, enhanced collaboration with international partners, and improved operational efficiency. While challenges associated with managing global operations exist, the benefits derived from a strong international footprint are essential for maintaining a competitive edge and securing long-term growth in an increasingly interconnected global market. The capacity to effectively manage and leverage global resources is a key differentiator for those seeking to attain and sustain a position among the elite in this industry.
Market share serves as a critical indicator of a company’s competitive position and overall success, particularly within the intensely competitive aerospace and defense sector. For the established entities recognized as leading organizations, robust market share reflects effective strategies, technological prowess, and a strong reputation. It also determines their influence on industry standards and their ability to secure future contracts.
- Defense Contracts and Government Influence
A significant portion of market share for organizations in the aerospace and defense sector is directly correlated to the acquisition of defense contracts from various governments globally. The ability to secure these contracts hinges on factors such as technological superiority, cost-effectiveness, and established relationships with government agencies. Lockheed Martin’s dominance in military aircraft and missile systems provides a clear example. Securing a major defense contract not only ensures substantial revenue but also enhances a company’s reputation and strengthens its market position, making it more attractive for future opportunities.
- Commercial Aerospace Dominance
In the commercial aerospace segment, market share is often dictated by the ability to design, manufacture, and deliver reliable and efficient aircraft. Boeing and Airbus, for instance, are prominent players, competing fiercely for orders from airlines worldwide. Factors such as fuel efficiency, passenger capacity, and technological innovation play crucial roles in airlines’ purchasing decisions. A larger market share in commercial aviation translates to increased revenue, enhanced brand recognition, and greater influence on industry standards related to aircraft design and safety.
- Technological Innovation and Product Differentiation
Companies that consistently invest in research and development and introduce innovative products and services are better positioned to capture and maintain market share. Technological advancements can lead to product differentiation, creating a competitive edge and attracting customers seeking cutting-edge solutions. Raytheon Technologies’ focus on advanced radar systems and missile defense technologies exemplifies this approach. By developing and deploying innovative solutions, companies can secure lucrative contracts and solidify their position within the aerospace and defense market.
- Mergers, Acquisitions, and Strategic Alliances
Market share can also be significantly impacted by strategic decisions such as mergers, acquisitions, and alliances. These actions can enable companies to expand their product portfolios, gain access to new technologies, and enter new markets. The merger between Raytheon and United Technologies, for example, created a diversified aerospace and defense conglomerate with a larger market share and a broader range of capabilities. Strategic alliances can also enable companies to pool resources and expertise, allowing them to compete more effectively against larger rivals.
These facets underscore the multifaceted nature of market share within the context of leading aerospace and defense organizations. Maintaining and expanding market share requires a combination of technological innovation, strategic relationships, and effective operational management. Ultimately, a strong market share reflects a company’s ability to adapt to changing market dynamics, meet customer needs, and maintain a competitive edge in the global aerospace and defense landscape.
5. Defense Contracts
The acquisition and successful execution of defense contracts are paramount for entities seeking or maintaining a position within the top tier of aerospace and defense organizations. These contracts, awarded by governments and military agencies, represent a substantial source of revenue, drive technological innovation, and shape strategic priorities. The ability to consistently secure and fulfill these contracts is a key differentiator between industry leaders and their competitors.
- Revenue Generation and Financial Stability
Defense contracts provide a predictable and often substantial revenue stream, contributing significantly to the financial stability of these companies. The long-term nature of many contracts allows for strategic financial planning and investment in research and development. Lockheed Martin’s consistent revenue from contracts related to the F-35 fighter jet program exemplifies this. This sustained income stream facilitates the development of advanced technologies and fuels further growth.
- Technological Advancement and Innovation
Defense contracts often stipulate the development of cutting-edge technologies and innovative solutions. These requirements drive companies to invest heavily in research and development, pushing the boundaries of aerospace and defense capabilities. The U.S. Department of Defense’s contracts for hypersonic weapons development, for example, are spurring companies to pioneer new materials, propulsion systems, and guidance technologies. This fosters innovation and enhances the overall technological competitiveness of these organizations.
- Geopolitical Influence and Strategic Partnerships
The awarding of defense contracts often carries significant geopolitical implications. Securing a major contract can strengthen a company’s relationship with a particular government or military agency, leading to further opportunities and strategic partnerships. BAE Systems’ involvement in various international defense programs illustrates this point. These partnerships foster collaboration and knowledge sharing, enhancing the company’s global influence and market reach.
- Employment and Economic Impact
Defense contracts create significant employment opportunities, both directly within the contracting company and indirectly through its supply chain. These contracts contribute to local and national economies by generating jobs and supporting related industries. Boeing’s defense contracts, for example, support thousands of jobs across multiple states, stimulating economic growth and technological development within those regions. The economic impact of these contracts extends beyond the immediate financial benefits, fostering long-term stability and innovation.
In essence, defense contracts are more than just revenue sources; they are strategic instruments that shape the technological trajectory, geopolitical influence, and economic impact of the leading aerospace and defense firms. The ability to successfully navigate the complex landscape of defense contracting is a hallmark of top-tier status in this industry, influencing both present-day performance and future prospects.
6. Aerospace Engineering
Aerospace engineering serves as a cornerstone for the leading entities within the aerospace and defense sector. It is the applied science and technology focused on the design, development, testing, and production of aircraft, spacecraft, and related systems. The capabilities and innovations stemming from aerospace engineering departments directly determine a company’s competitive advantage, its ability to secure lucrative contracts, and its overall position among the top organizations. The expertise of aerospace engineers is essential in every phase, from initial concept design and simulations to prototyping, testing, and ultimately, the manufacturing and deployment of aerospace products. For instance, Boeing’s ability to develop fuel-efficient commercial aircraft, like the 787 Dreamliner, is a direct result of advanced aerospace engineering principles applied to aerodynamics, materials science, and propulsion systems.
The importance of aerospace engineering is underscored by the considerable investment these companies allocate to research and development (R&D) within this discipline. Advanced simulation tools, wind tunnels, and testing facilities represent substantial financial commitments, reflecting the recognition that engineering prowess translates directly into market leadership. Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works, renowned for developing groundbreaking aircraft like the SR-71 Blackbird and the F-117 Nighthawk, exemplifies the importance of specialized engineering teams and cutting-edge R&D in achieving technological superiority. Furthermore, the increasing demand for sustainable aviation fuels and electric propulsion systems necessitates continuous innovation in aerospace engineering, driving collaborative efforts between companies, research institutions, and government agencies to achieve ambitious environmental targets.
In summary, the connection between aerospace engineering and the standing of top-tier aerospace and defense firms is undeniable. Aerospace engineering isn’t simply a component of these organizations; it’s the driving force behind their innovations, product development, and competitive advantage. Continuous investment in this field, fostering specialized expertise, and promoting research collaborations are crucial for any company aspiring to lead in the global aerospace and defense landscape. The success of these companies is inextricably linked to their capacity to attract, retain, and empower talented aerospace engineers to address the ever-evolving challenges of flight and space exploration.
Frequently Asked Questions about Leading Aerospace and Defense Corporations
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the major players within the aerospace and defense industries, providing factual and insightful answers to enhance understanding of this complex sector.
Question 1: What criteria define a corporation as belonging to the “top 10 aerospace and defense companies”?
Ranking typically relies on annual revenue derived from aerospace and defense-related activities. Additional factors considered include market share, technological innovation, and contract volume.
Question 2: How do these companies contribute to national security?
They develop and manufacture advanced military hardware, weapon systems, and defense technologies, supporting national defense strategies and safeguarding critical infrastructure.
Question 3: What role do these companies play in technological advancements?
They invest heavily in research and development, pioneering innovations in materials science, propulsion systems, cybersecurity, and other critical areas, often with spillover effects into civilian industries.
Question 4: How do these companies manage international collaborations and partnerships?
Strategic alliances and partnerships are vital for accessing diverse expertise, sharing risks, and securing access to international markets. These collaborations often involve joint ventures and technology transfer agreements.
Question 5: What are the ethical considerations for these companies given their involvement in defense activities?
Ethical considerations are paramount, involving responsible arms trading, adherence to international laws, and a commitment to minimizing unintended consequences of military technology.
Question 6: How do fluctuating geopolitical landscapes impact the financial performance of these corporations?
Geopolitical instability and changing defense budgets can significantly impact contract opportunities and revenue streams. Companies must adapt their strategies and diversify their portfolios to mitigate these risks.
In summary, understanding the factors defining industry leaders, their impact on national security and technological progress, and the ethical considerations they face is crucial for a comprehensive perspective on these important corporations.
The subsequent section will provide concluding thoughts regarding the top corporations and their future in this area.
Analysis of Leading Aerospace and Defense Entities
The preceding exploration has detailed critical attributes defining the top 10 aerospace and defense companies: revenue generation, technological innovation, global presence, market share, defense contracts, and aerospace engineering proficiency. These elements underscore the multifaceted nature of industry leadership, demanding not only financial strength but also a commitment to research, strategic partnerships, and global market penetration.
Sustained success in this sector requires continuous adaptation, ethical conduct, and vigilance in navigating a dynamic geopolitical landscape. Further analysis of these corporations’ strategic choices will serve to inform policy decisions and foster a deeper understanding of an industry vital to global security and technological advancement.