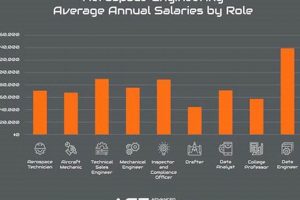
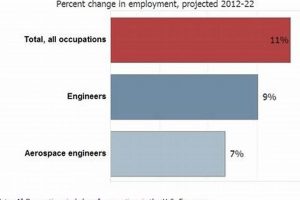
The convergence of medical expertise and aviation creates a specialized field where physicians apply clinical knowledge to the unique challenges posed by flight and space travel. These professionals focus on the health, safety, and performance of individuals operating in, or exposed to, the aerospace environment. Examples of such roles include providing medical support to astronauts, conducting research on the physiological effects of altitude and acceleration, and ensuring the health and fitness of pilots and aircrew.
This area of medical practice is vital for safeguarding human well-being during air and space operations. It contributes to enhanced flight safety by identifying and mitigating medical risks, developing countermeasures to physiological stressors, and establishing medical standards for aviation personnel. Historically, its development has been intrinsically linked to advancements in aviation and space exploration, constantly evolving to address new challenges and protect those who venture into the skies and beyond.
The following sections will delve deeper into the specific responsibilities, qualifications, and career paths associated with opportunities within this specialized medical discipline. Details regarding the necessary training, typical work environments, and the outlook for professionals in this field will be provided.
Tips for Pursuing Opportunities in Aerospace Medicine
This section offers guidance to individuals interested in securing roles that combine medical expertise with the specialized demands of flight and space environments. Following these tips can enhance prospects in this niche field.
Tip 1: Obtain Board Certification in a Relevant Medical Specialty. Possessing certification in internal medicine, family medicine, emergency medicine, or occupational medicine provides a strong foundation for further specialization in aerospace medicine.
Tip 2: Complete a Residency or Fellowship in Aerospace Medicine. Dedicated aerospace medicine training programs offer in-depth knowledge of aerospace physiology, environmental medicine, and operational considerations critical to the field.
Tip 3: Seek Experience in Aviation or Space-Related Environments. Volunteering, shadowing, or participating in research related to flight or space missions provides invaluable practical experience and networking opportunities.
Tip 4: Develop a Strong Understanding of Aviation Regulations and Safety Protocols. Familiarity with FAA regulations, ICAO standards, and other relevant guidelines is essential for ensuring patient safety in aerospace settings.
Tip 5: Cultivate Excellent Communication and Teamwork Skills. Collaboration with pilots, engineers, and other healthcare professionals is crucial for effective medical support and decision-making in aerospace operations.
Tip 6: Pursue Research Opportunities in Aerospace Medicine. Engaging in research enhances understanding of the physiological effects of flight and space, contributing to advancements in preventative care and treatment.
Tip 7: Network with Professionals in the Aerospace Medicine Community. Attending conferences, joining professional organizations, and connecting with experienced practitioners can facilitate career advancement.
Adhering to these guidelines strengthens qualifications and increases competitiveness for positions focused on protecting and promoting the health of those working and traveling in the aerospace domain. Prioritizing specialized training, practical experience, and professional development will significantly enhance career prospects.
The subsequent sections will provide additional resources and perspectives on career advancement within aerospace medicine, solidifying the reader’s comprehension of pathways to success in this challenging yet rewarding field.
1. Patient Health Maintenance
Patient health maintenance forms a cornerstone of practice combining medical expertise with the demands of aviation and space. The effect of this maintenance, when effectively implemented, manifests in the sustained operational readiness and safety of aircrew, astronauts, and potentially space tourists. This process requires proactive measures to detect and mitigate potential health risks before they compromise performance or become acute medical incidents during flight. It emphasizes preventative care and early intervention, significantly reducing the likelihood of in-flight medical emergencies. Examples include comprehensive medical evaluations, specialized screenings for cardiovascular and neurological conditions susceptible to aerospace stressors, and personalized health counseling. In-depth understanding is crucial as it directly relates to optimizing individual well-being and ensuring mission success.
Furthermore, continuous monitoring of physiological parameters, such as cardiovascular function and cognitive performance, contributes to the practical application of patient health maintenance. Aerospace physicians utilize advanced diagnostic tools and telemedicine capabilities to remotely assess and manage the health of personnel during missions. The data collected informs adaptive strategies, encompassing adjusted flight schedules, optimized environmental controls, and individualized medical interventions, enabling real-time management of physiological stresses and contributing to the overall goal of preserving health and promoting performance.
In summary, patient health maintenance is not merely a peripheral aspect of positions in this unique area of medicine, but an integral element directly influencing mission outcomes and individual safety. Challenges include adapting traditional medical practices to the constraints of operational environments and maintaining consistent monitoring amidst the dynamic nature of aerospace activities. Nevertheless, effective integration of proactive healthcare remains paramount to the continued advancement and safety of human activities within the aerospace domain.
2. Environmental Stress Mitigation
Environmental stress mitigation is a critical component of medical practice within the aerospace domain, directly impacting the health, safety, and performance of individuals operating in this challenging environment. Aerospace physicians are at the forefront of identifying, understanding, and counteracting the adverse effects of these stressors.
- Hypoxia Management
Hypoxia, or oxygen deficiency, is a primary concern at high altitudes. Aerospace physicians implement protocols for supplemental oxygen administration, monitor oxygen saturation levels, and educate aircrew and passengers on the symptoms of hypoxia. They also develop and refine altitude acclimatization procedures to enhance tolerance to reduced oxygen levels. Proper hypoxia management is vital for preventing cognitive impairment, loss of consciousness, and other adverse effects that could compromise flight safety.
- Acceleration (G-Force) Protection
Exposure to significant G-forces during flight, particularly in high-performance aircraft, can lead to physiological strain and potential loss of consciousness (G-LOC). Aerospace physicians are involved in the design and implementation of anti-G suits and breathing techniques to mitigate the effects of acceleration. They also conduct research to understand the physiological limits of G-force tolerance and develop strategies to enhance pilot resilience. These protective measures are indispensable for maintaining pilot performance and preventing G-LOC incidents.
- Radiation Exposure Mitigation
Astronauts and high-altitude aircrew are exposed to increased levels of ionizing radiation from cosmic rays and solar particle events. Aerospace physicians assess radiation risks, implement shielding strategies, and monitor radiation exposure levels. They also study the long-term health effects of radiation exposure and develop countermeasures to minimize radiation-induced damage. Radiation mitigation strategies are essential for protecting the health and well-being of individuals during extended space missions and high-altitude flights.
- Disorientation and Spatial Awareness
Spatial disorientation and impaired spatial awareness can occur due to sensory conflicts and vestibular disturbances during flight. Aerospace physicians use diagnostic tools to identify individuals susceptible to disorientation and implement training programs to enhance spatial orientation skills. They also develop cockpit displays and environmental cues to improve situational awareness and reduce the risk of spatial disorientation-related incidents. Promoting accurate spatial orientation is crucial for maintaining safe and effective flight operations.
The multifaceted nature of environmental stress mitigation requires aerospace physicians to possess a comprehensive understanding of human physiology, aerospace engineering, and operational constraints. By proactively addressing these environmental challenges, medical professionals contribute significantly to the safety and success of aerospace activities, furthering exploration and human presence in extreme environments.
3. Operational Medical Support
Operational medical support forms a core function within the purview of practitioners specializing in aerospace medicine. This area encompasses the provision of medical care, consultation, and emergency response services tailored to the unique demands of aerospace operations. Its effective execution is paramount to ensuring the health, safety, and performance of personnel engaged in flight and space-related activities.
- In-Flight Medical Management
This facet involves the remote diagnosis and treatment of medical conditions arising during flight. It necessitates the ability to assess patient status via telemedicine, provide guidance to onboard medical personnel or trained crew members, and coordinate with ground-based medical facilities for potential diversions or emergency landings. Real-world examples include assisting with managing cardiac events, severe allergic reactions, or traumatic injuries sustained during turbulence. Deficiencies in this area can have critical consequences, necessitating specialized training and robust communication protocols.
- Space Mission Medical Support
This aspect covers the comprehensive medical care provided to astronauts before, during, and after space missions. It includes pre-flight medical screening and conditioning, development of in-flight medical kits and procedures, and post-flight rehabilitation. An example would be managing bone density loss, cardiovascular deconditioning, and psychological stress associated with long-duration spaceflight. This requires an understanding of the physiological effects of microgravity and the development of countermeasures to mitigate these effects.
- Search and Rescue Medical Assistance
Aerospace medicine physicians may provide medical support during search and rescue operations involving aircraft incidents. This includes providing medical direction to rescue teams, triaging casualties, and coordinating medical evacuation. Real-world instances involve responding to downed aircraft in remote locations, necessitating expertise in wilderness medicine and disaster response. Effective coordination and resource management are essential in these time-sensitive scenarios.
- Aviation Disaster Response
In the event of a major aviation disaster, expertise may be called upon to assist in the medical response, including triage, mass casualty management, and psychological support to victims and their families. This role requires an understanding of disaster management principles, the ability to work effectively in a chaotic environment, and sensitivity to the emotional needs of those affected. Training in crisis communication and family assistance is also beneficial.
In summary, operational medical support is an indispensable aspect of the skills and responsibilities required. It encompasses a range of activities, from routine in-flight medical consultations to complex disaster response efforts, all aimed at protecting the health and well-being of those involved in aerospace operations. Proficiency in this area demands a unique blend of medical knowledge, operational awareness, and communication skills.
4. Research and Development
Research and development form an integral component of roles combining medical expertise with the domain of aviation and space. The inherent challenges posed by extreme environments and the limited data available concerning human physiology in these settings necessitate ongoing scientific investigation. These activities are not merely academic pursuits; they directly inform clinical practice, shape safety protocols, and drive technological innovation within this specialized field. For instance, research into the effects of prolonged microgravity on bone density has led to the development of targeted exercise regimens and pharmaceutical interventions for astronauts. Likewise, studies on the impact of cosmic radiation exposure have influenced spacecraft shielding designs and mission planning parameters.
Opportunities to engage in research and development exist across various sectors, including government agencies, academic institutions, and private aerospace companies. Physicians working in these capacities may conduct clinical trials to evaluate the efficacy of new medical countermeasures, investigate the biomechanics of injury mechanisms in flight environments, or develop advanced sensor technologies for physiological monitoring. Furthermore, advancements in telemedicine and artificial intelligence are creating new avenues for remote healthcare delivery and data analysis, requiring physicians with research expertise to validate and implement these technologies effectively. A concrete example is the use of AI-powered diagnostic tools to analyze astronaut health data in real-time, providing early warnings of potential medical issues.
In summary, research and development constitute a vital element of careers at the intersection of medicine and aerospace. It is the engine driving evidence-based practice, technological progress, and enhanced safety in extreme environments. Addressing the knowledge gaps regarding human health in the aerospace realm, coupled with the continuous pursuit of innovative solutions, ensures the continued well-being and operational effectiveness of those who venture into the skies and beyond. Ongoing scientific inquiry is essential to mitigate emerging risks and optimize human performance in future space exploration endeavors.
5. Regulatory Compliance Adherence
Regulatory compliance adherence is a fundamental aspect shaping the practice of medicine within the aerospace sector. These specialized physicians must navigate a complex web of regulations promulgated by national and international bodies to ensure the safety, health, and operational effectiveness of those working and traveling in the aerospace environment. Strict adherence to these guidelines is non-negotiable, forming the bedrock upon which ethical and responsible medical practice is built.
- FAA Medical Certification Standards
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) establishes rigorous medical standards for pilots, air traffic controllers, and other aviation personnel. Aerospace medicine physicians are often tasked with conducting medical examinations to determine if individuals meet these standards, adhering strictly to FAA guidelines for vision, hearing, cardiovascular health, and mental stability. Failure to comply with these standards can result in the denial or revocation of medical certificates, directly impacting an individual’s ability to perform their aviation-related duties. Examples include ensuring pilots meet visual acuity requirements without correction exceeding specified limits and evaluating cardiac risk factors to prevent in-flight incapacitation. Adherence to these FAA mandates is a core responsibility.
- International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) Regulations
The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) sets forth international standards and recommended practices for aviation safety, including medical requirements for flight crew. Aerospace medicine physicians operating in international contexts must be familiar with and adhere to ICAO regulations, which may differ from domestic standards. This necessitates a deep understanding of international aviation law and the ability to navigate varying medical certification processes across different countries. Ensuring compliance with ICAO standards is critical for maintaining interoperability and promoting aviation safety on a global scale. An example is the harmonization of medical assessment protocols to allow for seamless operation of flight crews across international borders.
- Space Agency Medical Guidelines
Space agencies, such as NASA, ESA, and Roscosmos, have stringent medical guidelines for astronauts participating in space missions. These guidelines address a wide range of issues, including pre-flight medical screening, in-flight medical care, and post-flight rehabilitation. Aerospace medicine physicians working with space agencies must be thoroughly familiar with these guidelines and ensure that astronauts meet the required health standards. Non-compliance can jeopardize mission safety and astronaut well-being. Strict adherence to protocols for quarantine and infectious disease control before and after spaceflights is a critical example.
- Data Privacy and Security Regulations (e.g., HIPAA)
Aerospace medicine physicians, like all healthcare professionals, are bound by data privacy and security regulations such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) in the United States. These regulations govern the handling of sensitive patient medical information, ensuring confidentiality and preventing unauthorized disclosure. Compliance with data privacy regulations is essential for maintaining patient trust and avoiding legal penalties. This includes implementing secure electronic health record systems, obtaining informed consent for data sharing, and safeguarding medical records from unauthorized access. Furthermore, unique challenges arise in the context of international collaborations and data transfer between space agencies and research institutions, demanding careful consideration of international data privacy laws.
The multifaceted nature of regulatory compliance in aerospace medicine necessitates a proactive and detail-oriented approach. Physicians in this field must continuously update their knowledge of evolving regulations and implement robust compliance programs within their respective organizations. These efforts are essential for upholding ethical standards, promoting patient safety, and ensuring the continued advancement of human exploration and utilization of the aerospace environment. Ultimately, thorough adherence to regulations safeguards both the individual and the broader aerospace community.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Opportunities Combining Medical Expertise with the Aerospace Field
This section addresses common inquiries and misconceptions related to career pathways for medical doctors seeking positions within aviation and space medicine.
Question 1: What are the fundamental differences between aerospace medicine and general practice?
Aerospace medicine focuses specifically on the physiological and psychological effects of flight and space travel on the human body, as well as the unique operational challenges presented by these environments. General practice encompasses a broader range of medical conditions and patient populations.
Question 2: What educational qualifications are typically required to pursue opportunities in this specialized medical field?
The standard requirements include a medical degree (MD or DO), completion of a residency in a primary care specialty (e.g., internal medicine, family medicine, emergency medicine), and specialized training in aerospace medicine, often through a residency or fellowship program. Board certification in aerospace medicine is also highly desirable.
Question 3: What are the typical work environments for medical professionals in this domain?
Work environments can vary widely, including government agencies (e.g., NASA, FAA), military facilities, commercial airlines, aerospace companies, and research institutions. The specific work environment depends on the nature of the role and the employer.
Question 4: What specific skills are particularly valuable in a career focusing on aviation or space-related medical care?
Valuable skills include a strong understanding of aerospace physiology, expertise in aviation safety and regulations, proficiency in emergency medical procedures, excellent communication and teamwork abilities, and the capacity to work effectively in stressful and dynamic environments.
Question 5: Is prior military experience a prerequisite for obtaining positions related to these roles?
While prior military experience can be beneficial, it is not always a strict requirement. Civilian opportunities exist within government agencies, commercial airlines, and private aerospace companies. However, military service often provides valuable training and experience in aerospace medicine.
Question 6: What is the career outlook for medical doctors specializing in this niche?
The career outlook remains generally positive, driven by continued growth in the aviation and space industries, increasing demand for medical expertise in these domains, and ongoing advancements in aerospace technology and exploration. Opportunities are expected to be competitive, however, emphasizing the importance of specialized training and relevant experience.
Key takeaways emphasize the significance of specialized training, adaptability, and a strong understanding of the unique medical challenges presented by flight and space travel.
The subsequent section will delve into resources and organizations offering support for those seeking to advance their expertise and secure positions in this specific field.
Conclusion Regarding Aerospace Medicine Physician Jobs
This exploration of opportunities in the field combining medicine with aviation and space has highlighted the unique responsibilities, required expertise, and diverse career paths available. Securing positions, often referred to as aerospace medicine physician jobs, necessitates specialized training, adaptability, and a commitment to protecting the health and safety of those who operate in extreme environments. The domains of research, operational support, and regulatory compliance form integral components of these roles, underscoring the multi-faceted nature of this medical discipline.
The continued advancement of aerospace technology and the increasing emphasis on human space exploration create a sustained demand for skilled medical professionals in this area. Prospective candidates are encouraged to pursue rigorous training, cultivate relevant experience, and remain vigilant regarding evolving regulatory standards. Successfully navigating the complexities of these positions yields opportunities to contribute meaningfully to the future of aviation and space endeavors, safeguarding the well-being of those who push the boundaries of human exploration.