Positions targeting individuals who have recently completed their academic qualifications in aerospace engineering, situated within New York City, are opportunities for initial professional experience. These roles typically involve assisting senior engineers in design, testing, research, and development within aerospace-related projects. A recent graduate contributing to a spacecraft component design under the supervision of a licensed engineer exemplifies such a position.
These openings are crucial for launching careers in a specialized field. They offer practical experience, mentorship, and networking opportunities, all vital for professional growth. Historically, the availability of such roles in a specific geographic location like New York City has reflected the presence and strength of aerospace-related industries and research institutions within that area.
The subsequent sections will delve into specific companies offering these opportunities, the required qualifications, potential career trajectories, and resources available to aid in securing such a position. Understanding these elements is essential for individuals seeking to establish themselves in the field within this metropolitan area.
Securing Opportunities
The following guidelines are designed to enhance the prospects of securing a beginning role in aerospace engineering within the New York City area. Diligence and strategic preparation are paramount for navigating this competitive field.
Tip 1: Targeted Resume Construction: A resume must highlight relevant coursework, projects, and software proficiency. Specify experience with CAD software, simulation tools, or specific aerospace engineering disciplines. For example, explicitly list any involvement in wind tunnel testing or finite element analysis projects.
Tip 2: Strategic Networking: Active participation in industry events and professional organizations, such as AIAA, is vital. Attend conferences, career fairs, and informational sessions to connect with potential employers and gain insights into the local job market.
Tip 3: Tailored Cover Letter: A generic cover letter is insufficient. Customize each cover letter to align with the specific requirements and values of the target company. Research the organization’s recent projects and articulate how skills and experience can contribute to their ongoing initiatives.
Tip 4: Proactive Portfolio Development: Create a portfolio showcasing relevant projects and skills. This can include design reports, simulation results, or contributions to engineering teams. A well-structured portfolio demonstrates practical abilities and a commitment to the field.
Tip 5: Internship Pursuit: Prior internship experience is highly valued. Actively seek internship opportunities with aerospace companies or related organizations to gain practical experience and establish professional connections.
Tip 6: Proficiency in Required Software: Demonstrate proficiency in industry-standard software. This may include MATLAB, SolidWorks, ANSYS, or other specialized tools used in aerospace engineering. Certifications or specific project experience using these tools will strengthen candidacy.
Tip 7: Local Job Market Research: Focus efforts on companies and research institutions with a presence in New York City. Understanding the specific needs and specializations of these organizations is crucial for tailoring applications.
Adhering to these recommendations will significantly increase the likelihood of securing a coveted beginning position in the aerospace sector within the New York City area. Consistent effort and a strategic approach are key to success.
The subsequent sections will explore specific companies and resources available to assist in the job search process.
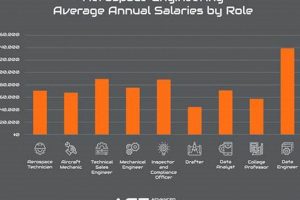
1. Salaries
Salaries represent a primary consideration for individuals pursuing beginning roles in aerospace engineering within New York City. Compensation packages directly influence the attractiveness of these positions and play a crucial role in attracting and retaining qualified personnel. The cost of living in New York City, significantly higher than the national average, necessitates competitive salaries to ensure a reasonable standard of living for entry-level engineers.
The impact of salary extends beyond basic necessities. It affects an individual’s ability to manage student loan debt, invest in professional development opportunities, and secure housing within reasonable commuting distance of employment locations. For instance, a higher starting salary may enable an engineer to afford housing closer to companies in Brooklyn or Manhattan, reducing commute times and enhancing overall quality of life. Conversely, a lower salary could necessitate longer commutes from more affordable outer boroughs or neighboring states, impacting work-life balance. Specific salary ranges vary based on the company, the precise role, and the candidate’s qualifications. Researching salary data from sources like the Bureau of Labor Statistics and industry-specific salary surveys is critical for negotiating a fair compensation package.
In summary, salary is a pivotal component of beginning roles in aerospace engineering jobs NYC. It influences an engineer’s financial well-being, career trajectory, and overall satisfaction. Understanding the prevailing salary landscape and negotiating effectively are essential for securing a position that aligns with both professional aspirations and financial needs. Furthermore, salaries often correlate with the types of projects an engineer will be involved in, for example, designing new drone technologies versus maintaining existing aviation systems.
2. Qualifications
The requisite qualifications significantly determine an individual’s eligibility for beginning roles in aerospace engineering within New York City. These requirements serve as filters, ensuring that candidates possess the fundamental knowledge, skills, and credentials necessary to contribute effectively to the field.
- Educational Attainment
A Bachelor’s degree in Aerospace Engineering, or a closely related field such as Mechanical Engineering with a specialization in aerospace, is typically mandatory. Coursework should include aerodynamics, propulsion, structures, and control systems. For instance, a graduate lacking formal training in computational fluid dynamics may be deemed unqualified for roles involving aerodynamic analysis. Furthermore, some positions may require or prefer a Master’s degree, particularly those involving research or advanced design.
- Technical Skills
Proficiency in relevant software is crucial. This includes CAD software (e.g., SolidWorks, CATIA), simulation tools (e.g., ANSYS, MATLAB), and programming languages (e.g., Python, C++). For example, an engineer tasked with designing satellite components must be adept at using CAD software to create detailed models and simulation tools to analyze their structural integrity. A lack of demonstrable skills in these areas can significantly impede candidacy.
- Internship Experience
Prior internship experience within the aerospace industry or a related field is highly advantageous. Internships provide practical, hands-on experience and allow candidates to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world problems. For instance, an internship at a company involved in aircraft maintenance or unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) development would demonstrate relevant experience and enhance an applicant’s qualifications. A lack of practical experience can often be a disadvantage in the competitive job market.
- Communication Skills
Effective communication skills, both written and verbal, are essential for collaborating with multidisciplinary teams, presenting technical findings, and documenting design processes. Aerospace engineers must be able to clearly articulate complex technical concepts to both technical and non-technical audiences. For example, an engineer may need to present a design proposal to management or explain a technical issue to a client. Deficiencies in communication skills can hinder collaboration and project success.
The alignment of an applicant’s qualifications with the specific requirements of beginning roles in aerospace engineering within New York City is paramount. Possessing the necessary educational background, technical skills, practical experience, and communication abilities significantly increases the likelihood of securing employment in this competitive field. These qualifications not only demonstrate competence but also reflect a commitment to professional development and a capacity for continuous learning, essential attributes for success in a rapidly evolving industry.
3. Companies
The presence and nature of aerospace companies within New York City directly influence the availability and characteristics of beginning roles in the aerospace engineering sector. The types of companies present shape the specific skills in demand and the nature of projects available to entry-level engineers.
- Established Aerospace Manufacturers
While large-scale aircraft manufacturing is not prevalent within New York City proper, companies involved in the supply chain, component manufacturing, or maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO) operations may exist. These firms offer positions in design support, quality control, and testing. For example, a company specializing in avionics systems might hire junior engineers to assist in the testing and validation of navigation equipment. The availability of these positions is contingent upon the overall health and growth of the wider aerospace manufacturing industry.
- Research and Development Firms
New York City hosts a number of research and development firms, some of which focus on aerospace-related technologies. These organizations may be involved in developing novel propulsion systems, advanced materials, or unmanned aerial vehicle technologies. They offer opportunities for beginning engineers to participate in cutting-edge research and contribute to the advancement of aerospace knowledge. However, the number of such positions may be limited and highly competitive.
- Government Agencies and Contractors
Government agencies and contractors often have a presence in major metropolitan areas. These entities may be involved in projects related to defense, space exploration, or air traffic management. They offer a range of positions for aerospace engineers, including roles in systems engineering, project management, and regulatory compliance. Securing employment with these organizations often requires U.S. citizenship and the ability to obtain security clearances.
- Consulting Firms
Engineering consulting firms that specialize in aerospace or aviation services also provide employment opportunities. These firms offer expertise to a variety of clients, including airlines, airports, and aerospace manufacturers. Beginning engineers may assist in tasks such as airport planning, aircraft performance analysis, or regulatory compliance audits. Consulting positions often require strong analytical and problem-solving skills.
The composition of the aerospace industry within New York City, characterized by a mix of established manufacturers, research firms, government contractors, and consulting services, shapes the landscape of beginning roles in aerospace engineering. Individuals seeking employment in this sector must research specific companies and tailor their qualifications to align with the skills and experience in demand by these organizations.
4. Location
The geographical element inherent in “entry level aerospace engineering jobs nyc” exerts a profound influence on career prospects and professional experiences. The city’s unique ecosystem, defined by its economic density, concentration of educational institutions, and specific industry clusters, directly shapes the opportunities available to aspiring aerospace engineers. Consequently, understanding the interplay between location and career trajectory becomes paramount.
The presence, or absence, of major aerospace manufacturing hubs within New York City directly impacts the type and quantity of available beginning roles. While New York City may lack the large-scale manufacturing facilities found in other regions, its proximity to research institutions, government agencies, and specialized engineering firms creates alternative pathways for entry-level engineers. For instance, positions might exist in aerospace-related research at universities like Columbia or NYU, or within smaller firms specializing in UAV technology or satellite communications. Commuting distance, transportation costs, and overall cost of living within the NYC metropolitan area further influence an engineer’s career choices and financial well-being. These factors underscore the practical necessity of considering location-specific opportunities and challenges when seeking “entry level aerospace engineering jobs nyc.”
The interplay between location and career extends beyond initial employment. Opportunities for professional development, networking events, and access to industry experts are often concentrated in major metropolitan areas like New York City. The city’s vibrant ecosystem fosters innovation and provides ongoing learning opportunities, essential for long-term career growth. However, the high cost of living presents a persistent challenge, requiring careful consideration of salary expectations and financial planning. Ultimately, understanding the opportunities and constraints associated with “entry level aerospace engineering jobs nyc” necessitates a comprehensive assessment of the location’s influence on career advancement and personal satisfaction. This analysis, informed by real-world examples and practical considerations, is essential for making informed career decisions.
5. Competition
Competition represents a significant element within the context of “entry level aerospace engineering jobs nyc.” The limited number of positions relative to the pool of qualified applicants creates a highly competitive environment. This competition directly impacts the difficulty of securing employment and necessitates a strategic approach to job searching. Factors contributing to this intense competition include the prestige associated with aerospace engineering, the concentration of universities producing aerospace graduates in the Northeast region, and the presence of a finite number of aerospace-related companies and organizations within the New York City metropolitan area. For example, a single opening at a company specializing in drone technology could attract hundreds of applications from recent graduates across the country.
The effects of this competitive landscape are multifaceted. It elevates the importance of academic excellence, relevant internship experience, and demonstrable technical skills. A candidate with a higher GPA, multiple internships at reputable firms, and proficiency in industry-standard software possesses a distinct advantage over other applicants. Moreover, strong networking skills and the ability to effectively communicate one’s qualifications become crucial differentiating factors. The competition also incentivizes individuals to pursue advanced degrees or specialized certifications to further enhance their marketability. Companies can leverage this high level of competition to select the most qualified candidates, ensuring a highly skilled workforce.
In summary, competition constitutes a fundamental reality of seeking “entry level aerospace engineering jobs nyc.” Recognizing the intensity of this competition and proactively addressing the factors that contribute to it are essential for aspiring aerospace engineers. This includes cultivating a strong academic record, acquiring practical experience, developing technical proficiency, honing communication skills, and strategically networking within the industry. Understanding the dynamics of competition is not merely an academic exercise but a practical necessity for navigating the job market and achieving career success. The subsequent section explores specific strategies for differentiating oneself in this competitive environment.
6. Opportunities
The availability of prospects constitutes a pivotal factor for individuals seeking beginning roles in the aerospace engineering field within New York City. The scope and character of these prospects directly influence career trajectories and professional development.
- Specialized Design and Analysis Roles
Engineering firms often require support in design, modeling, and simulation tasks. Entry-level engineers may be involved in finite element analysis, computational fluid dynamics simulations, or CAD modeling for aerospace components. An example includes assisting in the design of lightweight materials for aircraft structures or optimizing the aerodynamic performance of UAVs. These roles offer practical experience in applying engineering principles to real-world problems.
- Research and Development Positions
Universities and research institutions provide avenues for participating in cutting-edge research. These positions may involve experimental testing, data analysis, or the development of new aerospace technologies. Involvement in research projects focused on advanced propulsion systems or autonomous flight control algorithms exemplifies such opportunities. These experiences foster innovation and contribute to the advancement of the aerospace field.
- Systems Engineering and Integration
Opportunities exist in integrating various aerospace systems, ensuring their compatibility and functionality. Beginning engineers may assist in developing system requirements, conducting integration testing, or troubleshooting system malfunctions. An example includes integrating communication systems into satellite platforms or validating the performance of aircraft navigation systems. These roles provide a broad understanding of aerospace systems and their interactions.
- Quality Assurance and Testing
Ensuring the reliability and safety of aerospace components is crucial. Entry-level engineers may be involved in quality control inspections, non-destructive testing, or performance evaluations. An example includes conducting material testing on aircraft components to ensure they meet safety standards or performing functional tests on electronic systems used in spacecraft. These roles emphasize attention to detail and adherence to industry regulations.
These prospects, encompassing design, research, systems integration, and quality assurance, collectively shape the landscape of beginning roles in aerospace engineering within New York City. Securing these opportunities requires a combination of technical skills, practical experience, and a proactive approach to career development. Understanding the nature and scope of these prospects is crucial for aspiring aerospace engineers seeking to establish themselves in this field. For example, engineers involved in designing new drone technologies versus maintaining existing aviation systems illustrates the differences between research opportunities and existing engineering opportunities.
7. Growth
The long-term potential for advancement constitutes a critical element in evaluating “entry level aerospace engineering jobs nyc.” Initial positions, while providing foundational experience, should serve as stepping stones towards increased responsibility, expertise, and compensation. The availability of growth opportunities significantly influences the attractiveness of these roles and contributes to employee retention within specific companies and the broader aerospace sector in New York City. Companies offering structured career development programs, mentorship initiatives, or opportunities to pursue advanced training are more likely to attract ambitious entry-level engineers. For instance, a junior engineer joining a firm involved in designing satellite communication systems would ideally have a clear path towards becoming a project lead or a specialist in a particular area of satellite technology. Conversely, a role lacking clear opportunities for advancement may be less appealing, even with a competitive starting salary.
Several factors influence the availability of career growth within “entry level aerospace engineering jobs nyc.” The size and stability of the employing company, the company’s commitment to innovation and expansion, and the individual’s performance and skills development all play crucial roles. A smaller company focused on a niche market may offer limited opportunities for vertical advancement but potentially provide exposure to a wider range of responsibilities. Larger, more established companies may have structured career ladders, but advancement may require more time and competition. Moreover, the pursuit of relevant certifications (e.g., Professional Engineer license) and the acquisition of new technical skills are essential for maximizing growth potential. Attending industry conferences, publishing research papers, or contributing to open-source projects are all strategies for demonstrating a commitment to continuous learning and professional development.
In summary, the prospect of career “Growth” is an indispensable consideration when evaluating “entry level aerospace engineering jobs nyc.” Opportunities for advancement, driven by company policies, individual performance, and continuous learning, significantly impact long-term career satisfaction and earning potential. Aspiring aerospace engineers should carefully assess the growth potential associated with specific positions and proactively pursue strategies to enhance their skills and expertise, ensuring a trajectory of upward mobility within the industry.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding entry-level employment opportunities in aerospace engineering within the New York City area. These responses aim to provide clarity and guidance for prospective applicants.
Question 1: What academic qualifications are typically required for entry-level aerospace engineering positions in New York City?
A bachelor’s degree in aerospace engineering or a closely related field, such as mechanical engineering with an aerospace concentration, is generally required. Coursework should encompass core areas such as aerodynamics, propulsion, structures, and control systems. Some positions may prefer candidates with master’s degrees, particularly for research-oriented roles.
Question 2: What specific technical skills are most valued by employers offering entry-level aerospace engineering jobs in NYC?
Proficiency in industry-standard software packages is highly valued. This includes CAD software (e.g., SolidWorks, CATIA), simulation tools (e.g., ANSYS, MATLAB), and programming languages (e.g., Python, C++). Familiarity with finite element analysis and computational fluid dynamics is also beneficial.
Question 3: Is prior internship experience essential for securing entry-level aerospace engineering employment in New York City?
While not always explicitly required, prior internship experience is highly advantageous. Internships provide practical, hands-on experience and allow candidates to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world problems. Candidates with relevant internship experience are generally viewed more favorably.
Question 4: What is the typical salary range for entry-level aerospace engineering jobs in NYC, considering the city’s high cost of living?
Salary ranges vary depending on the company, the specific role, and the candidate’s qualifications. However, the high cost of living in New York City generally necessitates a competitive salary. Researching industry salary data and negotiating effectively is crucial.
Question 5: What types of companies in New York City offer entry-level aerospace engineering positions?
Opportunities may be found at aerospace manufacturers, research and development firms, government agencies and contractors, and engineering consulting firms. The specific types of companies present in New York City influence the skills in demand.
Question 6: How competitive is the job market for entry-level aerospace engineers in New York City?
The job market is generally highly competitive due to the limited number of positions and the large pool of qualified applicants. Candidates should strive to distinguish themselves through academic excellence, practical experience, and strong communication skills.
Securing a beginning role in aerospace engineering within New York City demands rigorous preparation and a strategic approach. Addressing these frequently asked questions is an initial step toward navigating this competitive landscape.
The following section will explore actionable steps to enhance your candidacy and increase your chances of securing employment in this field.
The preceding analysis has explored critical facets of “entry level aerospace engineering jobs nyc.” Key considerations encompass academic qualifications, technical skills, industry sectors, location-specific challenges, competitive dynamics, career growth prospects, and associated financial implications. A comprehensive understanding of these elements is paramount for aspiring aerospace engineers seeking to establish themselves professionally within the New York City metropolitan area.
Successfully securing a position in this field requires proactive planning, targeted skill development, and diligent networking. Aspiring professionals are encouraged to leverage the insights provided herein to inform their career strategies and maximize their potential for success. The pursuit of “entry level aerospace engineering jobs nyc” represents a significant undertaking, and informed preparation remains the most reliable path toward achieving professional goals.