Positions for professionals skilled in the design, development, and testing of aircraft and spacecraft within the San Diego metropolitan area represent a specific segment of the engineering employment landscape. These roles typically involve applying principles of physics, mathematics, and engineering to create innovative solutions in aviation and space exploration. An example might include a structural engineer working on the next generation of unmanned aerial vehicles at a local defense contractor.
Opportunities in this sector contribute significantly to the regional economy, fostering technological advancement and providing high-skilled employment. San Diego’s history as a hub for aviation and defense industries has led to a concentration of companies and research institutions actively seeking qualified professionals. This concentration provides numerous avenues for career growth and specialization within the broader field.
The following sections will examine the specific industries employing these professionals in San Diego, the requisite skills and qualifications for securing such a role, and resources available for those seeking employment in this technically demanding and rewarding field. Further, it will elaborate on salary expectations and career trajectory for the aerospace industry in San Diego.
Tips for Securing Opportunities in the San Diego Aerospace Sector
The pursuit of a position in this competitive field requires strategic preparation and focused effort. The following tips offer guidance to those seeking to establish or advance their careers in the region’s aerospace industry.
Tip 1: Cultivate a Strong Academic Foundation: A bachelor’s or master’s degree in aerospace engineering, mechanical engineering, or a related field is generally required. Focus on coursework relevant to specific areas of interest, such as aerodynamics, propulsion, or structural analysis.
Tip 2: Gain Practical Experience Through Internships: Seek internship opportunities with local aerospace companies or research institutions. Practical experience demonstrates a commitment to the field and provides valuable hands-on training.
Tip 3: Develop Proficiency in Relevant Software and Tools: Familiarize yourself with industry-standard software packages such as CAD (Computer-Aided Design), CAE (Computer-Aided Engineering), and simulation tools. Proficiency in these technologies is highly valued by employers.
Tip 4: Network with Industry Professionals: Attend industry conferences, career fairs, and networking events to connect with potential employers and learn about available opportunities. Professional organizations can also provide valuable networking resources.
Tip 5: Tailor Your Resume and Cover Letter: Highlight relevant skills and experiences that align with the specific requirements of each position. Emphasize accomplishments and quantifiable results to demonstrate your capabilities.
Tip 6: Obtain Relevant Certifications: Consider obtaining certifications in specific areas of expertise, such as project management or systems engineering. Certifications can enhance credibility and demonstrate a commitment to professional development.
Tip 7: Research Target Companies Thoroughly: Before applying for positions, research the company’s history, products, and services. Understand their mission and values to demonstrate genuine interest during the interview process.
These strategies, when implemented thoughtfully, can significantly enhance an individual’s prospects within this competitive employment landscape. Consistent effort and proactive engagement are essential for navigating the intricacies of the San Diego aerospace sector.
The subsequent section will delve into the specifics of the application process, including resume optimization and interview preparation, to further equip job seekers with the necessary tools for success.
1. Defense Contractors
Defense contractors represent a primary source of employment opportunities for aerospace engineers within the San Diego region. These companies are instrumental in the research, development, and manufacturing of advanced aerospace and defense technologies, significantly shaping the local job market.
- Research and Development Activities
Defense contractors invest heavily in research and development, leading to a consistent demand for engineers specializing in areas such as aerodynamics, propulsion, and materials science. These activities directly translate into positions involving the design and testing of new aircraft, spacecraft, and related systems. For instance, companies involved in the development of advanced unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) frequently require engineers to optimize flight performance and integrate novel technologies.
- Manufacturing and Production
The manufacturing and production phases of aerospace projects also create numerous engineering positions. These roles focus on ensuring that designs are effectively translated into tangible products, involving tasks such as process optimization, quality control, and supply chain management. Specifically, engineers might be responsible for overseeing the assembly of aircraft components, implementing efficient manufacturing processes, and resolving technical challenges that arise during production.
- Systems Integration
Systems integration is a critical area where aerospace engineers are needed. This involves combining various components and subsystems into a cohesive and functional aerospace system. Engineers working in systems integration must possess a broad understanding of different engineering disciplines and be capable of troubleshooting complex interactions between systems. Examples include integrating communication systems into aircraft and ensuring seamless operation of avionics.
- Testing and Evaluation
Rigorous testing and evaluation are essential to validate the performance and reliability of aerospace systems. Defense contractors employ engineers to design and conduct tests, analyze data, and identify areas for improvement. These activities help to ensure that aerospace products meet stringent requirements and operate safely. Examples include conducting wind tunnel tests on aircraft prototypes, evaluating the performance of propulsion systems, and performing structural integrity assessments.
In summary, defense contractors are fundamental to the availability of these positions within San Diego, encompassing a wide range of roles from research and development to manufacturing and testing. The continued investment in aerospace and defense technologies by these entities ensures a sustained demand for skilled engineers in the region. San Diego’s concentration of these contractors solidifies its status as a key hub for the aerospace engineering profession.
2. Research Institutions
Research institutions in the San Diego area play a critical role in the demand for aerospace engineers. These institutions, including universities and specialized research centers, conduct cutting-edge research in areas directly relevant to the aerospace industry. This research generates a need for highly skilled engineers to design experiments, analyze data, and develop new technologies, thereby creating a direct source of related employment opportunities. For example, research on advanced materials for aircraft construction at a local university often leads to positions for engineers with expertise in materials science and structural analysis. The presence of these institutions enhances the regional ecosystem.
The effect of these institutions extends beyond direct employment. They also serve as training grounds for future aerospace engineers, providing students with advanced knowledge and practical experience through research projects and internships. These graduates then enter the workforce, contributing to the pool of qualified candidates for positions in local aerospace companies. The collaborative partnerships between research institutions and industry further strengthen this relationship, fostering innovation and creating opportunities for engineers to apply their skills in real-world applications. For instance, a joint project between a university and a defense contractor to develop a new propulsion system would require engineers with expertise in both theoretical research and practical engineering design.
In summary, research institutions are indispensable components of the region’s aerospace employment landscape. They contribute to the industry both by directly creating employment through research activities and by training and supplying qualified engineers. Understanding this connection is practically significant for both job seekers and industry stakeholders. The link ensures the continued growth and innovation in the aerospace sector within the San Diego region.
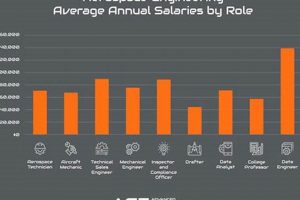
3. Salary Expectations
Remuneration for engineering professionals in the aerospace sector within San Diego is influenced by several factors, including experience, education, specialization, and the specific employer. An understanding of prevailing salary ranges is critical for both prospective employees and organizations seeking to attract and retain talent. Higher levels of education and specialized skills typically command higher salaries, reflecting the complexity and demands of the work. For example, an engineer with a Ph.D. in aerospace engineering and expertise in computational fluid dynamics can expect to earn more than an entry-level engineer with a bachelor’s degree. Also, positions at larger defense contractors may offer different compensation packages compared to those at smaller, specialized firms.
Cost of living in San Diego significantly impacts salary expectations. The relatively high cost of housing and general expenses necessitates competitive compensation to attract and retain qualified engineers. Organizations must account for these regional economic realities when determining salary offers. The demand for skilled engineers in the area also plays a role, with increased demand potentially driving up salaries. For instance, a surge in contracts for unmanned aerial systems in the region could lead to increased competition for engineers with relevant expertise, consequently increasing compensation levels.
In summary, compensation within this field is multifaceted, influenced by individual qualifications, regional economic conditions, and industry demand. Accurate assessment and understanding of salary expectations is crucial for both employers and professionals in the San Diego aerospace industry to ensure equitable compensation and career satisfaction. Moreover, comprehending these factors enables individuals to make informed career decisions and helps organizations remain competitive in attracting top talent.
4. Required Skills
The availability of opportunities in the San Diego aerospace engineering sector is directly contingent upon a specific set of technical proficiencies and professional attributes. The acquisition and demonstration of these skills are not merely advantageous but rather prerequisites for securing positions within this highly competitive market. A demonstrable aptitude for utilizing computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided engineering (CAE) software, for instance, is essential, as these tools are fundamental to the design and analysis of aircraft and spacecraft components. Furthermore, a solid understanding of aerodynamics, propulsion systems, and materials science is expected, given the nature of work inherent in such roles. The success of an aerospace project relies on the engineer’s ability to apply these skills to meet the rigorous requirements of the aerospace environment. Without these foundational elements, navigation of the challenges inherent in aerospace engineering is not possible.
Beyond technical expertise, certain soft skills are equally vital for professional success. Effective communication, teamwork, and problem-solving abilities are crucial in collaborative engineering environments, where projects often involve multidisciplinary teams working toward a common goal. The ability to articulate complex technical concepts clearly and concisely, both verbally and in writing, is essential for conveying design decisions, presenting research findings, and collaborating with colleagues from diverse backgrounds. The capacity to work effectively in teams, contributing to a positive and productive work environment, is also highly valued by employers. Furthermore, the ability to analyze complex problems, identify potential solutions, and implement effective strategies is necessary for addressing technical challenges and ensuring project success. An applicant’s portfolio would ideally showcase a combination of hard and soft skills relevant to the needs of potential employers.
In summary, the successful acquisition and application of required skills are fundamental to securing positions in the aerospace sector. A deep understanding of relevant technical concepts, combined with strong communication, teamwork, and problem-solving capabilities, is essential for navigating the complex challenges and contributing to the success of engineering projects. The presence of these key qualities is central to long-term growth and stability within the industry, shaping both individual career trajectories and the overall landscape of the San Diego aerospace community.
5. Educational Background
A strong educational foundation serves as a crucial determinant in accessing opportunities for aerospace engineers in San Diego. The specific academic qualifications attained directly influence an individual’s eligibility and competitiveness for these specialized roles.
- Undergraduate Degree Requirements
A bachelor’s degree in aerospace engineering, or a closely related field such as mechanical engineering, is generally the minimum requirement for entry-level engineering positions. Core coursework typically includes thermodynamics, fluid dynamics, structural analysis, and control systems. For example, a graduate with a bachelor’s degree may qualify for positions involving design support or testing, but advanced roles often necessitate further academic credentials. Employers actively seek graduates from accredited engineering programs, ensuring a baseline level of competence.
- Advanced Degree Opportunities
A master’s or doctoral degree can significantly enhance career prospects and earning potential in the aerospace sector. Advanced degrees allow for specialization in areas such as propulsion, composite materials, or autonomous systems. Individuals with advanced degrees are often preferred for research and development positions, leading to opportunities for innovation and leadership. An engineer with a master’s degree, for example, may lead a team designing a new aircraft wing, whereas a Ph.D. holder might focus on developing novel propulsion technologies. Many employers offer tuition reimbursement or other incentives to encourage employees to pursue advanced degrees.
- Accreditation and Program Reputation
The accreditation status and reputation of an engineering program play a crucial role in shaping employer perceptions. Programs accredited by ABET (Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology) demonstrate adherence to rigorous academic standards, providing assurance of a high-quality education. Graduates from well-regarded programs often have a competitive advantage in the job market, as employers recognize the value of a rigorous curriculum and experienced faculty. For example, a graduate from a top-ranked engineering program like UC San Diego may be more likely to secure an interview with a leading aerospace company.
- Specialized Coursework and Certifications
Beyond the core curriculum, specialized coursework and certifications can further enhance an engineer’s skillset and marketability. Courses in areas such as computational fluid dynamics (CFD), finite element analysis (FEA), and systems engineering can provide valuable expertise in high-demand areas. Industry-recognized certifications, such as those offered by professional organizations like the American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics (AIAA), can also demonstrate competence and commitment to professional development. Employers often prioritize candidates with specialized skills relevant to their specific projects, making targeted education and certifications a strategic investment. An engineer specializing in UAV technology, for example, may benefit from coursework in control systems and certifications in unmanned aircraft operations.
The link between educational background and available opportunities for aerospace engineers in San Diego is both direct and consequential. The depth and quality of the education, coupled with specialized skills and certifications, directly impact an individual’s career trajectory and earning potential. A proactive approach to academic and professional development is essential for navigating the competitive landscape of the San Diego aerospace industry. Individuals are well served by carefully considering their educational choices and specializing in areas aligned with industry demand to maximize their potential for success.
6. Industry Growth
Expansion within the aerospace sector directly influences the availability of positions for skilled professionals in San Diego. Positive growth trends, characterized by increased investment, technological advancement, and expanded production, lead to a corresponding rise in demand for qualified engineers. This relationship reflects the fundamental principle that an expanding industry necessitates a larger workforce to support its operations. For example, a surge in demand for unmanned aerial systems (UAS) results in companies increasing their engineering staff to design, test, and manufacture these systems. Such expansion translates into additional jobs and career opportunities for individuals with the requisite expertise.
The geographic concentration of aerospace companies in San Diego amplifies the effect of industry growth on job availability. The region’s established infrastructure and skilled workforce create a favorable environment for aerospace businesses, fostering innovation and attracting new investment. As companies expand their operations, they often seek to recruit local talent, thereby creating additional positions within the community. Illustratively, if a San Diego-based aerospace firm secures a large contract for satellite development, this growth would directly translate to a need for more engineers specializing in areas such as spacecraft design, propulsion systems, and communications technology. These newly created roles provide career paths and opportunities for advancement for both recent graduates and experienced professionals.
In summary, industry growth serves as a primary driver of opportunity in the San Diego aerospace engineering job market. The region’s established aerospace ecosystem amplifies this effect, resulting in a concentration of companies and jobs within the area. An understanding of this relationship is crucial for both job seekers and industry stakeholders, enabling informed career decisions and strategic workforce planning. Continual monitoring of industry trends, coupled with the development of relevant skills, is essential for navigating the dynamic landscape of aerospace employment.
7. Geographic Concentration
The prevalence of opportunities in San Diego for professionals in the design, development, and testing of aircraft and spacecraft is not uniformly distributed across the state, or even the county. A notable clustering of aerospace companies and related research institutions within specific areas of the San Diego metropolitan area significantly shapes the employment landscape for the industry. This localized concentration of resources results in a higher density of related employment opportunities within those targeted zones, such as areas near major defense contractors or research universities with prominent aerospace programs. The presence of a substantial talent pool and established supply chains further reinforces this geographic pattern.
The establishment of key aerospace facilities in certain regions has created a feedback loop. For instance, the presence of major defense contractors like General Atomics and Northrop Grumman attracts a concentration of skilled engineers seeking proximity to employment prospects. This, in turn, encourages educational institutions to offer relevant training programs, further solidifying the region’s status as a hub for the industry. The result is a symbiotic relationship between industry, education, and workforce that promotes continued growth and innovation. This effect also extends to supporting industries, such as suppliers of specialized components and software developers catering to the aerospace sector, compounding the employment opportunities within the region.
In summary, the uneven distribution of aerospace companies and related resources within San Diego leads to a clear geographic concentration of employment opportunities for specialized engineering professionals. This geographic pattern has practical implications for job seekers, requiring them to focus their search on specific areas within the region. Understanding this spatial dynamic is crucial for both individuals seeking employment and for policymakers aiming to support the continued growth and development of the aerospace sector within San Diego.
Frequently Asked Questions About Aerospace Engineering Opportunities in San Diego
The following addresses common inquiries concerning employment prospects in the aerospace engineering sector within the San Diego metropolitan area. These responses are designed to provide clear and concise information.
Question 1: What level of education is typically required to secure such a position?
A bachelor’s degree in aerospace engineering, mechanical engineering, or a closely related field is generally considered the minimum requirement. However, advanced degrees, such as a Master’s or Ph.D., are often preferred for specialized roles and research positions.
Question 2: What types of companies commonly offer engineering positions?
Defense contractors, aerospace manufacturers, research institutions, and government agencies represent the primary employers. Specific examples within the San Diego region include General Atomics, Northrop Grumman, and various divisions of the Department of Defense.
Question 3: What skills are highly valued by employers in this field?
Proficiency in CAD/CAE software, a strong understanding of aerodynamics and propulsion systems, and experience with materials science are commonly sought after. Strong analytical, problem-solving, and communication skills are also highly valued.
Question 4: How does the cost of living in San Diego impact salary expectations?
The relatively high cost of living in San Diego generally necessitates competitive compensation packages. Entry-level salaries may be adjusted upward to attract and retain qualified engineers.
Question 5: What role do research institutions play in the employment landscape?
Research institutions, such as UC San Diego, conduct cutting-edge research and provide training for future aerospace engineers. They also offer research and development positions, further contributing to employment opportunities.
Question 6: How significant is geographic concentration within the region?
Aerospace-related opportunities are primarily concentrated in specific areas of San Diego, often near major defense contractors and research facilities. Focusing job search efforts on these regions is advisable.
In summary, a combination of relevant education, technical skills, and strategic job searching is essential for success in the San Diego aerospace engineering sector.
The subsequent section will outline resources available to support individuals pursuing employment in this field.
Aerospace Engineer Jobs San Diego
This exposition has illuminated the landscape of opportunities in the design, development, and testing of aircraft and spacecraft within the San Diego area. It has outlined the significance of defense contractors and research institutions, detailed requisite skills and educational qualifications, and addressed prevalent salary expectations. The implications of industry growth and geographic concentration have also been thoroughly explored.
The information presented is intended to serve as a valuable resource for both professionals seeking employment and stakeholders involved in the San Diego aerospace community. Continued diligence in skill development and strategic planning remains paramount for navigating this competitive and dynamic sector. The sustained growth and innovation within the industry offer promising prospects for those prepared to meet its rigorous demands.