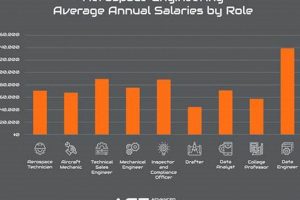
Positions overseeing projects within the aviation and space exploration sectors require a unique blend of technical expertise and leadership capabilities. These roles are responsible for the successful planning, execution, monitoring, and closure of initiatives related to aircraft, spacecraft, satellites, and related technologies. Individuals in this field ensure projects adhere to strict budgets, timelines, and quality standards, navigating complex regulatory landscapes and technological advancements.
Effective management of these projects is critical for maintaining safety, driving innovation, and achieving organizational objectives within the aerospace industry. Historically, these positions have played a crucial role in landmark achievements such as the development of commercial airliners, the exploration of space, and the advancement of defense technologies. Their contributions directly impact economic growth, technological progress, and national security.
The following sections will delve into the specific responsibilities, required skills, career paths, and compensation expectations associated with these managerial positions within the aerospace domain. Information regarding educational qualifications, certification requirements, and industry outlook will also be provided to offer a comprehensive overview of this career field.
Essential Guidance
The following recommendations are designed to provide valuable insight for individuals pursuing or currently engaged in project management roles within the aviation and space exploration domains. These are geared toward enhancing performance, navigating challenges, and maximizing career potential.
Tip 1: Cultivate Technical Proficiency: A comprehensive understanding of aerospace engineering principles, materials science, and relevant technologies is paramount. This knowledge base enables informed decision-making and effective communication with technical teams. Pursue continuing education opportunities to remain current with industry advancements.
Tip 2: Master Risk Management: Aerospace projects inherently involve complex risks. Proactively identify potential threats, assess their impact, and develop mitigation strategies. Implement robust risk tracking and reporting systems to ensure timely intervention.
Tip 3: Prioritize Regulatory Compliance: The aerospace industry is heavily regulated. Maintain a thorough understanding of applicable regulations, standards, and certification requirements. Implement rigorous compliance protocols to avoid costly penalties and ensure safety.
Tip 4: Develop Strong Communication Skills: Effective communication is essential for coordinating diverse teams, managing stakeholder expectations, and resolving conflicts. Hone written, verbal, and presentation skills to convey information clearly and persuasively.
Tip 5: Embrace Collaboration: Aerospace projects often involve multidisciplinary teams and external partners. Foster a collaborative environment that encourages open communication, knowledge sharing, and mutual respect. Build strong relationships with stakeholders at all levels.
Tip 6: Implement Robust Project Controls: Establish clear project objectives, milestones, and performance metrics. Implement comprehensive project tracking and reporting systems to monitor progress, identify deviations, and take corrective action. Utilize earned value management techniques to assess project performance objectively.
Tip 7: Seek Mentorship Opportunities: Guidance from experienced professionals can provide invaluable insights and accelerate career development. Seek out mentorship opportunities to learn from the expertise of seasoned project managers and expand professional networks.
Adherence to these recommendations will contribute to enhanced project outcomes, improved leadership effectiveness, and sustained professional growth. A proactive approach to skill development and a commitment to excellence are essential for success in this demanding field.
The following sections will build upon this guidance, providing a deeper exploration of career advancement opportunities and the evolving landscape of the aerospace industry.
1. Technical Expertise
Technical Expertise constitutes a foundational pillar for success in managerial positions within the aerospace sector. It empowers project managers to make informed decisions, effectively communicate with technical teams, and proactively address complex engineering challenges inherent in aviation and space exploration initiatives. This expertise is not merely theoretical but encompasses practical application and continuous learning within a rapidly evolving technological landscape.
- Systems Engineering Understanding
A thorough grasp of systems engineering principles is crucial for overseeing the design, development, and integration of complex aerospace systems. This includes proficiency in requirements management, interface control, and system verification and validation. For example, a project manager involved in the development of a new satellite must understand the interplay between various subsystems, such as power, communication, and propulsion, to ensure seamless integration and optimal performance. Misunderstanding of these systems can lead to design flaws, project delays, and increased costs.
- Materials and Manufacturing Processes
Knowledge of aerospace-grade materials and manufacturing processes is essential for making informed decisions regarding material selection, fabrication techniques, and quality control. Project managers must understand the properties of materials like titanium, composites, and alloys, as well as the limitations and capabilities of manufacturing processes such as machining, welding, and additive manufacturing. For instance, selecting the appropriate composite material for an aircraft wing requires understanding its strength-to-weight ratio, fatigue resistance, and environmental durability. Incorrect material selection can compromise structural integrity and safety.
- Aerodynamics and Propulsion Principles
A fundamental understanding of aerodynamics and propulsion principles is necessary for managing projects related to aircraft and spacecraft design and performance. This includes familiarity with concepts such as lift, drag, thrust, and specific impulse. A project manager overseeing the development of a new rocket engine must understand the thermodynamic principles governing combustion and nozzle design to optimize engine performance and efficiency. Insufficient knowledge in this area can lead to inefficient designs and compromised mission objectives.
- Software and Avionics Integration
Modern aerospace systems heavily rely on sophisticated software and avionics systems. Project managers must understand the principles of software engineering, real-time operating systems, and avionics integration. This includes familiarity with programming languages, communication protocols, and sensor technologies. For example, a project manager involved in the development of an autonomous flight control system must understand the algorithms and software architecture that govern the aircraft’s navigation and control. Lack of expertise in this domain can result in software bugs, system failures, and compromised safety.
These facets of technical expertise, taken together, empower those in managerial roles within the aerospace arena to navigate complexity, mitigate risks, and drive innovation. This foundation not only informs strategic decisions but also facilitates effective communication with specialized engineering teams, fostering a collaborative environment conducive to achieving project objectives and advancing the boundaries of aerospace technology.
2. Leadership Acumen
In the demanding field of aerospace project management, leadership acumen is not merely a desirable trait, but a fundamental requirement for success. The complexity of projects, involving intricate technical details, stringent regulatory compliance, and significant financial investment, necessitates a leader capable of providing clear direction, fostering collaboration, and making critical decisions under pressure. A project manager with strong leadership acumen can effectively navigate the inherent challenges, mitigate risks, and ultimately deliver projects on time and within budget. This involves the ability to inspire and motivate diverse teams of engineers, scientists, and other specialists, ensuring they work cohesively toward a common goal.
Instances of compromised leadership underscore the consequences of its absence. For example, a project focused on developing a new generation of satellites may encounter unforeseen technical issues during testing. A project manager lacking the necessary leadership acumen might struggle to effectively communicate the problem to stakeholders, leading to delays in decision-making and implementation of corrective actions. Such delays can result in cost overruns, missed deadlines, and even project cancellation. Conversely, a project manager with strong leadership skills would proactively address the issue, convene a team of experts, and collaboratively develop a solution, thereby minimizing the impact on the project’s overall timeline and budget. This proactive approach builds trust and confidence among team members and stakeholders, fostering a more resilient and effective project environment.
In summary, leadership acumen is inextricably linked to the successful execution of aerospace projects. It enables project managers to effectively guide complex initiatives, manage diverse teams, and navigate challenges inherent in the industry. Cultivating these skills is not merely beneficial, but essential for individuals aspiring to excel in this challenging and rewarding field. The capability to inspire, motivate, and make informed decisions under pressure ultimately distinguishes successful aerospace project managers and contributes to the advancement of innovation and progress within the industry.
3. Regulatory Compliance
Adherence to regulatory frameworks is a critical facet of roles overseeing projects within the aerospace sector. These frameworks, established by national and international bodies, govern the design, production, operation, and maintenance of aircraft, spacecraft, and related systems. Project managers in this field bear the responsibility of ensuring that all project activities align with these regulations, which address safety standards, environmental considerations, and operational protocols. The impact of non-compliance can range from project delays and financial penalties to catastrophic safety failures, underscoring the paramount importance of this component of the role.
Consider, for instance, a project involving the development of a new commercial aircraft. This project must adhere to stringent regulations set forth by aviation authorities such as the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) in the United States or the European Aviation Safety Agency (EASA). These regulations encompass aspects such as aircraft design, materials testing, manufacturing processes, and operational procedures. The project manager must ensure that all stages of the project, from initial design to final certification, comply with these requirements. Failure to do so could result in the aircraft being grounded or, in severe cases, lead to accidents and loss of life. Similarly, projects involving space exploration must comply with international treaties and regulations governing the use of outer space, including limitations on the placement of weapons and the prevention of space debris. Effective management of these compliance requirements demands meticulous documentation, rigorous testing, and ongoing communication with regulatory agencies.
In conclusion, regulatory compliance forms an indispensable element of managerial positions in the aerospace domain. The challenges inherent in navigating complex regulatory landscapes necessitate a thorough understanding of applicable rules, meticulous attention to detail, and a proactive approach to risk management. The practical significance of this understanding lies in safeguarding public safety, ensuring operational efficiency, and maintaining the integrity of the aerospace industry. A failure to prioritize compliance can have far-reaching consequences, both financially and ethically, highlighting the critical role project managers play in upholding the highest standards of regulatory adherence.
4. Budget Management
Effective allocation and oversight of financial resources are central to the role of a project manager within the aerospace industry. This responsibility extends beyond simple cost tracking to encompass strategic financial planning, risk assessment, and value optimization across the project lifecycle.
- Cost Estimation and Forecasting
Accurate cost estimation is paramount for securing project funding and establishing realistic financial targets. Aerospace projects often involve cutting-edge technology, unique manufacturing processes, and stringent quality control measures, all of which contribute to significant expenses. Project managers must employ sophisticated forecasting techniques to anticipate potential cost drivers, such as material price fluctuations, labor rate changes, and unforeseen technical challenges. Failure to accurately estimate costs can lead to budget overruns, project delays, and compromised scope.
- Financial Control and Monitoring
Maintaining strict financial control throughout the project lifecycle is essential for ensuring that expenditures remain within approved budget limits. This involves implementing robust tracking systems, conducting regular budget reviews, and proactively identifying and addressing potential cost variances. Project managers must also be adept at managing change requests, which often have significant budgetary implications. For instance, a change in design specifications may necessitate the procurement of new materials or the implementation of revised manufacturing processes, leading to increased costs. Effective financial control ensures that projects stay on track and deliver the intended value.
- Value Engineering and Cost Reduction
Value engineering is a systematic approach to identifying and eliminating unnecessary costs without compromising project performance or quality. Project managers play a key role in facilitating value engineering workshops, which bring together stakeholders from various disciplines to brainstorm cost-saving ideas. These ideas may involve the use of alternative materials, the simplification of design features, or the optimization of manufacturing processes. For example, switching from a traditional machining process to an additive manufacturing technique may reduce material waste and lead to significant cost savings. Successful implementation of value engineering initiatives can enhance project profitability and improve competitiveness.
- Contract Negotiation and Management
Aerospace projects often involve multiple contractors and subcontractors, each with their own financial terms and conditions. Project managers must possess strong negotiation skills to secure favorable contract terms and effectively manage contractor performance. This includes reviewing invoices, tracking progress payments, and resolving contract disputes. Effective contract management is essential for minimizing financial risks and ensuring that contractors deliver services and products in accordance with project requirements. For example, a project manager may negotiate a performance-based contract with a supplier, incentivizing them to meet or exceed established quality and delivery targets.
These interconnected facets underscore the critical role of budgetary competence in overseeing endeavors within the sector. Skillful management of resources not only sustains financial stability but also directly influences the successful realization of project objectives, solidifying its relevance in the realm of aerospace project management roles.
5. Risk Mitigation
Effective risk mitigation is an indispensable component of roles in the management of projects within the aerospace sector. The inherent complexity and technological sophistication of these projects, coupled with stringent regulatory oversight and significant financial investment, expose them to a wide spectrum of potential risks. These range from technical failures and supply chain disruptions to regulatory changes and economic downturns. Project managers must proactively identify, assess, and mitigate these risks to ensure projects achieve their objectives within defined timelines and budgets. Failure to do so can result in costly delays, performance degradation, and, in extreme cases, project cancellation. For instance, the development of a new spacecraft may be vulnerable to risks related to the reliability of critical components, the availability of launch facilities, and the potential for unforeseen technical challenges during integration and testing. Without a robust risk mitigation plan, these challenges can escalate into major setbacks, jeopardizing the entire mission.
Successful implementation of risk mitigation strategies often involves a combination of proactive planning, diligent monitoring, and adaptive responses. This may include conducting thorough risk assessments to identify potential threats, developing contingency plans to address specific risks, and implementing robust quality control measures to minimize the likelihood of technical failures. Project managers must also establish clear communication channels to ensure that all stakeholders are aware of potential risks and mitigation strategies. A practical example is the use of redundant systems in aircraft design to mitigate the risk of single-point failures. If a critical component malfunctions, the redundant system can automatically take over, preventing a catastrophic event. Another example is the establishment of backup suppliers for critical components to mitigate the risk of supply chain disruptions. These proactive measures demonstrate the practical application of risk mitigation principles in the aerospace industry.
In summary, proficient risk mitigation is fundamentally linked to successful outcomes in project management within the aerospace domain. It enables project managers to anticipate and address potential challenges, minimize disruptions, and ensure the reliable and efficient execution of projects. Given the high stakes and complex nature of these projects, the ability to effectively manage risk is not merely desirable, but essential for safeguarding investments, ensuring operational safety, and driving innovation within the aerospace sector.
6. Team Coordination
Successful execution of endeavors within aerospace projects hinges upon effective coordination among multidisciplinary teams. Roles that oversee these projects inherently demand exceptional team coordination skills due to the complex nature of the work. These roles often involve engineers, scientists, technicians, and specialists from various fields, each contributing specific expertise. Ineffective coordination can lead to miscommunication, duplicated efforts, conflicting priorities, and project delays, ultimately impacting project success. Therefore, the capability to synchronize activities and foster collaboration is a crucial element of these managerial positions.
Consider a project involving the design and construction of a new satellite. This endeavor necessitates the coordinated efforts of electrical engineers responsible for the satellite’s power systems, mechanical engineers designing the structural components, software engineers developing the onboard software, and communication specialists managing the data transmission systems. If these teams operate in silos without clear communication channels and shared goals, the project can quickly devolve into chaos. For example, a design change made by the mechanical engineering team may inadvertently affect the performance of the electrical power system, leading to costly rework. In contrast, a project manager who fosters open communication, establishes clear roles and responsibilities, and facilitates regular team meetings can mitigate these risks and ensure seamless integration of all subsystems. This project coordination extends beyond internal teams to include external contractors and suppliers, requiring the aerospace project manager to manage various stakeholders simultaneously.
The ability to harmonize the contributions of diverse teams is thus a central determinant of success in those managerial positions within the aerospace sector. Proper management of team coordination fosters efficiency, minimizes errors, and promotes innovation, ultimately contributing to the realization of project objectives. Given the complexity and the high-stakes nature of aerospace projects, the importance of this skillset cannot be overstated. Those seeking success in these positions would do well to prioritize the development and refinement of their team coordination abilities.
7. Strategic Vision
A long-term perspective is an essential attribute for managerial roles in the aerospace field. Such vision necessitates anticipating industry trends, technological advancements, and evolving market demands. These professionals should formulate strategic objectives that align with organizational goals and contribute to sustained competitiveness.
- Long-Term Planning and Forecasting
Formulating strategies and predicting future trends allows project managers to make decisions that not only address current project needs but also align with long-term organizational objectives. This involves analyzing market trends, technological advancements, and potential risks to ensure projects remain relevant and competitive over time. For example, a project focused on developing a new satellite communication system may need to consider the emergence of new technologies like quantum communication and the evolving needs of satellite imagery and data transmission.
- Innovation and Technology Adoption
Identifying and integrating innovative technologies is critical for maintaining a competitive edge in the aerospace sector. These roles should proactively seek out new technologies and assess their potential impact on project outcomes and organizational capabilities. This can include evaluating the feasibility of using additive manufacturing for aircraft components or exploring the application of artificial intelligence for autonomous flight control systems. Project managers with a forward-thinking mindset can position their organizations to capitalize on emerging opportunities and adapt to changing market conditions.
- Resource Allocation and Prioritization
Strategic vision influences how resources are allocated and prioritized across multiple projects and initiatives. These individuals must evaluate the potential return on investment for each project, considering factors such as market demand, technological feasibility, and strategic alignment. This involves making difficult choices about which projects to pursue, which technologies to invest in, and how to allocate limited resources. Effective resource allocation ensures that the organization focuses on initiatives that have the greatest potential to drive long-term growth and profitability.
- Stakeholder Engagement and Communication
Strategic perspective informs how a project manager engages with stakeholders, including senior executives, government agencies, and external partners. These managers must communicate the strategic rationale behind project decisions and solicit input from stakeholders to ensure alignment and buy-in. This involves articulating the potential benefits of the project, addressing concerns, and building consensus around a shared vision. Effective stakeholder engagement is essential for securing funding, obtaining regulatory approvals, and building strong relationships with key partners.
These elements intertwine to create a holistic understanding of how strategic vision is fundamental to success in this field. Individuals in these managerial positions not only focus on immediate project deliverables but also anticipate future trends, integrate innovative technologies, allocate resources strategically, and engage stakeholders effectively. These aspects will help ensure long term success and value.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following addresses prevalent inquiries regarding responsibilities, prerequisites, and career trajectories associated with managerial positions in the aerospace field.
Question 1: What are the typical educational qualifications sought for positions overseeing projects within the aerospace industry?
A bachelor’s degree in aerospace engineering, mechanical engineering, or a related field is generally required. A master’s degree in engineering, business administration, or project management is often preferred, particularly for senior-level positions.
Question 2: Are there specific certifications that enhance an applicant’s prospects in this career field?
Yes, certifications such as Project Management Professional (PMP) or Program Management Professional (PgMP) are widely recognized and valued by employers in the aerospace sector. These certifications demonstrate a commitment to professional standards and proficiency in project management methodologies.
Question 3: What are the core technical skills expected of individuals in these roles?
Proficiency in areas such as systems engineering, aerospace materials, manufacturing processes, and avionics systems is essential. A strong understanding of aerospace regulations and safety standards is also critical.
Question 4: What non-technical skills are crucial for success in this career path?
Leadership, communication, problem-solving, and decision-making skills are paramount. The ability to effectively manage diverse teams, navigate complex stakeholder relationships, and adapt to changing project requirements is also highly valued.
Question 5: What is the typical career progression for professionals in this field?
Entry-level positions often involve roles as project engineers or assistant project managers. With experience and demonstrated performance, individuals can advance to project manager, senior project manager, program manager, and ultimately, director-level positions with oversight of multiple projects or programs.
Question 6: What are the primary challenges associated with managing projects in the aerospace sector?
Common challenges include managing complex technical requirements, adhering to strict regulatory standards, mitigating risks associated with cutting-edge technologies, and coordinating diverse teams across multiple locations. Budget constraints and tight deadlines can also present significant challenges.
In summary, managerial roles within aviation and space endeavors necessitate a blend of technical proficiency, leadership capabilities, and commitment to regulatory compliance. Candidates are encouraged to cultivate expertise, obtain professional credentials, and refine soft skills to thrive in this field.
The subsequent sections will explore strategies for career advancement and offer insights into emerging trends shaping the future of positions within aerospace projects.
Conclusion
This exploration has provided a comprehensive overview of “aerospace project manager jobs”, detailing the requisite skills, responsibilities, and challenges inherent in these roles. A clear understanding of technical principles, regulatory frameworks, and effective leadership techniques is crucial for success. The ability to manage budgets, mitigate risks, coordinate teams, and maintain a strategic vision are also essential competencies.
As the aerospace sector continues to evolve, the demand for skilled project managers will likely increase. Professionals who proactively develop their expertise and embrace continuous learning will be well-positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities and contribute to the advancement of aviation and space exploration. The commitment to excellence and a thorough grasp of project management principles remain paramount for those seeking to excel in this field.