The duration required to complete education in the field focused on designing, developing, testing, and producing aircraft, spacecraft, and related systems is a significant consideration for prospective students. This period encompasses theoretical coursework, practical application, and often, research or internship experiences.
Understanding the typical timeframe for academic preparation is crucial for career planning and financial management. A well-structured educational path provides a solid foundation for future professional contributions within the aeronautics and astronautics industries. The depth of knowledge and practical skills acquired during this period directly influence an engineer’s ability to innovate and solve complex challenges in the field.
The following sections will detail the typical educational pathways, exploring the common durations for bachelor’s, master’s, and doctoral degrees, as well as the influence of specialized programs and accelerated options on the overall time commitment.
Successfully managing the time investment required for aerospace engineering studies demands careful planning and a proactive approach. The following tips aim to guide aspiring aerospace engineers in optimizing their educational journey.
Tip 1: Establish a Clear Academic Plan: Mapping out the courses required for graduation and understanding the prerequisites for each is fundamental. This ensures a streamlined progression through the curriculum.
Tip 2: Prioritize Core Courses: Foundational courses in mathematics, physics, and introductory engineering principles are essential. Mastering these subjects early on will greatly facilitate understanding more advanced topics later in the program.
Tip 3: Explore Internship Opportunities: Integrating internships into the academic calendar provides valuable practical experience and helps consolidate theoretical knowledge. Internships can also influence career trajectory and potential employers.
Tip 4: Seek Mentorship: Connecting with professors, alumni, or industry professionals offers access to valuable insights and guidance. Mentors can provide advice on course selection, research opportunities, and career paths.
Tip 5: Develop Time Management Skills: The curriculum is demanding, necessitating effective time management. Utilizing scheduling tools and establishing consistent study habits is essential to manage workload and avoid academic stress.
Tip 6: Consider Specialization Early: While a broad foundation is crucial, identifying a specific area of interest within aerospace engineering (e.g., propulsion, aerodynamics, structures) early allows for focused study and potentially shorter paths to specialized roles.
Tip 7: Utilize Available Resources: Universities offer a range of academic support services, including tutoring, writing centers, and career counseling. Proactively engaging with these resources can enhance academic performance and career prospects.
These strategies will assist in navigating the commitment for aerospace engineering education with greater efficiency and maximizing the benefits derived from the learning process.
With a clear understanding of timelines and strategies to manage the learning process, prospective aerospace engineers can approach their studies with confidence and achieve their career aspirations.
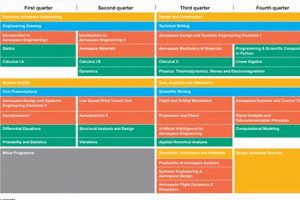
1. Typical bachelor's duration
The completion of a bachelor’s degree forms the cornerstone of aerospace engineering education and significantly influences the total time commitment required for professional entry. The duration of this foundational program establishes a baseline for understanding the overall academic investment.
- Core Curriculum Requirements
The standard aerospace engineering bachelor’s curriculum mandates completion of core courses in mathematics, physics, and fundamental engineering disciplines. These prerequisites often span the first two years of the program, establishing a rigorous foundation. Successfully navigating this core curriculum is essential for progressing to more specialized aerospace engineering topics and completing the program within the typical four-year timeframe. Delays in mastering core concepts can extend the overall duration of study.
- Aerospace-Specific Coursework
The latter half of the bachelor’s program concentrates on aerospace-specific topics, including aerodynamics, propulsion, flight mechanics, and spacecraft design. The depth and breadth of these subjects necessitate dedicated study and application of previously acquired knowledge. The number of aerospace-specific courses required, and their sequential nature, significantly impact the program’s duration. Meeting the required credit hours in these specialized areas is crucial for graduation.
- Laboratory and Project Work
Aerospace engineering curricula integrate laboratory work and design projects to reinforce theoretical understanding and develop practical skills. These hands-on experiences often require significant time investment outside of scheduled class hours. The successful completion of laboratory experiments and design projects within allotted timeframes is a critical factor in maintaining the standard bachelor’s degree timeline.
- University and Accreditation Standards
The duration of a bachelor’s program is influenced by university-specific graduation requirements and accreditation standards set by organizations like ABET (Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology). Meeting these standards, which often involve specific credit hour requirements and course distribution guidelines, ensures the programs quality and adherence to industry norms. Failure to comply with these requirements may necessitate additional coursework, extending the time needed for graduation.
The interplay of core curriculum demands, aerospace-specific coursework, laboratory requirements, and adherence to university and accreditation standards collectively shapes the “typical bachelor’s duration” and serves as a primary determinant of the overall time required to acquire an aerospace engineering education. Successfully navigating these factors is essential for completing the program within the anticipated four-year timeframe.
2. Master's program length
The duration of a master’s program represents a substantial addition to the overall time investment in aerospace engineering education. Master’s studies build upon the foundational knowledge acquired during a bachelor’s degree, providing specialized expertise in a chosen area. The program length is directly proportional to the depth of knowledge and research experience attained, thus extending the time required for comprehensive training in the field.
Program structures and curriculum design significantly influence the time required for completion. Thesis-based programs, which involve original research and a substantial written document, generally require a longer commitment than non-thesis options. Similarly, programs with a heavy emphasis on practical application, such as those incorporating extensive design projects or internships, may also extend the duration. For example, a master’s program specializing in advanced propulsion systems might necessitate additional laboratory work and computational modeling, increasing the time needed for completion. The choice between a thesis and non-thesis option, along with the program’s practical component, critically impacts the total study duration.
The decision to pursue a master’s degree directly influences the timeline for becoming a fully qualified aerospace engineer. While a bachelor’s degree provides entry-level opportunities, a master’s degree often opens doors to more advanced research positions, specialized engineering roles, and leadership opportunities. This advanced degree therefore increases the overall time commitment to education in exchange for enhanced career prospects within the aerospace engineering profession. The selection of program type and the extent of specialized coursework are key determinants of how program length affects the full course of study.
3. Doctoral study timeframe
The pursuit of a doctoral degree in aerospace engineering represents the most extensive commitment to formal education within the field. The “Doctoral study timeframe” significantly extends “how long does it take to study aerospace engineering”, reflecting the depth of research and specialized knowledge acquired.
- Research Proposal Development and Approval
Initiating doctoral studies involves crafting a comprehensive research proposal. This process, which includes identifying a novel research question, conducting a literature review, and outlining a methodology, can take several months to a year. Securing approval from a faculty committee is a critical milestone that directly impacts the overall timeframe. Delays in proposal approval extend the time before substantive research can commence, thereby increasing the total duration of study.
- Original Research and Data Collection
The core of doctoral work consists of conducting original research, often involving experimental investigations, computational modeling, or theoretical analysis. Data collection, depending on the complexity of the research question and the accessibility of resources, can span several years. Unexpected experimental challenges or difficulties in obtaining data can further prolong this phase, contributing to an extended “how long does it take to study aerospace engineering”.
- Dissertation Writing and Defense
The culmination of doctoral research is the writing and defense of a dissertation. This process involves synthesizing research findings, documenting methodologies, and presenting a coherent argument that contributes to the body of knowledge. Writing a dissertation is time-consuming and requires rigorous editing and revision. The defense, a formal presentation and questioning by a faculty committee, represents the final assessment of the doctoral candidate’s research and scholarship. A successful defense is necessary for degree completion, and any required revisions will further impact the final “how long does it take to study aerospace engineering”.
- Publication Requirements and Peer Review
Many doctoral programs require candidates to publish their research findings in peer-reviewed journals or conferences. The publication process, including manuscript preparation, submission, review, and revision, can add significant time to the doctoral study timeframe. Delays in publication due to reviewer feedback or journal acceptance rates can extend the overall duration of study. Fulfilling publication requirements is often a prerequisite for dissertation defense and degree conferral, directly influencing “how long does it take to study aerospace engineering”.
These interconnected stages underscore that the doctoral study timeframe is a significant factor extending the investment for aerospace engineering education. The time required for completing each stage impacts the duration and complexity involved in achieving advanced expertise in aerospace engineering.
4. Accelerated program options
Accelerated program options directly influence “how long does it take to study aerospace engineering” by offering an alternative pathway to degree completion in a reduced timeframe. These programs cater to students seeking to enter the aerospace engineering profession more quickly or those aiming to advance their careers with greater efficiency.
- Condensed Course Schedules
Accelerated programs typically compress the standard curriculum into shorter semesters or trimesters, increasing the intensity of coursework. This approach necessitates a higher level of commitment and a faster pace of learning. For example, a traditional 15-week semester might be condensed into 10 weeks, requiring students to absorb the same material at a more rapid rate. This compression directly reduces the overall time spent in formal education, impacting “how long does it take to study aerospace engineering.”
- Summer Course Integration
Many accelerated programs incorporate summer courses to allow students to earn credits year-round. Utilizing summer sessions effectively shortens the duration of the program. A student who consistently takes summer courses might complete a four-year degree in three years or less. This strategy serves as a primary mechanism for decreasing “how long does it take to study aerospace engineering.”
- Dual Enrollment and Advanced Placement Credits
Students who enter university with Advanced Placement (AP) credits or dual enrollment credits earned during high school can significantly reduce their undergraduate course load. These credits allow students to bypass introductory courses and progress more quickly to advanced aerospace engineering topics. The acceptance of these credits can shorten “how long does it take to study aerospace engineering” by allowing students to graduate earlier.
- Intensive Specialization Tracks
Some accelerated programs offer specialized tracks that focus on specific areas of aerospace engineering. By narrowing the curriculum, these tracks eliminate non-essential courses and allow students to concentrate on their chosen specialization. This streamlined approach reduces the breadth of knowledge acquired, and significantly impacts “how long does it take to study aerospace engineering.”
These program variations represent distinct approaches to decreasing the time required for aerospace engineering education. The structure of accelerated options can lead to a condensed period to enter the workforce, which, while efficient, needs a serious commitment and fast pacing learning.
5. Internship requirements
Internship requirements are an integral component of aerospace engineering education, directly influencing the overall timeframe for degree completion. The structure and duration of required internships can either extend or, in some cases, integrate seamlessly into the established academic schedule.
- Mandatory Internship Length and Program Structure
Many aerospace engineering programs mandate a minimum internship duration, typically ranging from one semester to a full year. The structure of these internships, whether full-time during the summer or part-time during the academic year, affects the overall “how long does it take to study aerospace engineering”. A full-year internship may extend the total time to graduation, while strategically scheduled summer internships might be completed without adding extra semesters.
- Impact on Course Sequencing and Availability
Internship requirements can influence the sequencing and availability of certain courses. Students may need to defer advanced coursework to accommodate internship commitments. This deferral can extend the program if the required courses are only offered during specific semesters. Careful planning and coordination between academic advisors and students are essential to minimize any potential delays linked to internship scheduling.
- Credit Hour Recognition and Academic Integration
Some programs offer academic credit for completed internships, effectively integrating practical experience into the curriculum. This integration can reduce the number of traditional course credits required for graduation, potentially shortening the “how long does it take to study aerospace engineering”. However, the criteria for credit hour recognition vary, and not all internships qualify. Successful integration requires adherence to program guidelines and approval from academic advisors.
- Influence on Career Path and Post-Graduation Opportunities
Internship experiences often shape a student’s career path and provide valuable connections for post-graduation employment. While the internship itself might extend the initial academic timeline, the resulting career opportunities can lead to faster professional advancement. The long-term benefits of internship experience are therefore an important consideration when evaluating the total value and efficiency of aerospace engineering education, though there may be no direct impact on “how long does it take to study aerospace engineering”.
The interplay between internship requirements, program structure, course sequencing, and credit hour recognition shapes the total timeframe for aerospace engineering education. Balancing the practical experience gained through internships with the need to complete academic coursework is critical to optimize the educational pathway and shorten “how long does it take to study aerospace engineering” while ensuring a good experience and a good career.
6. Research project timeline
The “Research project timeline” stands as a significant determinant influencing “how long does it take to study aerospace engineering,” particularly at the graduate level. The successful execution of research projects, ranging from thesis work for master’s students to dissertation research for doctoral candidates, requires meticulous planning and adherence to a realistic schedule. Delays in any stage of the research process, from literature review to data analysis, directly extend the overall duration of study. For instance, if a doctoral candidate encounters unforeseen challenges in experimental design or data acquisition, the dissertation timeline will inevitably be prolonged, impacting the time needed to complete the degree. The inherent complexity of aerospace engineering research, often involving advanced modeling, simulation, or experimental testing, contributes to the potential for timeline extensions. The successful management of the research project timeline is therefore crucial for minimizing the overall duration of study.
The structure and funding of research projects also play a critical role in determining their duration and, consequently, the length of the degree program. Research projects funded by external grants often have specific deadlines and milestones that must be met to ensure continued funding. Failure to adhere to these deadlines can result in funding cuts, which can severely impede progress and extend the research timeline. Conversely, well-funded projects with clear objectives and adequate resources are more likely to be completed within the planned timeframe. Furthermore, the availability of faculty mentorship and access to research facilities significantly impact the efficiency of the research process. A supportive research environment can help students overcome challenges and stay on track, while inadequate mentorship or limited access to resources can lead to delays.
In summary, the research project timeline constitutes a vital component of “how long does it take to study aerospace engineering,” especially for graduate students. Effective management of the research process, secure funding, and a supportive research environment are essential for completing research projects within a reasonable timeframe. A realistic timeline, coupled with proactive problem-solving and access to adequate resources, represents a critical strategy for minimizing the overall duration of aerospace engineering studies. The impact of a well-structured “Research project timeline” often reduces the “how long does it take to study aerospace engineering”.
7. Specialized curriculum impact
The degree of specialization within an aerospace engineering curriculum exerts a significant influence on the overall duration required for degree completion. The depth and breadth of the chosen specialization directly affect course selection, research opportunities, and the development of specific skill sets, ultimately impacting “how long does it take to study aerospace engineering.”
- Course Depth and Breadth
A highly specialized curriculum, such as one focused solely on propulsion systems or composite materials, may require students to take a greater number of advanced courses within that specific area. This increased course load can extend the total time needed to meet graduation requirements. Conversely, a more general curriculum that covers a wider range of aerospace engineering topics may allow for a faster progression through the program, but may also lack the depth of specialization needed for some career paths. For example, a student specializing in astrodynamics may need to complete additional courses in celestial mechanics and orbital control, extending the duration compared to a student pursuing a broader aerospace engineering degree.
- Research Focus and Dissertation Requirements
Specialized curricula often necessitate research projects aligned with the chosen area of expertise. The complexity and scope of these research projects can directly impact the time required for dissertation completion. A research project involving experimental testing of advanced materials, for instance, may require extensive laboratory work and data analysis, potentially prolonging the dissertation timeline compared to a more theoretical project. Moreover, the availability of faculty mentorship and research funding within the chosen specialization can significantly influence the pace of research and the overall duration of doctoral studies.
- Industry-Specific Skill Development
Specialized curricula often incorporate hands-on training and industry-specific skill development to prepare students for specific roles within the aerospace sector. This practical experience may include internships, design projects, and the use of specialized software tools. While these experiences enhance a student’s employability, they may also require additional time investment, particularly if the internship is a full-time commitment. For example, a curriculum focused on aircraft design may require students to complete a capstone project involving the design and construction of a prototype aircraft, which can extend the program by a semester or more.
- Accreditation and Certification Requirements
Certain specialized areas of aerospace engineering may require accreditation or certification by professional organizations. Meeting these requirements can necessitate specific coursework or training modules, which may add to the overall duration of the program. For example, a curriculum focused on aviation safety may need to include specific courses on human factors and accident investigation to meet the requirements for certification as a safety professional. Adhering to these external accreditation and certification standards directly impacts the educational and professional development timeline.
In conclusion, the specialized curriculum impact demonstrates that a deliberate choice of specialization plays a pivotal role in defining “how long does it take to study aerospace engineering.” Factors such as course depth, research focus, skill development, and accreditation requirements can collectively extend or, in some cases, streamline the academic journey. Careful consideration of career goals and program requirements is therefore essential when selecting a specialization within the aerospace engineering discipline.
Frequently Asked Questions about Aerospace Engineering Education Duration
The following questions address common inquiries regarding the time commitment associated with pursuing aerospace engineering degrees. These answers provide a factual overview of typical durations and influencing factors.
Question 1: What is the standard duration for a bachelor’s degree in aerospace engineering?
A bachelor’s degree in aerospace engineering typically requires four years of full-time study. This timeframe encompasses core engineering courses, specialized aerospace engineering subjects, and laboratory work.
Question 2: How long does it take to complete a master’s degree in aerospace engineering?
A master’s degree in aerospace engineering typically takes one to two years of full-time study to complete. This duration varies based on program structure, research requirements, and specialization.
Question 3: What is the typical timeframe for doctoral studies in aerospace engineering?
Doctoral studies in aerospace engineering generally require three to five years beyond a master’s degree. This timeframe is dedicated to original research, dissertation writing, and defense.
Question 4: Do accelerated programs shorten the time required to obtain an aerospace engineering degree?
Yes, accelerated programs can shorten the duration of aerospace engineering studies. These programs condense coursework, utilize summer sessions, and may offer advanced placement options to reduce the overall timeframe.
Question 5: How do internship requirements affect the overall length of an aerospace engineering program?
Internship requirements can either extend or integrate into the standard program timeline. A mandatory full-year internship may extend the overall duration, while strategically scheduled summer internships may have minimal impact.
Question 6: Can a specialized curriculum influence the time it takes to complete an aerospace engineering degree?
Yes, a specialized curriculum can influence the duration of aerospace engineering studies. Deeper course depth, focused research, and industry-specific skill development may extend or streamline the academic journey.
These answers offer a foundational understanding of the time commitment involved in aerospace engineering education. The specific duration varies depending on individual circumstances and program choices.
The subsequent sections will explore strategies for managing the academic workload and maximizing the efficiency of the learning process.
Concluding Remarks on Aerospace Engineering Study Duration
The preceding analysis underscores the multifaceted nature of “how long does it take to study aerospace engineering.” The total duration is contingent upon several factors, including the degree level pursued, the program structure, the presence of internship or research requirements, and the degree of specialization within the chosen curriculum. A clear understanding of these elements is crucial for prospective students to formulate realistic academic plans and manage their time effectively.
Ultimately, the investment in aerospace engineering education represents a commitment to intellectual growth and professional development. Aspirants should carefully evaluate their individual goals and resources to optimize their educational path. A strategic approach to academic planning, coupled with a dedication to rigorous study, will facilitate the efficient acquisition of the knowledge and skills necessary for success in this demanding and rewarding field.





![Learn Aerospace Engineering with Khan Academy - [Year] Guide Innovating the Future of Flight with Reliable Aviation Solutions Learn Aerospace Engineering with Khan Academy - [Year] Guide | Innovating the Future of Flight with Reliable Aviation Solutions](https://mixaerospace.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/03/th-236-300x200.jpg)
