Opportunities within the field involve the design, development, testing, and manufacturing of aircraft, spacecraft, and related systems in a specific major Canadian city. These roles can span various specializations, from aerodynamics and propulsion to structural analysis and avionics, all situated within the Greater Toronto Area.
The availability of positions in this technical discipline contributes to the economic growth and technological advancement of the region. The presence of established aerospace companies, research institutions, and a skilled workforce creates a beneficial ecosystem for innovation and career development. Historically, the area has played a significant role in Canadian aerospace endeavors, fostering a continued demand for qualified professionals.
The following sections will delve into the specific sectors within the industry in the Greater Toronto Area, the typical requirements for securing employment, and the overall outlook for those seeking to advance their careers. This analysis will also address salary expectations and resources useful for job seekers.
Strategies for Securing Employment in the Field
The following advice is intended to aid individuals navigating the employment landscape related to aircraft and spacecraft technology in the Greater Toronto Area. These strategies are designed to improve the likelihood of success in a competitive job market.
Tip 1: Tailor Application Materials. Resumes and cover letters should be explicitly tailored to each specific job posting. Highlight relevant skills and experience that directly align with the requirements outlined by the employer for positions in the Greater Toronto Area.
Tip 2: Emphasize Relevant Education and Certifications. Academic qualifications in aerospace engineering, or related fields, are essential. Industry-recognized certifications and specialized training in relevant software or technologies can significantly enhance an applicant’s candidacy for aircraft-related employment.
Tip 3: Cultivate a Strong Professional Network. Actively engage with industry professionals through networking events, conferences, and online platforms. Building relationships can provide valuable insights into available opportunities and facilitate introductions within the Toronto-area aerospace community.
Tip 4: Gain Practical Experience. Internships, co-op programs, and research opportunities provide invaluable hands-on experience. Prioritize opportunities that align with career interests and demonstrate practical skills applicable to the design, testing, or manufacturing of aircraft or spacecraft systems.
Tip 5: Showcase Technical Proficiency. Demonstrate expertise in relevant software and engineering tools. Include projects, publications, or presentations that highlight technical abilities applicable to aircraft and spacecraft technology in the Greater Toronto Area.
Tip 6: Highlight Problem-Solving Skills. Aerospace engineering often requires innovative solutions to complex challenges. Provide specific examples in application materials and interviews illustrating successful problem-solving approaches relevant to the field.
Tip 7: Prepare Thoroughly for Interviews. Research the company and the specific role. Practice answering common interview questions, and be prepared to discuss technical concepts and projects in detail. Demonstrating enthusiasm and a strong understanding of the aerospace landscape in the Greater Toronto Area is crucial.
Implementing these strategies can significantly increase the likelihood of securing a rewarding career in the design, development, and maintenance of airborne vehicles and related systems in the specified geographic area.
The subsequent sections will discuss specific companies and organizations that offer related employment in this vibrant Canadian market.
1. Specializations Available
The spectrum of specializations directly shapes the composition of the aerospace engineering job market within Toronto. The availability of specific roles, from aerodynamicists to propulsion engineers, is a direct consequence of the diverse needs of companies operating in this sector. For example, a company specializing in unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) would necessitate specialists in flight control systems and autonomous navigation, creating demand for engineers with those skills. The prevalence, or absence, of opportunities in a particular specialization directly reflects the technological focus of Toronto-based aerospace firms.
Consider the impact of advanced materials research. If several companies in Toronto are actively involved in developing lighter, stronger materials for aircraft structures, there will be a corresponding surge in demand for materials engineers and structural analysts. Similarly, the growing emphasis on sustainable aviation fuels necessitates expertise in chemical engineering and combustion technology. These examples illustrate how technological trends drive the need for specialized skill sets and, consequently, define the landscape of the “aerospace engineering jobs Toronto” market. This understanding enables job seekers to strategically target their skills and training toward areas of high demand.
In summary, a careful examination of available specializations reveals the core technological competencies driving Toronto’s aerospace industry. The demand for specific engineering disciplines mirrors the strategic priorities and ongoing projects within the region’s aerospace companies. By understanding this connection, individuals can more effectively tailor their education and career paths to capitalize on existing and emerging opportunities in this dynamic field, addressing challenges related to skills gap and aligning with the broader theme of economic development in the high-tech sector.
2. Required Education
The prerequisite academic qualifications significantly influence access to opportunities in aircraft and spacecraft systems design and development within the Greater Toronto Area. A foundational education, typically a Bachelor’s degree in Aerospace Engineering or a closely related field such as Mechanical Engineering with an aerospace specialization, serves as a minimum entry point. More advanced positions, particularly those involving research, development, or specialized design, often necessitate a Master’s degree or a Doctorate. The absence of the appropriate educational background acts as a primary barrier to entry, regardless of practical experience or other qualifications. For instance, roles involving complex simulation or advanced structural analysis frequently require post-graduate degrees with specific coursework in finite element methods or computational fluid dynamics.
The curriculum associated with these educational programs provides the fundamental knowledge and analytical skills essential for success. Coursework in areas such as aerodynamics, propulsion, control systems, and materials science directly translates into the ability to perform tasks related to aircraft design, performance analysis, and system integration. Further, accredited programs often incorporate practical components like design projects, laboratory experiments, and industry internships, thus providing exposure to real-world engineering challenges. Examples include participation in student design competitions focused on aircraft or spacecraft design and construction, or co-op placements at local aerospace companies. Such experiences are viewed favorably by employers, serving to validate theoretical knowledge with practical application.
In summary, appropriate academic qualifications are a crucial determinant of eligibility and competitiveness in the Greater Toronto Area job market. The emphasis on higher education and specialized knowledge reflects the complexity and technical sophistication of the aerospace industry. Individuals seeking to pursue careers in this sector must prioritize obtaining the requisite degrees and relevant certifications to effectively contribute to the design, development, and maintenance of aircraft and spacecraft systems. This focus on education directly aligns with the industry’s commitment to innovation, safety, and performance, underscoring the critical role of a well-educated workforce in driving technological advancement.
3. Industry Sectors
Understanding the diverse industry sectors within the aerospace domain is crucial for individuals seeking employment opportunities in the Greater Toronto Area. These sectors dictate the specific types of roles available, the skills in demand, and the overall career trajectories for engineering professionals.
- Commercial Aviation
This sector encompasses the design, manufacturing, and maintenance of passenger and cargo aircraft. Opportunities within commercial aviation focus on improving fuel efficiency, enhancing passenger comfort, and ensuring regulatory compliance. Examples include positions at aircraft manufacturers, airlines, and maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO) facilities. Implications for available roles in the Greater Toronto Area are determined by the regional presence of companies involved in these activities.
- Defense and Military Aerospace
This area involves the development and production of military aircraft, unmanned aerial systems, and related technologies for national defense. Positions may involve working on advanced weapons systems, surveillance technologies, or secure communication networks. The extent of defense-related contracts awarded to Toronto-area companies directly influences the demand for engineers with specialized expertise in these fields.
- Space Exploration and Satellite Technology
This sector focuses on the design, development, and operation of satellites, launch vehicles, and space-based infrastructure. Roles may encompass satellite communications, remote sensing, and scientific research. The presence of companies and research institutions involved in space activities in the Greater Toronto Area creates opportunities for engineers specializing in areas such as orbital mechanics, spacecraft propulsion, and payload design.
- Aerospace Manufacturing and Supply Chain
This sector encompasses the manufacturing of aircraft components, materials, and systems, as well as the management of the supply chain that supports these activities. Opportunities involve working on advanced manufacturing processes, quality control, and supply chain optimization. The strength and efficiency of the local aerospace manufacturing base is a significant factor in determining the availability of engineering positions in the Greater Toronto Area.
The interconnectedness of these industry sectors contributes to the overall dynamism of the aerospace engineering job market in the Greater Toronto Area. Each sector has unique requirements and growth prospects, shaping the demand for engineers with specific skill sets and experience. Understanding these dynamics enables job seekers to strategically target their career paths and maximize their opportunities within this specialized field.
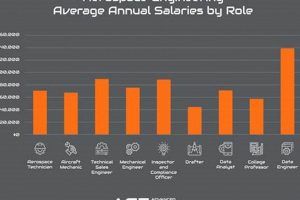
4. Salary Expectations
Compensation within the aerospace engineering field in the Greater Toronto Area is a complex function of multiple interdependent factors. Anticipated earnings directly influence career decisions and significantly impact the attractiveness of “aerospace engineering jobs toronto” to both new graduates and experienced professionals.
- Experience Level
Entry-level positions, typically requiring a Bachelor’s degree and minimal experience, command lower salaries compared to roles demanding extensive industry experience. Mid-career engineers with five to ten years of experience can expect a substantial increase in compensation. Senior-level engineers, often with advanced degrees and specialized expertise, receive the highest salaries. This tiered structure incentivizes professional development and rewards accumulated knowledge.
- Specialization
Certain specializations within aerospace engineering are in higher demand and command premium salaries. For example, engineers specializing in avionics, control systems, or advanced materials may earn more than those in more general roles. This reflects the relative scarcity of expertise and the criticality of these skills to specific projects. The correlation between specialization and salary directly impacts career choices for those entering or transitioning within the field.
- Company Size and Type
Larger, established aerospace companies often offer more competitive salaries and benefits packages compared to smaller firms or startups. Government research institutions and defense contractors may also have distinct salary structures. Furthermore, unionized positions may have predetermined salary scales that differ from non-unionized roles. These variations influence job seekers’ preferences and decisions regarding potential employers.
- Education Level
While a bachelor’s degree is often the minimum requirement, possessing a master’s degree or doctorate can lead to higher starting salaries and faster career advancement. Advanced degrees demonstrate specialized knowledge and research capabilities, which are highly valued by employers. The investment in higher education directly correlates with increased earning potential in the field of “aerospace engineering jobs toronto.”
Salary expectations within the Greater Toronto Area’s aerospace sector are significantly shaped by these combined influences. Individuals evaluating opportunities should consider these factors in conjunction with their personal goals and career aspirations. A comprehensive understanding of these dynamics is crucial for informed decision-making and successful career progression within this highly specialized engineering discipline.
5. Key Employers
Key employers directly dictate the characteristics and availability of opportunities related to aircraft and spacecraft system expertise within the Greater Toronto Area. The presence, size, and strategic focus of these organizations fundamentally shape the demand for specialized engineering skills. Consequently, understanding the major players in this market is crucial for individuals seeking related positions. These employers act as the primary drivers of innovation and economic activity within the sector, establishing the prevailing standards for technical competency and professional development. The concentration of specific companies directly correlates with the prevalence of certain types of engineering roles. For example, if a particular firm specializes in satellite technology, the area will likely have an abundance of opportunities related to orbital mechanics, communications systems, and payload design.
Significant employers often include established aerospace manufacturers with extensive production facilities in the Greater Toronto Area. These companies tend to offer a range of positions, from entry-level design roles to senior management positions overseeing complex engineering projects. Defense contractors also contribute substantially to the job market, providing opportunities in areas such as avionics, radar systems, and unmanned aerial vehicle technology. Furthermore, government research institutions and agencies play a pivotal role in fostering innovation and developing cutting-edge technologies, requiring highly skilled engineers with advanced degrees and specialized knowledge. The specific projects undertaken by these institutions, whether focused on fuel efficiency, materials science, or propulsion systems, directly translate into the demand for particular engineering skill sets.
In summary, identifying and understanding the key employers within the Greater Toronto Area’s aerospace sector is essential for navigating employment prospects. These companies serve as the primary source of available positions, defining the skills, experience, and educational background required for success. By focusing on the needs and priorities of these organizations, individuals can effectively tailor their career paths and maximize their opportunities in this specialized and competitive field. This alignment is critical for ensuring both individual career success and the continued growth and innovation of the region’s aerospace industry.
6. Growth Outlook
The anticipated expansion of the aerospace sector significantly influences the availability and nature of opportunities related to aircraft and spacecraft system expertise within the Greater Toronto Area. The projected trajectory of industry growth serves as a critical indicator for individuals seeking long-term career prospects in this specialized field. Expansion creates new roles, drives demand for specialized skills, and fosters innovation, collectively shaping the dynamics of the local job market.
- Technological Advancements
Continuous innovation in areas such as advanced materials, electric propulsion, and autonomous systems fuels industry expansion. The development of new technologies creates a demand for engineers with specialized expertise in these domains. For example, the increasing adoption of composite materials in aircraft construction requires engineers skilled in materials science and structural analysis. This technological progress translates directly into the creation of new roles and the need for a highly skilled workforce in the Greater Toronto Area.
- Government Investment and Policy
Government funding for aerospace research and development, as well as supportive regulatory policies, can significantly stimulate industry growth. Investments in infrastructure, such as airport expansions or spaceport facilities, create further opportunities for aerospace engineers. For instance, government initiatives aimed at promoting sustainable aviation fuels can drive demand for engineers with expertise in biofuel production and combustion technologies. The overall policy environment plays a critical role in fostering a conducive ecosystem for aerospace innovation and job creation within the region.
- Global Market Demand
Increasing demand for air travel, space-based services, and defense systems drives the expansion of the aerospace industry on a global scale. Toronto-area companies that serve these markets benefit from this increased demand, leading to greater production volumes and the creation of new engineering positions. For example, a surge in demand for commercial aircraft from emerging economies can stimulate growth in the local aerospace manufacturing sector. The integration of Toronto-area companies into global supply chains further amplifies the impact of worldwide market trends.
- Aging Workforce and Skills Gap
The impending retirement of experienced aerospace engineers, coupled with a potential skills gap in emerging technologies, presents both a challenge and an opportunity. The need to replace retiring engineers creates demand for new graduates and mid-career professionals. Simultaneously, the industry’s rapid technological evolution requires ongoing training and upskilling to address the skills gap. These demographic and technological shifts emphasize the importance of continuous learning and professional development for individuals seeking long-term success in the aerospace field.
These facets collectively influence the growth outlook for aerospace engineering positions in Toronto, underscoring the interplay between technology, policy, global economics, and workforce dynamics. The combined effect of these influences creates a constantly evolving environment, emphasizing the importance of adaptability and a commitment to continuous learning for those pursuing a career in the area.
7. Skill Demands
The prevailing skill demands within the aerospace sector are a primary determinant of the availability and nature of engineering positions in the Greater Toronto Area. Employers seek a specific combination of technical proficiency, analytical capabilities, and practical experience, directly influencing the composition of the “aerospace engineering jobs toronto” market. These demands reflect the complex challenges associated with designing, developing, and maintaining advanced aircraft and spacecraft systems.
- Technical Proficiency in Engineering Software
Expertise in industry-standard software tools, such as CAD/CAM, CAE, and simulation software, is essential. Engineers must be proficient in using these tools for design, analysis, and optimization tasks. For example, proficiency in CATIA for 3D modeling or ANSYS for finite element analysis is frequently required for structural design roles. The absence of such proficiency limits an applicant’s competitiveness in securing roles involving the design and analysis of aircraft components within the Toronto area.
- Knowledge of Aerospace Materials and Manufacturing Processes
A thorough understanding of aerospace materials, including composites, alloys, and ceramics, is crucial. Engineers must also be familiar with manufacturing processes such as machining, welding, and additive manufacturing. For instance, knowledge of the properties and processing techniques for carbon fiber reinforced polymers is vital for engineers working on lightweight aircraft structures. This understanding directly impacts the ability to select appropriate materials and manufacturing methods for aerospace applications in Toronto.
- Systems Engineering Expertise
A systems engineering approach is critical for integrating various subsystems and components into a cohesive and functional aerospace system. This involves defining requirements, managing interfaces, and conducting trade-off studies. For example, systems engineers are responsible for ensuring that the avionics, propulsion, and control systems of an aircraft operate seamlessly together. Proficiency in systems engineering principles is essential for managing the complexity of modern aircraft and spacecraft systems within Toronto-based companies.
- Problem-Solving and Analytical Skills
The ability to identify, analyze, and solve complex engineering problems is a fundamental requirement. This includes the ability to apply engineering principles, conduct experiments, and interpret data. For example, engineers may be tasked with troubleshooting performance issues, diagnosing system failures, or developing innovative solutions to improve aircraft efficiency. Strong problem-solving and analytical skills are essential for addressing the challenges inherent in designing and operating aerospace systems in Toronto.
In conclusion, these skill demands represent the core competencies sought by employers in the Greater Toronto Area’s aerospace sector. The emphasis on technical proficiency, materials knowledge, systems engineering expertise, and problem-solving skills reflects the multifaceted nature of the industry. The ability to demonstrate these competencies is crucial for individuals seeking to secure and advance within “aerospace engineering jobs toronto”.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following addresses common inquiries regarding career opportunities related to aircraft and spacecraft technology within the Greater Toronto Area. The intent is to provide clarity and guidance based on the current industry landscape.
Question 1: What is the typical educational path to obtain related employment in the Greater Toronto Area?
A Bachelor’s degree in Aerospace Engineering, or a closely related field such as Mechanical Engineering with an aerospace specialization, is generally required. Advanced positions may necessitate a Master’s degree or a Doctorate. Specialized certifications can also enhance candidacy.
Question 2: Which specific engineering disciplines are most in-demand in the local aerospace sector?
Demand varies based on company focus, but common in-demand disciplines include structural analysis, avionics, propulsion, systems engineering, and materials science. Expertise in emerging technologies, such as additive manufacturing and electric propulsion, is also increasingly valued.
Question 3: What are the primary industry sectors that offer related positions within the Greater Toronto Area?
Key sectors include commercial aviation (aircraft manufacturing and maintenance), defense and military aerospace, space exploration and satellite technology, and aerospace manufacturing and supply chain. Each sector demands distinct skill sets and experience.
Question 4: How does experience level affect salary expectations in this field in the specified geographic area?
Salary is directly correlated with experience. Entry-level positions typically command lower salaries compared to mid-career and senior-level roles. Advanced degrees and specialized expertise can also positively influence compensation.
Question 5: What software and technical skills are most valued by employers in this sector in the Greater Toronto Area?
Proficiency in industry-standard software tools such as CATIA, ANSYS, and MATLAB is essential. Knowledge of aerospace materials, manufacturing processes, and systems engineering principles is also highly valued.
Question 6: What is the overall growth outlook for the aerospace engineering job market in the Greater Toronto Area?
The growth outlook is generally positive, driven by technological advancements, government investment, global market demand, and the need to address the aging workforce and skills gap. Continuous learning and adaptation are crucial for long-term career success.
In summary, pursuing a career in aerospace engineering in the Greater Toronto Area requires a combination of relevant education, specialized skills, and adaptability to evolving industry demands. Understanding the local market dynamics is essential for informed career planning.
The following section will provide resources for finding “aerospace engineering jobs toronto”.
Aerospace Engineering Jobs Toronto
This examination has outlined the key facets of opportunities related to aircraft and spacecraft engineering within the Greater Toronto Area. Essential components, including required education, specialization demands, industry sectors, salary expectations, and prominent employers, have been detailed. The discussion emphasized the influence of technological advancements, market dynamics, and workforce trends on the overall employment landscape. These combined elements provide a foundational understanding for individuals seeking careers in this technical domain.
Prospective engineers are encouraged to continually develop relevant expertise, adapt to evolving industry needs, and strategically align skills with market demands. Sustained effort and a commitment to professional growth are essential for navigating the complexities and capitalizing on the opportunities within the “aerospace engineering jobs toronto” sector. The ongoing advancement of this field holds significant implications for the region’s technological progress and economic prosperity, necessitating a dedicated and skilled workforce.