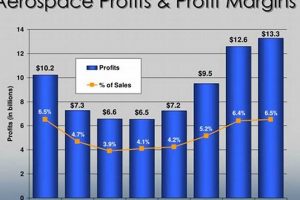
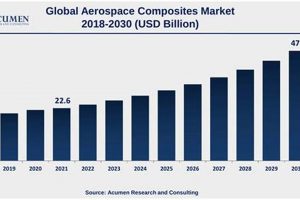
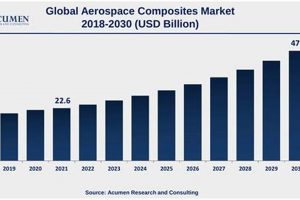
The manufacturing and service activities centered around aircraft, spacecraft, related components, and systems within the United Kingdom constitutes a significant economic sector. This sector encompasses a broad range of activities, from the design and production of entire aircraft to the development of specialized parts, avionics, and software. It involves both civil and military applications, contributing substantially to the nation’s research and development capabilities and its standing in global trade.
This high-technology sector is a crucial contributor to the British economy, providing high-skilled jobs and generating significant export revenue. Its historical roots trace back to the early days of aviation, and it has evolved into a sophisticated and innovative enterprise. It fosters technological advancements that often spill over into other sectors, enhancing the overall competitiveness of the national economy. Furthermore, it plays a vital role in national security and defense capabilities.
The following discussion will delve into various facets of this vital sector, including its key players, current challenges and opportunities, technological advancements, and its overall impact on the nation’s economic and social landscape. The intention is to provide a detailed and objective overview of its current state and future prospects.
Strategic Considerations for Engaging with the UK Aerospace Sector
Achieving success within this sector demands careful planning and a thorough understanding of its complexities. The following considerations offer guidance for stakeholders seeking to navigate this landscape effectively.
Tip 1: Foster Collaborative Partnerships: Success frequently hinges on robust collaborations. Establishing partnerships with established firms, research institutions, and government agencies can facilitate knowledge transfer, resource sharing, and access to specialized expertise.
Tip 2: Prioritize Innovation and Technological Advancement: Continuous investment in research and development is paramount. Staying at the forefront of emerging technologies, such as advanced materials, autonomous systems, and sustainable aviation solutions, is critical for maintaining a competitive edge.
Tip 3: Comply with Stringent Regulatory Standards: The sector operates under rigorous safety and quality regulations. Adherence to these standards, including those set by the Civil Aviation Authority (CAA) and the European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA), is non-negotiable for operational viability.
Tip 4: Develop a Skilled Workforce: A highly skilled workforce is the backbone of the sector. Investing in training programs, apprenticeships, and educational initiatives ensures a steady pipeline of talent with the necessary engineering, manufacturing, and technical expertise.
Tip 5: Focus on Supply Chain Optimization: An efficient and resilient supply chain is essential. Diversifying suppliers, implementing robust risk management strategies, and embracing digital technologies for supply chain visibility can mitigate potential disruptions.
Tip 6: Embrace Sustainability Initiatives: Growing environmental concerns are driving demand for sustainable aviation solutions. Integrating environmentally friendly practices into operations, such as reducing emissions and developing fuel-efficient technologies, is crucial for long-term sustainability.
Tip 7: Understand the Geopolitical Landscape: International relations and trade policies exert a significant influence. Staying abreast of geopolitical developments, trade agreements, and government policies is vital for informed decision-making.
By focusing on collaboration, innovation, regulatory compliance, workforce development, supply chain resilience, sustainability, and geopolitical awareness, stakeholders can enhance their prospects for success. These strategic considerations represent crucial building blocks for establishing a strong presence and achieving sustainable growth.
The application of these strategic insights will be critical to capitalizing on the opportunities and navigating the challenges discussed in the subsequent sections of this article.
1. Manufacturing Capabilities
The manufacturing capabilities within the UK aerospace sector form a foundational pillar of its economic significance and global competitiveness. These capabilities, encompassing a diverse range of activities from component fabrication to final assembly, dictate the sector’s capacity to innovate, compete, and contribute to national prosperity.
- Airframe Production
This area involves the design and construction of the structural components of aircraft, including wings, fuselages, and tail assemblies. Companies like BAE Systems contribute substantially to this domain, particularly in the defense sector. The sophistication of airframe production directly influences aircraft performance, safety, and overall operational efficiency.
- Engine Manufacturing
Engine manufacturing is arguably the most critical and technologically advanced facet, exemplified by Rolls-Royce’s global leadership in this field. This includes the design, development, and production of jet engines for both civil and military aircraft. Advancements in engine technology drive improvements in fuel efficiency, emissions reduction, and thrust-to-weight ratios, directly impacting operational costs and environmental footprint.
- Avionics and Systems Integration
This encompasses the design, development, and integration of electronic systems onboard aircraft, including navigation, communication, and flight control systems. The UK possesses considerable expertise in this area, with numerous companies specializing in the development of cutting-edge avionics technologies. The integration of these systems is crucial for enhancing situational awareness, improving safety, and enabling advanced operational capabilities.
- Component Manufacturing
A vast network of specialized companies supply critical components to the aerospace sector. These range from precision-machined parts to specialized materials and electronic components. The efficiency and reliability of this supply chain are essential for ensuring the timely and cost-effective production of aircraft and related systems.
These manufacturing capabilities collectively represent a strategic asset for the United Kingdom. The ability to design, develop, and produce advanced aerospace systems domestically not only secures high-skilled jobs and generates export revenue but also enhances national security and technological sovereignty. Continued investment in these capabilities is essential for maintaining the UK’s position as a global leader in aerospace manufacturing.
2. Research & Development
Research and development (R&D) constitutes a crucial engine for growth and competitiveness within the UK aerospace industry. The sector’s ability to maintain its global standing hinges directly on its capacity to innovate and adopt cutting-edge technologies. Investment in R&D drives advancements in areas such as fuel efficiency, emissions reduction, materials science, and autonomous systems, directly impacting aircraft performance, operational costs, and environmental sustainability. For example, the Aerospace Technology Institute (ATI), a joint government-industry initiative, funds and coordinates aerospace R&D projects across the UK, supporting the development of technologies with the potential to transform the sector. Similarly, universities such as Cambridge and Oxford contribute through fundamental research, often partnering with industry to translate findings into practical applications.
The connection between R&D and manufacturing capabilities is symbiotic. R&D breakthroughs often lead to the development of new manufacturing processes and techniques, enhancing productivity and reducing costs. For instance, the development of advanced composite materials has enabled the production of lighter and stronger aircraft structures, requiring new manufacturing methods and equipment. Furthermore, R&D fosters the creation of high-skilled jobs in engineering, science, and technology, bolstering the UK’s talent pool and attracting foreign investment. Airbus, a major player in the UK aerospace sector, invests significantly in R&D activities at its facilities in the UK, creating opportunities for British engineers and scientists.
In conclusion, R&D is not merely an adjunct to the UK aerospace industry but a fundamental driver of its success. Sustained investment in R&D is critical for maintaining a competitive edge, addressing environmental challenges, and ensuring long-term prosperity. The challenge lies in fostering a supportive ecosystem that encourages innovation, facilitates collaboration between industry and academia, and translates research findings into commercially viable products and services. The UK’s future as a leading aerospace nation depends on its ability to effectively harness the power of R&D.
3. Global Supply Chains
The operational efficacy of the UK aerospace industry is inextricably linked to its participation in intricate global supply chains. These networks facilitate the flow of components, materials, and services necessary for the design, manufacture, and maintenance of aircraft and related systems. The health and resilience of these chains are vital for the sector’s competitiveness and its ability to meet both domestic and international demands.
- Component Sourcing and International Partnerships
The UK aerospace industry relies on a vast network of international suppliers for specialized components, raw materials, and sub-assemblies. This sourcing strategy allows companies to access the best available technologies and materials from around the world. Strategic partnerships with foreign firms are common, fostering collaboration on research and development, as well as production. For instance, Rolls-Royce sources components from numerous countries for its aero-engines, while UK-based companies participate in the supply chains of major international aircraft manufacturers like Boeing and Airbus.
- Logistics and Transportation Networks
Efficient logistics and transportation networks are essential for the timely delivery of components and finished products within global supply chains. The UK benefits from well-developed infrastructure, including ports, airports, and road networks, facilitating the movement of goods. However, challenges such as customs procedures, border controls, and transportation costs can impact the efficiency of these networks. Brexit has introduced new complexities to the logistics landscape, requiring companies to adapt to new regulations and procedures.
- Supply Chain Risk Management
Global supply chains are inherently vulnerable to disruptions caused by geopolitical events, natural disasters, economic fluctuations, and other unforeseen circumstances. The UK aerospace industry must implement robust risk management strategies to mitigate these vulnerabilities. This includes diversifying suppliers, monitoring potential threats, and developing contingency plans to ensure business continuity. The COVID-19 pandemic exposed the fragility of global supply chains, highlighting the need for greater resilience and agility.
- Technology Integration and Digitalization
The integration of digital technologies, such as blockchain, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things (IoT), is transforming global supply chains. These technologies enhance visibility, improve efficiency, and facilitate collaboration among supply chain partners. The UK aerospace industry is increasingly adopting these technologies to optimize its supply chains and gain a competitive advantage. For example, predictive analytics can be used to forecast demand, optimize inventory levels, and identify potential bottlenecks.
In summary, participation in global supply chains is both a necessity and a strategic imperative for the UK aerospace industry. Navigating the complexities of these networks requires careful planning, robust risk management, and a commitment to innovation. The ability to forge strong international partnerships, optimize logistics, and embrace digital technologies will determine the sector’s long-term success in a competitive global marketplace. Securing the supply chains guarantees the sustainability of the manufacturing capabilities.
4. Government Regulation
Government regulation exerts a profound influence on the UK aerospace industry, shaping its operational landscape and strategic direction. These regulations, enacted through bodies like the Civil Aviation Authority (CAA) and in alignment with international standards, are not merely bureaucratic hurdles but are fundamental to ensuring safety, security, and environmental responsibility within the sector. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in significant penalties, reputational damage, and, most critically, compromise the safety of passengers and personnel. The regulations span diverse areas, including aircraft design and certification, air traffic management, pilot licensing, and maintenance procedures. The CAA, as the primary regulatory body, enforces these rules through audits, inspections, and enforcement actions.
The impact of government regulation on the industry is multifaceted. Stringent safety standards, for example, drive innovation in aircraft design and manufacturing, prompting companies to invest in advanced technologies and materials. Environmental regulations, aimed at reducing emissions and noise pollution, encourage the development of more fuel-efficient engines and alternative propulsion systems. Government regulations also foster a level playing field, ensuring fair competition and preventing anti-competitive practices. The impact of Brexit, altering the regulatory framework governing aviation between the UK and the EU, illustrates the sensitivity of the sector to regulatory changes. The need to adapt to new regulations concerning certification, airworthiness, and traffic rights has presented significant challenges for the industry, requiring companies to invest in compliance and navigate new bureaucratic processes.
In conclusion, government regulation is an indispensable component of the UK aerospace industry. It provides a framework for safe and sustainable operations, encourages innovation, and ensures fair competition. While compliance can be costly and complex, it is essential for maintaining the industry’s integrity and its reputation for excellence. Navigating the regulatory landscape effectively requires a deep understanding of the rules and a proactive approach to compliance. The future of the UK aerospace industry depends, in part, on the ability of both government and industry to work together to create a regulatory environment that promotes safety, innovation, and sustainable growth.
5. Skilled Workforce
The availability of a highly skilled workforce is a critical determinant of success for the UK aerospace industry. This sector’s capacity for innovation, manufacturing excellence, and sustained competitiveness depends directly on the quality and expertise of its personnel.
- Engineering Expertise
The industry requires a substantial number of highly trained engineers across various disciplines, including aeronautical, mechanical, electrical, and software engineering. These professionals are essential for the design, development, testing, and certification of aircraft, engines, and related systems. Institutions such as Cranfield University and Imperial College London produce graduates who form the backbone of the industry’s engineering talent pool. BAE Systems, for example, employs thousands of engineers in its UK operations, contributing to the design and manufacturing of advanced military aircraft. A shortage of qualified engineers can constrain the industry’s growth potential.
- Manufacturing Technicians and Skilled Trades
Beyond engineering, a skilled workforce of manufacturing technicians and tradespeople is crucial for the efficient and precise production of aerospace components and systems. This includes machinists, welders, electricians, and composite materials specialists. Apprenticeship programs, offered by companies like Rolls-Royce, play a vital role in training these skilled workers. The increasing adoption of advanced manufacturing technologies, such as robotics and automation, requires technicians with expertise in these areas. A lack of skilled tradespeople can lead to production bottlenecks and quality control issues.
- Research and Development Scientists
Research and development relies heavily on scientists with expertise in materials science, aerodynamics, propulsion, and other specialized fields. These scientists conduct fundamental and applied research, contributing to breakthroughs in aerospace technology. Government-funded research institutions, such as the Aerospace Technology Institute (ATI), support the training and development of research scientists. Collaboration between industry and academia is crucial for translating research findings into practical applications. A strong research base is essential for maintaining the UK’s position as a leader in aerospace innovation.
- Management and Business Professionals
Effective management and business leadership are essential for the success of any aerospace company. This includes professionals with expertise in project management, finance, marketing, and supply chain management. These individuals are responsible for planning, organizing, and executing complex aerospace projects, as well as managing the financial and commercial aspects of the business. Business schools such as London Business School provide training in these areas. Strong leadership and business acumen are critical for navigating the challenges and opportunities of the global aerospace market.
The UK aerospace industry’s ability to attract, train, and retain a skilled workforce is a key factor in its long-term competitiveness. Investment in education, training, and apprenticeship programs is essential for ensuring a steady pipeline of talent. Furthermore, creating a supportive and inclusive work environment can help attract and retain top talent. Continued focus on skills development will enable the UK aerospace industry to meet the challenges of the future and maintain its position as a global leader.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common queries regarding the United Kingdom’s aerospace sector, providing concise and factual responses to enhance understanding of its complexities and significance.
Question 1: What defines the scope of the UK aerospace industry?
The sector encompasses companies and organizations engaged in the design, development, manufacturing, and maintenance of aircraft, spacecraft, and related systems and components within the United Kingdom.
Question 2: What is the economic importance of this sector to the UK?
The aerospace industry is a major contributor to the UK economy, generating significant export revenue, supporting high-skilled jobs, and fostering technological innovation that benefits other sectors.
Question 3: Which are the major companies operating within this sector in the UK?
Key players include BAE Systems, Rolls-Royce, Airbus (with significant UK operations), and a vast network of smaller suppliers and specialized technology firms.
Question 4: How does government regulation affect the UK aerospace industry?
Government regulations, primarily enforced by the Civil Aviation Authority (CAA), ensure safety, security, and environmental compliance. These regulations impact aircraft design, air traffic management, and maintenance procedures.
Question 5: What are the primary challenges facing the UK aerospace industry currently?
Challenges include global competition, technological disruption, the impact of Brexit on supply chains and regulations, and the need to address environmental concerns related to aviation.
Question 6: How important is research and development to the sector’s future?
Research and development are critical for maintaining the UK’s competitive edge in aerospace. Innovation in areas such as fuel efficiency, materials science, and autonomous systems is essential for long-term sustainability.
In conclusion, the UK aerospace industry is a complex and dynamic sector that plays a vital role in the nation’s economy and security. Understanding its key characteristics and challenges is crucial for policymakers, industry stakeholders, and anyone with an interest in the future of British technology and manufacturing.
The following section will explore potential future trends impacting the UK aerospace industry.
Conclusion
This exposition has illuminated the multifaceted nature of the UK aerospace industry, emphasizing its manufacturing prowess, commitment to research and development, reliance on global supply chains, the impact of government regulation, and the crucial role of a skilled workforce. The interconnectedness of these elements dictates the industry’s overall health and global competitiveness, highlighting both its strengths and vulnerabilities in an increasingly challenging environment. Maintaining this sector is essential to the UK’s long-term economic stability.
Sustained investment, strategic policy decisions, and a commitment to innovation are imperative to secure the future of this vital industry. Stakeholders must collaborate to address the challenges posed by global competition, technological advancements, and evolving geopolitical landscapes. The ongoing success of the sector is not merely a matter of economic prosperity, but a matter of national strategic importance. The continued health of the sector secures British interests both now and in the future.