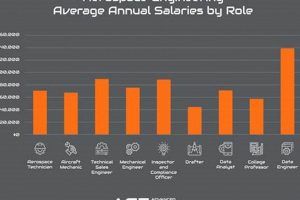
Positions within the aeronautics and astronautics sectors that offer the greatest financial compensation often require specialized skills, advanced education, and significant experience. These roles frequently involve leading-edge technology, complex project management, and critical decision-making responsibilities. For example, a Chief Technology Officer at a major aerospace manufacturer generally commands a substantial salary due to their strategic oversight of technological innovation.
The significance of these high-remuneration positions lies in their contribution to industry advancement, economic growth, and national security. Historically, investment in aerospace technology has spurred job creation and driven technological breakthroughs across various fields. Benefits associated with these roles extend beyond monetary compensation, encompassing intellectual stimulation, opportunities for global collaboration, and the potential to shape the future of air and space travel.
Subsequent sections will delve into specific examples of these roles, detailing the qualifications, responsibilities, and earning potential associated with each. The focus will be on providing a comprehensive overview of career paths that offer both financial reward and significant impact within the aeronautical and astronautical domains.
Securing a position among the most financially rewarding careers in the aeronautics and astronautics fields requires strategic planning, dedicated effort, and a proactive approach to professional development. The following tips offer guidance for aspiring professionals seeking to maximize their earning potential within these industries.
Tip 1: Pursue Advanced Education: A master’s degree or doctorate in a specialized field, such as aerospace engineering, materials science, or advanced propulsion systems, can significantly enhance earning potential. For instance, a Ph.D. in computational fluid dynamics can open doors to research and development roles with higher salary expectations.
Tip 2: Acquire Specialized Skills: Develop expertise in high-demand areas like unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) technology, satellite communication systems, or cybersecurity for aerospace applications. Proficiency in these areas makes candidates more attractive to employers seeking specialized knowledge.
Tip 3: Gain Practical Experience: Internships, co-op programs, and entry-level positions provide valuable hands-on experience. Actively seek opportunities to work on complex projects, demonstrating the ability to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world challenges.
Tip 4: Obtain Relevant Certifications: Certifications such as Professional Engineer (PE) or project management certifications (PMP, PRINCE2) demonstrate competence and commitment to professional standards. These credentials can distinguish candidates from their peers.
Tip 5: Network Strategically: Attend industry conferences, join professional organizations (e.g., AIAA, IEEE), and connect with experienced professionals in the field. Building a strong network can provide access to job opportunities and valuable mentorship.
Tip 6: Develop Leadership Abilities: Cultivate leadership skills through involvement in team projects, volunteer activities, or professional development programs. Demonstrating the ability to lead and motivate others is crucial for advancement to higher-paying management positions.
Tip 7: Stay Informed About Industry Trends: Continuously monitor advancements in aerospace technology, regulatory changes, and market trends. Maintaining up-to-date knowledge is essential for adapting to evolving industry demands and identifying emerging opportunities.
By focusing on advanced education, specialized skills, practical experience, and strategic networking, aspiring professionals can significantly increase their likelihood of securing a position among the most financially rewarding careers within the aerospace sector. A proactive and dedicated approach is essential for navigating this competitive landscape and achieving long-term career success.
The subsequent conclusion will provide a final overview of considerations when pursuing high-paying roles within the aerospace industry.
1. Education
Educational attainment serves as a primary determinant in accessing the most financially rewarding positions within the aerospace sector. The rigor and specialization of academic training directly influence an individual’s capacity to perform complex tasks, innovate, and lead within this highly technical industry. Investment in advanced education often translates to significantly enhanced earning potential.
- Advanced Degrees (Master’s and Doctoral)
Possessing a Master’s degree or a Ph.D. in aerospace engineering, or a related field such as mechanical engineering or physics, provides a strong foundation for specialized roles. These degrees signify a deeper understanding of complex concepts and methodologies, enabling graduates to contribute to cutting-edge research, design, and development. For instance, a Ph.D. in computational fluid dynamics is often a prerequisite for leading research teams focused on optimizing aircraft aerodynamics, a role commanding a substantial salary. The advanced knowledge and research skills developed during doctoral studies are highly valued by aerospace companies.
- Specialized Coursework and Training
Targeted coursework and specialized training programs are critical for developing specific expertise in high-demand areas. Fields such as avionics, propulsion systems, and space mission design require in-depth knowledge gained through specialized academic programs. Certifications and training in areas like systems engineering or project management can further enhance a candidate’s qualifications. These focused educational experiences equip individuals with the practical skills and theoretical knowledge necessary to excel in specialized roles, such as designing and implementing complex aerospace systems.
- Research Experience and Publications
Active participation in research projects and the publication of scholarly articles are indicators of a candidate’s ability to conduct independent inquiry, analyze data, and contribute to the advancement of knowledge. Research experience demonstrates a commitment to pushing the boundaries of aerospace technology and a capacity for innovation. Candidates with a strong publication record are often highly sought after for research and development positions, which are typically among the most financially rewarding in the industry. For example, publishing research on new materials for aerospace applications can lead to opportunities in advanced materials engineering roles with premium salaries.
- Accreditation and Institutional Reputation
Graduation from an accredited university with a strong reputation in aerospace engineering significantly enhances career prospects. Accreditation ensures that a program meets rigorous academic standards and provides students with a high-quality education. Employers often prioritize candidates from well-regarded institutions due to the perceived rigor and quality of their academic programs. The prestige associated with certain universities can open doors to exclusive networking opportunities and internships, further enhancing career prospects and access to higher-paying positions. Furthermore, a strong alumni network from a reputable institution can provide valuable connections and mentorship opportunities throughout one’s career.
In summary, the level and type of education attained directly influences access to positions at the upper echelons of compensation within the aerospace field. Advanced degrees, specialized training, research experience, and the reputation of the educational institution are all factors contributing to an individual’s earning potential. Continued investment in education and professional development remains a critical pathway to career advancement and financial success in this highly competitive industry.
2. Experience
Practical experience represents a cornerstone in securing high-remuneration roles within the aerospace sector. Beyond theoretical knowledge, demonstrable proficiency in applying skills to real-world challenges is highly valued by employers seeking candidates for leadership and specialized positions.
- Project Leadership and Management
Leading and managing complex aerospace projects, from design to implementation, is a critical factor in achieving higher earning potential. This includes demonstrable experience in managing budgets, timelines, and teams, while ensuring projects meet technical specifications and regulatory requirements. For instance, successfully overseeing the development of a new aircraft wing design from initial concept to prototype testing directly correlates with elevated compensation due to the demonstrated ability to deliver tangible results.
- Technical Expertise and Problem Solving
Significant experience in solving complex technical challenges within specific aerospace domains, such as propulsion systems, avionics, or structural engineering, is highly prized. This entails a proven track record of identifying and resolving technical issues, implementing innovative solutions, and optimizing system performance. Example of this is a specialist with extensive experience in troubleshooting and enhancing the efficiency of jet engines is often highly compensated due to the specialized nature and critical importance of their skills.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration
The ability to effectively collaborate with diverse teams across different functional areas, such as engineering, manufacturing, and marketing, is essential for success in high-level aerospace positions. Experience in facilitating communication, resolving conflicts, and integrating diverse perspectives is crucial for achieving project goals. For example, an engineer with a proven track record of collaborating effectively with both design and manufacturing teams to optimize product manufacturability is highly valued.
- Regulatory Compliance and Safety
Extensive experience in navigating and complying with complex regulatory frameworks, such as those imposed by the FAA or NASA, is essential for roles involving aircraft design, manufacturing, and operation. This includes a thorough understanding of safety standards, certification processes, and risk management protocols. For example, an engineer with significant experience in ensuring aircraft designs meet stringent safety regulations is highly compensated due to the critical importance of their role in preventing accidents and ensuring passenger safety.
These facets of experience collectively contribute to an individual’s market value within the aerospace sector. Demonstrable expertise in project leadership, technical problem-solving, cross-functional collaboration, and regulatory compliance are key indicators of a candidate’s ability to contribute to the success of complex aerospace ventures and command top-tier compensation.
3. Specialization
The correlation between specialization and positions of high remuneration within the aerospace industry is significant. Advanced technical fields demand concentrated expertise. The higher the degree of specialization, the greater the likelihood of assuming roles with complex responsibilities, critical decision-making authority, and, consequently, elevated compensation. The cause is the demand for specific knowledge, and the effect is increased earnings for those who possess it. For instance, an aerospace engineer specializing in hypersonic propulsion systemsa field with limited experts and high technological challengesis likely to command a salary substantially greater than a general aerospace engineer. This is because their niche skillset directly addresses critical needs in advanced aerospace projects.
Examples of specializations leading to increased financial reward are numerous. Consider experts in autonomous flight control systems for unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). As UAV technology expands into commercial and defense applications, demand for these specialists escalates, driving up salaries. Similarly, professionals with expertise in cybersecurity for aerospace systems are highly valued due to the increasing threat of cyberattacks on aircraft and satellites. Expertise in areas like advanced materials, quantum computing applications in aerospace, or novel propulsion methods also lead to high-paying positions. These areas require deep knowledge and innovative thinking, making specialists indispensable.
Understanding the relationship between specialization and compensation is of practical significance for those pursuing careers in aerospace. By identifying areas of critical need and investing in specialized training, engineers and scientists can strategically position themselves for high-paying roles. However, it is crucial to note that specialization also brings challenges. The rapidly evolving nature of technology requires continuous learning and adaptation to maintain relevance. Furthermore, niche specializations can limit career mobility if the specific technology becomes obsolete. Despite these challenges, strategic specialization remains a key factor in accessing the highest-paying aerospace jobs, demanding continuous learning and adaptation within a dynamic technological environment.
4. Location
Geographic location exerts a substantial influence on compensation levels within the aerospace sector. Certain regions, characterized by a high concentration of aerospace companies, research institutions, and government facilities, offer significantly greater opportunities for high-remuneration positions.
- Aerospace Hubs and Clusters
Areas designated as aerospace hubs, such as Seattle, Washington; Los Angeles, California; and the Space Coast of Florida, typically exhibit higher salary ranges due to the competitive demand for skilled professionals. The presence of major aerospace manufacturers, suppliers, and research facilities creates a concentrated job market where companies actively compete for talent. For example, engineers with similar qualifications may command higher salaries in Seattle, home to Boeing, compared to regions with a less concentrated aerospace industry.
- Cost of Living Adjustments
Compensation structures often incorporate cost-of-living adjustments to reflect the economic realities of different geographic locations. Regions with higher living expenses, such as the San Francisco Bay Area or New York City, may offer higher salaries to offset the increased cost of housing, transportation, and other essential goods and services. However, it is crucial to consider the net disposable income after accounting for these expenses when evaluating job offers in different locations.
- Proximity to Research and Development Centers
Positions located near major research and development centers, such as NASA facilities or leading university aerospace engineering departments, tend to offer greater opportunities for high-paying roles. These locations often attract highly skilled researchers, engineers, and scientists who contribute to cutting-edge advancements in aerospace technology. Proximity to these centers facilitates collaboration, knowledge sharing, and access to specialized resources, leading to enhanced career prospects and higher salaries.
- Government and Defense Spending
Regions with a significant presence of government and defense contractors often experience increased demand for aerospace professionals, resulting in higher compensation levels. Areas with military bases, aerospace-related government agencies, and major defense contractors benefit from consistent investment in aerospace technology and infrastructure. This demand creates a stable job market and provides opportunities for engineers and scientists to work on critical national security projects, commanding premium salaries.
These interconnected factors highlight the importance of location in determining compensation within the aerospace industry. Proximity to aerospace hubs, cost-of-living considerations, access to research and development centers, and the presence of government and defense spending collectively shape the earning potential for aerospace professionals in different geographic regions. Strategically selecting a location that aligns with one’s career goals and financial aspirations can significantly impact long-term career success.
5. Industry Sector
The specific industry sector within aerospace significantly influences earning potential. Variations in funding, technological focus, and market demand across sectors create disparities in compensation for similar roles. Understanding these sector-specific dynamics is critical for professionals seeking the most financially rewarding positions.
- Commercial Aviation
The commercial aviation sector, encompassing aircraft manufacturers, airlines, and maintenance providers, offers a range of high-paying positions, particularly in engineering, management, and executive leadership. Demand for fuel-efficient aircraft, advanced avionics, and improved passenger experience drives investment and innovation, leading to increased compensation for skilled professionals. For example, chief engineers overseeing the design of next-generation aircraft or airline executives managing fleet operations often command substantial salaries.
- Defense and Government
The defense and government sector, including defense contractors, government agencies like NASA, and military branches, represents a significant source of high-paying aerospace jobs. Roles in research and development, systems engineering, and program management within this sector are often highly compensated due to the complexity of the projects, the criticality of national security, and the specialized expertise required. Program managers overseeing the development of advanced missile systems or scientists conducting research on hypersonic flight are examples of positions with significant earning potential.
- Space Exploration
The space exploration sector, encompassing companies involved in satellite development, launch services, and space tourism, presents unique opportunities for high-paying positions. The technological challenges inherent in space exploration, such as developing advanced propulsion systems, designing radiation-hardened electronics, and ensuring life support in extreme environments, require highly specialized skills and expertise. Engineers designing spacecraft for deep-space missions or mission controllers managing satellite operations are examples of roles with significant financial rewards.
- Emerging Technologies
The sector focused on emerging technologies, including companies involved in electric aircraft, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), and advanced air mobility (AAM), is experiencing rapid growth and offers increasing opportunities for high-paying aerospace jobs. The innovative nature of these technologies, coupled with significant venture capital investment, creates a competitive market for skilled professionals. Engineers designing electric propulsion systems for eVTOL aircraft or software developers creating autonomous flight control systems for UAVs are examples of positions with substantial earning potential in this rapidly evolving sector.
The varied priorities and investment levels within each aerospace sector directly impact the compensation landscape. While certain roles may be common across multiple sectors, the financial rewards can vary significantly based on the specific industry dynamics, technological focus, and funding available. Thus, strategic consideration of the industry sector is paramount for professionals seeking the most financially rewarding positions within the aerospace domain.
6. Leadership
Effective leadership serves as a crucial determinant in accessing positions of high remuneration within the aerospace sector. The capacity to guide teams, strategize effectively, and drive innovation directly correlates with an individual’s ability to contribute to organizational success, thereby justifying higher compensation. Aerospace, characterized by intricate projects and stringent safety requirements, demands leaders who can navigate complexity and foster a culture of excellence. A chief engineer, for example, must not only possess technical expertise but also demonstrate leadership in coordinating a team of engineers to meet rigorous design specifications and project deadlines.
The importance of leadership extends beyond technical proficiency. Aerospace leaders are often tasked with making critical decisions involving significant financial investments and potential risks. For instance, a program manager responsible for developing a new satellite system must possess strong leadership skills to manage budget constraints, mitigate technical challenges, and ensure project success. Furthermore, effective communication, conflict resolution, and the ability to inspire and motivate teams are essential attributes for leaders in this sector. Consider the CEO of an aerospace manufacturing company; their strategic vision and leadership style directly influence the company’s performance and market position.
In summary, leadership is inextricably linked to positions offering high compensation in aerospace. The ability to guide teams, manage complex projects, and drive innovation are critical for success in this demanding industry. Aspiring aerospace professionals should prioritize the development of leadership skills as a means of enhancing their career prospects and maximizing their earning potential. Investing in leadership training, seeking mentorship opportunities, and actively participating in team-based projects are valuable strategies for cultivating these essential capabilities. The demand for effective leaders in aerospace remains consistently high, making leadership a vital attribute for those seeking the most financially rewarding positions.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following questions address common inquiries regarding careers within the aeronautics and astronautics industries offering the highest levels of financial compensation. This section aims to provide clarity on specific roles, required qualifications, and factors influencing earning potential.
Question 1: What specific educational qualifications are most beneficial for accessing positions with top-tier salaries in aerospace?
Advanced degrees, specifically a Master’s or Doctorate, in fields such as aerospace engineering, mechanical engineering, or physics are highly advantageous. Specialized coursework and certifications in areas like systems engineering, avionics, or project management can also significantly enhance career prospects.
Question 2: What types of experience are most valued by employers when considering candidates for high-paying aerospace positions?
Extensive experience in project leadership, technical problem-solving, cross-functional collaboration, and regulatory compliance are highly valued. Demonstrable proficiency in managing complex projects, leading teams, and ensuring adherence to safety standards is critical.
Question 3: Which specializations within aerospace engineering offer the greatest potential for high salaries?
Specializations in high-demand areas, such as hypersonic propulsion, autonomous flight control systems, cybersecurity for aerospace systems, and advanced materials development, often lead to increased earning potential due to the critical need for specialized knowledge.
Question 4: How does geographic location impact salary levels within the aerospace sector?
Areas designated as aerospace hubs, such as Seattle, Los Angeles, and the Space Coast of Florida, typically exhibit higher salary ranges due to the competitive demand for skilled professionals. Cost-of-living adjustments also play a role in determining compensation levels in different regions.
Question 5: In which specific industry sectors within aerospace are the highest salaries typically found?
High salaries are frequently found in the defense and government sector, particularly within defense contractors and government agencies like NASA. The commercial aviation sector and emerging technology areas, such as electric aircraft and unmanned aerial vehicles, also offer significant earning potential.
Question 6: What role does leadership ability play in securing high-paying positions within the aerospace industry?
Effective leadership is crucial for advancement to high-paying management and executive positions. Demonstrating the ability to guide teams, manage complex projects, and drive innovation is essential for success in leadership roles within the aerospace sector.
In conclusion, access to high-remuneration aerospace careers necessitates a combination of advanced education, relevant experience, specialized skills, strategic location choices, and demonstrated leadership capabilities. A proactive approach to professional development is paramount for maximizing earning potential within this competitive industry.
The next section will provide a summary of the key considerations for aspiring aerospace professionals seeking high-paying positions.
Highest Paying Aerospace Jobs
This exploration of highest paying aerospace jobs has highlighted the confluence of factors that dictate compensation levels within this demanding field. Advanced education, particularly in specialized engineering disciplines, is a fundamental prerequisite. Extensive and demonstrable experience in project leadership, technical problem-solving, and regulatory compliance further enhances earning potential. Strategic specialization in high-demand areas, such as cybersecurity, hypersonics, or autonomous systems, also exerts a significant influence. Geographic location within aerospace hubs, and the industry sectorwhether commercial aviation, defense, or emerging technologiesfurther shape compensation opportunities. Paramount is the development and demonstration of strong leadership skills to manage complex projects.
The pursuit of highest paying aerospace jobs demands a long-term commitment to continuous learning, professional development, and strategic career planning. While financial rewards are significant, they are commensurate with the intellectual rigor, technical expertise, and leadership capabilities required to excel in this dynamic and vital industry. The future of aerospace hinges on the talent and dedication of skilled professionals who are committed to innovation and advancing the boundaries of air and space travel, driving the field forward for generations to come.