Positions within the aeronautics and space sector located in the Kingdom of Spain encompass a diverse range of occupations. These roles span engineering, manufacturing, research, and management, all contributing to the design, development, and maintenance of aircraft, spacecraft, and related technologies within the specific geographic region. For example, an aerospace engineer in Madrid might be involved in designing the next generation of commercial aircraft wings, while a technician in Seville could be assembling components for a satellite.
The presence of these employment opportunities fosters technological advancement, economic growth, and skilled workforce development within the nation. Historically, Spain has positioned itself as a significant player in the European aerospace industry, leveraging strategic partnerships and government investment to cultivate a robust sector. This involvement generates high-value employment, stimulates innovation, and contributes to the country’s overall competitiveness in the global market.
The following sections will delve into specific areas such as prominent companies involved, necessary qualifications, regional hubs for the industry, and resources for individuals seeking career paths in this dynamic field within the Iberian Peninsula.
Strategic Approaches to Securing Opportunities in the Spanish Aeronautics and Space Sector
The following guidance provides actionable strategies for individuals seeking professional integration within the Spanish aeronautics and space domain. These recommendations emphasize proactive preparation and targeted engagement.
Tip 1: Cultivate Relevant Expertise: A foundational step involves acquiring specialized knowledge and skills applicable to the field. This may include pursuing advanced degrees in aerospace engineering, mechanical engineering, or related disciplines. Furthermore, obtaining certifications in areas such as CAD/CAM software, project management, or specific aerospace technologies can enhance candidate profiles.
Tip 2: Enhance Linguistic Proficiency: Given the location-specific nature, fluency in Spanish is often a prerequisite for successful integration. Actively develop language skills through formal courses, immersion programs, or language exchange partnerships. The ability to communicate effectively with local colleagues and stakeholders is critical for collaboration and career advancement.
Tip 3: Target Key Employers: Identify leading companies and research institutions operating within the sector in Spain. Research their specific activities, projects, and technological focus areas. Tailor applications and cover letters to demonstrate a clear understanding of their needs and how individual skills align with their organizational goals. Airbus Spain, Indra, and the Spanish National Institute of Aerospace Technology (INTA) represent potential targets.
Tip 4: Network Strategically: Attend industry conferences, trade shows, and professional events in Spain to build connections with industry professionals. Join relevant professional organizations such as the Spanish Association of Aerospace Engineers (COIAE). Networking can provide valuable insights into unadvertised opportunities and facilitate introductions to hiring managers.
Tip 5: Leverage Online Platforms: Utilize online job boards, professional networking sites (e.g., LinkedIn), and company career pages to identify and apply for suitable vacancies. Optimize online profiles to highlight relevant skills, experience, and qualifications. Actively engage in industry-related discussions and groups to demonstrate knowledge and build professional visibility.
Tip 6: Consider Internships and Entry-Level Programs: Participate in internships or entry-level training programs offered by aerospace companies in Spain. These programs provide valuable hands-on experience, mentorship opportunities, and potential pathways to full-time employment. Many universities and technical colleges have partnerships with aerospace firms to facilitate student placements.
Tip 7: Understand Spanish Labor Laws and Regulations: Familiarize yourself with the legal requirements for working in Spain, including visa regulations, work permits, and employment contracts. Seek advice from immigration lawyers or employment agencies to ensure compliance with all applicable laws and regulations.
By prioritizing relevant education, language skills, targeted networking, and a thorough understanding of the Spanish labor market, individuals can significantly enhance their prospects of securing coveted positions.
The subsequent sections will explore common challenges encountered by job seekers and offer additional resources for career development.
1. Engineering Specializations
The availability and nature of positions are fundamentally shaped by the breadth and depth of specialized engineering expertise within the sector. Specific engineering disciplines serve as the foundation upon which various roles are built. For example, a structural engineer with expertise in composite materials may find opportunities in aircraft design or manufacturing, contributing to lighter and more fuel-efficient aircraft. Similarly, avionics engineers are essential for developing and integrating the complex electronic systems that control flight, navigation, and communication in modern aircraft and spacecraft. The demand for each specialization fluctuates depending on current industry trends, ongoing projects, and emerging technologies. A surge in unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) development, for instance, would likely increase the need for engineers specializing in autonomous systems, robotics, and sensor technology.
Furthermore, the concentration of specific engineering skills in certain regions of Spain can influence the geographical distribution of positions. Areas with established aerospace manufacturing facilities, such as Seville, often require a higher concentration of manufacturing engineers, quality control specialists, and process optimization experts. Research-intensive locations, such as those near universities or research institutions, may foster a greater demand for research engineers specializing in areas like aerodynamics, propulsion, or materials science. The practical application of specialized engineering knowledge is therefore critical to driving innovation and maintaining competitiveness in the Spanish aerospace industry.
In summary, specialized engineering expertise forms a critical component of positions, determining the skill sets required, the geographical distribution of employment, and the overall direction of technological advancement. Recognizing the demand for specific skills and proactively developing expertise in high-growth areas is paramount for individuals seeking to enter or advance within the Spanish aerospace sector. Continuous adaptation to technological changes ensures the sustained relevance of engineering talent in this dynamic industry.
2. Manufacturing Expertise
Manufacturing expertise constitutes a critical element in the landscape. The capability to efficiently and precisely produce components, systems, and complete aircraft underpins the viability and competitiveness of firms operating within the Spanish aerospace domain. This expertise encompasses a range of specialized skills, including machining, assembly, quality control, and supply chain management, each directly impacting production efficiency, product quality, and adherence to stringent industry standards. A real-world example can be observed in Airbus Spain’s production facilities, where specialized technicians and engineers employ advanced manufacturing techniques to produce aircraft components for global programs. Their expertise not only fulfills existing orders but also contributes to the companys long-term strategic objectives.
The availability of skilled manufacturing personnel, particularly those proficient in areas such as composite materials processing, precision engineering, and automated assembly systems, directly influences the ability to attract investment and secure high-value contracts. Spain’s capacity to deliver high-quality aerospace products depends heavily on its capacity to cultivate and retain a workforce equipped with the requisite manufacturing skills. Furthermore, effective manufacturing expertise necessitates rigorous adherence to quality management systems (QMS) and compliance with international aerospace standards (e.g., AS9100). This guarantees product integrity, safety, and conformance to customer specifications, further strengthening the nation’s standing within the global market.
In conclusion, expertise forms an essential cornerstone of the industry. Competency in manufacturing processes is directly linked to the creation and sustenance of high-skilled roles, contributing significantly to the countrys economic prosperity and technological advancement. Addressing challenges related to skills gaps, promoting training initiatives, and investing in advanced manufacturing technologies remain crucial for maintaining a competitive edge and solidifying Spain’s position as a prominent player in the international arena.
3. Research opportunities
Research opportunities within the aerospace sector in Spain are intrinsically linked to the creation and advancement of related professional roles. These opportunities span a spectrum of scientific and technological domains, driving innovation and fostering the development of a highly skilled workforce. The presence and funding of research initiatives directly influence the availability and nature of employment within the industry.
- Materials Science and Engineering
Research in this area focuses on developing advanced materials with enhanced strength-to-weight ratios, thermal resistance, and corrosion protection. For example, research into new composite materials or alloys can lead to employment in material testing, characterization, and manufacturing process development. The successful integration of these materials into aircraft components or spacecraft structures directly necessitates skilled engineers and technicians for production and maintenance.
- Aerodynamics and Flight Control
Aerodynamic research explores ways to improve aircraft efficiency, reduce drag, and enhance maneuverability. These studies may involve computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations, wind tunnel testing, and flight experiments. The results of this research can translate into improvements in aircraft design, fuel consumption, and overall performance, generating new roles in aircraft design, flight testing, and control systems development.
- Propulsion Systems
Research and development in propulsion systems concentrate on improving engine efficiency, reducing emissions, and exploring alternative fuels. This area encompasses jet engines, rocket engines, and electric propulsion systems. Advancements in propulsion technology lead to opportunities in engine design, testing, and maintenance, as well as in the development of sustainable aviation technologies.
- Space Technologies
Research in space technologies encompasses a broad range of areas, including satellite communication, remote sensing, and space exploration. The development of new satellite technologies, such as advanced imaging systems or communication payloads, creates roles in satellite design, manufacturing, launch operations, and data analysis. Furthermore, the exploration of new space missions and technologies fosters opportunities in robotics, autonomous systems, and spacecraft engineering.
These research activities serve as a catalyst for innovation and economic growth within the industry. The translation of research findings into practical applications requires a skilled workforce capable of developing, implementing, and maintaining advanced technologies. The presence of robust research programs attracts talent, stimulates investment, and positions Spain as a competitive player in the global aerospace market. Therefore, the investment and promotion of research opportunities are vital for the continued growth and prosperity of the professional landscape.
4. Geographic Distribution
The geographic distribution of activities significantly influences the availability and nature of opportunities within the aeronautics and space sector in Spain. Specific regions have emerged as centers of excellence due to historical factors, strategic investments, and the concentration of key industry players.
- Andalusia (Seville and Cdiz)
This region serves as a primary hub for aircraft manufacturing, particularly related to Airbus Defence and Space activities. Positions here often involve structural assembly, composite materials processing, and systems integration. This concentration necessitates a workforce skilled in aerospace engineering, manufacturing processes, and quality control. The implications are that job seekers with these skills are more likely to find opportunities within this specific geographic area.
- Madrid Metropolitan Area (Madrid and Getafe)
The Madrid area functions as a center for engineering design, research and development, and corporate headquarters. Positions in this region tend to be focused on aircraft design, systems engineering, and program management. This concentration attracts highly skilled engineers and researchers, creating a competitive environment. The presence of major universities and research institutions further supports this concentration, fostering a talent pipeline.
- Basque Country (Zamudio)
The Basque Country possesses a strong industrial base and has developed capabilities in aerospace components manufacturing and advanced materials. Positions in this region are often linked to precision machining, tooling, and supply chain management. The implications are that individuals with expertise in these areas can find opportunities within the region’s network of aerospace suppliers and manufacturers.
- Castilla-La Mancha (Illescas)
The Illescas region is a growing hub with an increasing number of aerospace manufacturing and maintenance activities. Positions available may cover aircraft maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO), as well as aircraft manufacturing processes. This offers chances for technicians and engineers specialized in this industry sector.
The geographic concentration of activities directly impacts career prospects. Understanding regional specializations enables job seekers to target their efforts and align their skills with specific industry needs. This knowledge is critical for optimizing job search strategies and maximizing the likelihood of securing a desirable position.
5. Required Qualifications
The availability and accessibility of positions within the aeronautics and space sector in Spain are intrinsically linked to specific qualifications. These prerequisites serve as gatekeepers, determining candidate eligibility and influencing the overall composition of the workforce. A direct causal relationship exists between possessing the necessary credentials and securing gainful employment within the industry. For example, most engineering roles mandate a degree in aerospace, mechanical, or electrical engineering from an accredited university. Furthermore, specialized positions in areas such as avionics or composite materials often require advanced degrees or professional certifications demonstrating expertise in these specific domains. The absence of these fundamental requirements invariably precludes an individual from consideration for relevant openings. This is due to both regulatory requirements and internal standards of professional competence.
The significance of these qualifications extends beyond mere symbolic value; they directly impact the quality, safety, and reliability of aerospace products and services. Consider the role of a licensed aircraft maintenance engineer. This professional’s certification is not merely a formality but a legal and practical necessity to ensure the safe operation and maintenance of aircraft. Similarly, quality control personnel require certifications demonstrating proficiency in inspection techniques and adherence to industry standards such as AS9100. The presence of a qualified workforce directly contributes to the overall competitiveness of the Spanish aerospace sector, attracting international partnerships and fostering innovation. Companies investing in this sector require assurances that the local workforce possesses the necessary skills and credentials to meet stringent quality and safety requirements.
In conclusion, the attainment of relevant qualifications represents a critical pathway into the aeronautics and space sector in Spain. These prerequisites not only enhance individual employability but also contribute to the broader success and sustainability of the industry. Addressing skills gaps through targeted training programs and promoting access to higher education in relevant fields remains essential for maintaining a skilled and competitive workforce. The continued emphasis on professional development and certification reinforces Spain’s standing as a significant participant in the global aerospace arena.
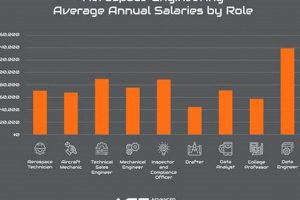
6. Salary expectations
Remuneration considerations form a crucial aspect of assessing the attractiveness and viability of employment opportunities within the Spanish aeronautics and space sector. These expectations are shaped by a complex interplay of factors including experience, qualifications, specialization, and geographical location.
- Experience Level
Entry-level positions typically command lower salaries compared to roles requiring several years of relevant experience. An engineer with less than three years of experience can expect a significantly different compensation package compared to a senior engineer with a decade or more of experience leading complex projects. The specific gap will also depend on the size and type of organization, with larger multinational corporations often offering more competitive entry-level salaries than smaller, local firms.
- Academic Qualifications and Specializations
Advanced degrees and specialized certifications typically correlate with higher earning potential. Possessing a doctorate in aerospace engineering, or holding a specialized certification in a niche area such as composite materials repair, can translate into a premium in the labor market. Furthermore, certain in-demand specializations, such as avionics engineering or cybersecurity within aerospace, may command higher salaries due to a relative scarcity of qualified professionals.
- Geographic Location within Spain
Salary levels can vary significantly across different regions of Spain. Major metropolitan areas such as Madrid and Barcelona, where the cost of living is generally higher, tend to offer more competitive salaries compared to smaller cities or rural areas. Furthermore, regions with a high concentration of aerospace activity, such as Andalusia, may experience localized variations in compensation due to the demand for specific skill sets.
- Company Size and Type
Multinational corporations typically offer more competitive compensation and benefits packages compared to smaller, local firms. Public sector organizations may also have different salary scales compared to private companies. The scope and complexity of projects undertaken by an organization also influence salary levels. Companies involved in cutting-edge research and development or large-scale manufacturing projects may be willing to pay more to attract top talent.
These factors interact to determine the salary landscape. Job seekers should conduct thorough research to understand prevailing salary norms for specific roles and regions. Resources such as industry surveys, online salary databases, and professional networking can provide valuable insights. Considering these expectations is paramount for both attracting and retaining skilled professionals, ensuring the continued growth and competitiveness of the Spanish aeronautics and space sector.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following section addresses common inquiries and provides clarification regarding employment within the Spanish aeronautics and space domain. This information aims to provide a factual overview to assist individuals in their career planning.
Question 1: What are the primary educational requirements for entry-level engineering positions?
A bachelor’s or master’s degree in aerospace engineering, mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, or a closely related field is generally required. Specific coursework relevant to the desired specialization (e.g., aerodynamics, structures, propulsion) is also highly recommended. Practical experience through internships or research projects can significantly enhance a candidate’s profile.
Question 2: Is fluency in Spanish a mandatory requirement for all positions?
While English proficiency is often sufficient for multinational corporations, fluency in Spanish is generally considered a significant advantage, and frequently a necessity, particularly for roles involving direct interaction with local stakeholders, suppliers, or regulatory agencies. Companies based solely in Spain typically require Spanish language skills.
Question 3: What are the most common certifications sought by employers in this industry?
Certifications demonstrating expertise in specific technologies or processes are highly valued. These may include certifications in CAD/CAM software, project management (e.g., PMP), quality management systems (e.g., AS9100), or specific aerospace standards. The relevance of specific certifications depends on the nature of the role and the company’s activities.
Question 4: Which regions of Spain offer the most employment opportunities?
Andalusia (Seville and Cdiz), the Madrid Metropolitan Area (Madrid and Getafe), and the Basque Country (Zamudio) are prominent hubs for activity, with varying specializations. Andalusia is primarily focused on manufacturing, Madrid on engineering and research, and the Basque Country on component manufacturing. Castilla-La Mancha (Illescas) is an emerging area focused on Maintenance, Repair and Overhaul (MRO) and manufacturing.
Question 5: How does the Spanish aerospace sector compare to other European countries?
Spain holds a significant position within the European industry, particularly in aircraft manufacturing and maintenance. The sector benefits from strategic investments, strong industry-government partnerships, and a skilled workforce. While other nations such as France and Germany may have larger overall aerospace sectors, Spain offers unique opportunities and specializations within specific domains.
Question 6: What are the key challenges facing individuals seeking to secure opportunities?
Common challenges include language barriers, a competitive job market, and the need for specialized skills and certifications. Adapting to the Spanish work culture and navigating the local labor laws also present hurdles. Proactive networking, continuous professional development, and targeted job search strategies are essential for overcoming these obstacles.
In summary, securing opportunities requires a combination of relevant education, specialized skills, linguistic proficiency, and proactive career planning. Understanding the specific requirements and dynamics of the Spanish market is crucial for success.
The following article provides insights and tips to excel aerospace interviews.
Aerospace Jobs in Spain
The preceding analysis has presented a comprehensive overview of positions within the Spanish aeronautics and space domain. The examination has underscored the critical role of specialized engineering expertise, advanced manufacturing capabilities, and robust research initiatives in shaping the landscape. Geographic distribution, required qualifications, and salary expectations have also been addressed, providing a multifaceted perspective for individuals navigating this professional sector.
The continued advancement of the Spanish industry necessitates a proactive approach to skills development and strategic investment in emerging technologies. A dedication to excellence and innovation is essential for maintaining a competitive edge and fostering sustained growth within this vital segment of the national economy. Stakeholders are encouraged to leverage the presented insights to inform future planning and contribute to the ongoing success of the Spanish endeavor.






![Top States: Best States for Aerospace Jobs in [Year] Innovating the Future of Flight with Reliable Aviation Solutions Top States: Best States for Aerospace Jobs in [Year] | Innovating the Future of Flight with Reliable Aviation Solutions](https://mixaerospace.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/th-441-300x200.jpg)