Positions within the aeronautics and astronautics fields in the Italian labor market are specialized roles focused on the design, development, testing, and production of aircraft, spacecraft, and related systems. These careers often involve applying scientific and mathematical principles to solve complex engineering challenges related to flight and space exploration within the geographical boundaries of Italy. For example, a propulsion engineer might work on improving the fuel efficiency of commercial aircraft manufactured in Italy, or a structural engineer could contribute to the design of satellite components for a space mission managed by an Italian organization.
Careers in this sector contribute significantly to Italy’s technological advancement and economic growth. They foster innovation, drive research and development, and enhance the nation’s competitiveness in the global aerospace industry. Historically, Italy has a strong tradition in aviation and space exploration, with companies and research institutions playing pivotal roles in both national and international projects. Securing related employment provides opportunities to contribute to a legacy of aerospace excellence and to participate in cutting-edge technological advancements.
The following sections will delve into the specific types of available roles, the skills and qualifications required for success, the primary employing companies and organizations, and the factors influencing career prospects within the Italian aerospace sector.
Guidance for Aspiring Professionals
The following provides informational advice to those seeking employment within the Italian aerospace sector, focusing on strategies for career advancement and successful job acquisition.
Tip 1: Cultivate Specialized Knowledge: Demonstrating expertise in a niche area of aerospace engineering, such as propulsion systems, aerodynamics, or avionics, enhances marketability. Specialization can be achieved through advanced coursework, research projects, or professional certifications aligned with Italian industry standards.
Tip 2: Acquire Proficiency in Italian: While English is often the language of engineering, fluency in Italian is advantageous, particularly for roles involving collaboration with local teams, clients, or regulatory bodies. Actively pursue language training to improve communication and cultural understanding.
Tip 3: Target Key Employers: Research and identify the primary aerospace companies and research institutions operating in Italy. Tailor applications and networking efforts to align with the specific needs and interests of these organizations.
Tip 4: Network Strategically: Attend industry conferences, seminars, and workshops to connect with professionals currently working in the Italian aerospace field. Building relationships can provide valuable insights and potential career opportunities.
Tip 5: Highlight Relevant Experience: Emphasize internships, research experiences, or project work that directly relates to the requirements of the position being sought. Quantify accomplishments whenever possible to demonstrate the impact of contributions.
Tip 6: Understand Italian Work Culture: Familiarize oneself with the norms and expectations of the Italian workplace. This includes understanding communication styles, hierarchy, and approaches to teamwork. This cultural awareness can facilitate smoother integration into a new professional environment.
Tip 7: Leverage University Connections: Italian universities with strong aerospace engineering programs often maintain close ties with industry partners. Utilize career services, alumni networks, and faculty connections to gain access to employment leads and mentorship opportunities.
By focusing on targeted skill development, strategic networking, and a deep understanding of the Italian aerospace landscape, aspiring professionals can increase their likelihood of securing fulfilling and impactful related positions.
The subsequent sections will provide additional insights into salary expectations, career progression pathways, and the long-term outlook for this industry within Italy.
1. Design and Development
Design and development forms a foundational pillar of aerospace engineering careers within Italy. It encompasses the conceptualization, planning, and execution of new aircraft, spacecraft, and related technologies. The success of the Italian aerospace sector hinges on the continuous innovation and refinement of these engineering processes, directly impacting the types of available employment and the required skill sets.
- Aerodynamic Design
Aerodynamic design focuses on optimizing the flow of air around aircraft and spacecraft to enhance performance, stability, and fuel efficiency. In Italy, this involves using computational fluid dynamics (CFD) software and wind tunnel testing to refine designs. Positions in this area may involve working on the next generation of regional aircraft or contributing to the aerodynamic efficiency of satellites. The implications are significant, as improved aerodynamic performance translates to reduced operating costs and environmental impact.
- Structural Engineering
Structural engineering ensures that aircraft and spacecraft can withstand the forces encountered during flight and space travel. Within the Italian aerospace context, this involves selecting appropriate materials, designing load-bearing structures, and conducting stress analyses using finite element analysis (FEA) software. Engineers in this field might work on designing lightweight composite structures for aircraft or developing robust frames for space probes. Structural integrity is paramount for safety and mission success.
- Propulsion Systems
Propulsion system design focuses on the engines and related components that provide thrust for aircraft and spacecraft. Italian aerospace engineers in this area may work on improving the efficiency and reducing the emissions of gas turbine engines, developing new rocket propulsion systems, or exploring alternative fuels. Responsibilities can encompass designing engine components, conducting performance simulations, and overseeing testing. Advanced propulsion systems are critical for achieving higher speeds, longer ranges, and reduced environmental footprint.
- Avionics and Control Systems
Avionics and control systems design involves the development of the electronic systems that control and monitor aircraft and spacecraft. This includes flight control systems, navigation systems, communication systems, and sensor systems. Within Italy’s aerospace industry, this might entail developing autonomous flight control algorithms, designing advanced sensor systems for Earth observation satellites, or integrating communication systems for interplanetary missions. Sophisticated avionics are essential for ensuring safe and efficient operation of aircraft and spacecraft.
These interconnected facets of design and development underscore the dynamic and technically demanding nature of aerospace engineering jobs in Italy. The continued growth and competitiveness of the Italian aerospace sector relies on attracting and retaining highly skilled engineers capable of contributing to these critical areas. The interplay between these elements directly shapes the future of flight and space exploration within the country.
2. Research Opportunities
Significant research opportunities are inextricably linked to career prospects within Italy’s aerospace sector. Academic institutions and industrial enterprises in Italy foster research programs that drive innovation and technological advancement. Such initiatives directly influence the demand for specialized engineers and scientists. These opportunities span a wide spectrum, from theoretical studies of advanced materials to the practical development of novel propulsion systems. The availability of research funding and the presence of cutting-edge facilities serve as catalysts for attracting and retaining talent in this specialized field.
An example of this connection can be seen in the Clean Sky Joint Undertaking, a European research program in which Italian aerospace companies and universities actively participate. This initiative focuses on developing cleaner, quieter, and more efficient aircraft technologies. Consequently, demand increases for engineers with expertise in areas such as aerodynamics, combustion, and noise reduction. Similarly, the Italian Space Agency (ASI) funds numerous research projects related to satellite technology, space exploration, and Earth observation. This funding fuels the need for specialists in areas such as satellite communication, remote sensing, and orbital mechanics. Understanding these research trends is crucial for students and professionals seeking to align their skills with the evolving needs of the Italian aerospace industry.
In summary, research opportunities are not merely an academic pursuit, but rather a critical component of the aerospace engineering job market in Italy. These opportunities drive technological progress, shape the skill requirements for engineers, and contribute to the overall competitiveness of the Italian aerospace sector. Recognizing the dynamic interplay between research and employment is essential for individuals aiming to establish successful careers in this field. Future trends in research funding and technological priorities will continue to shape the landscape of career options within Italy’s aerospace domain.
3. Regulatory Compliance
Adherence to stringent regulatory standards is paramount within the Italian aerospace sector, directly shaping the roles and responsibilities inherent in related engineering positions. Aerospace activities in Italy, including design, manufacturing, and maintenance, are governed by national and international regulations to ensure safety, airworthiness, and environmental protection. Compliance is not merely a procedural formality; it is integral to maintaining public trust, safeguarding passenger safety, and enabling the continued operation of the industry. For example, engineers involved in aircraft design must demonstrate compliance with European Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) regulations, meticulously documenting design choices and testing results to prove airworthiness. Failure to meet these standards can lead to severe penalties, including grounding of aircraft and revocation of operating licenses. Therefore, expertise in regulatory frameworks is a critical asset for professionals seeking employment in this domain.
The impact of regulatory compliance extends beyond design and engineering to encompass manufacturing processes and maintenance procedures. Engineers oversee quality control measures to ensure that components and systems meet specified standards. Maintenance engineers must adhere to strict maintenance schedules and procedures to guarantee the continued airworthiness of aircraft. Furthermore, environmental regulations concerning noise and emissions require engineers to develop and implement technologies to minimize the environmental impact of aviation. The demand for professionals with in-depth knowledge of these regulations is consistently high, as companies seek to mitigate risks and maintain operational integrity. This demand translates into specialized roles focusing on regulatory affairs, quality assurance, and environmental compliance within aerospace engineering organizations.
In conclusion, regulatory compliance is not merely a constraint but a fundamental aspect of aerospace engineering employment in Italy. It dictates design choices, manufacturing processes, and operational procedures, necessitating a workforce with comprehensive knowledge of applicable regulations and a commitment to maintaining the highest standards of safety and quality. The continued growth and sustainability of the Italian aerospace sector rely heavily on the expertise of engineers who can navigate the complex regulatory landscape and ensure that all activities are conducted in accordance with applicable laws and standards. This understanding is crucial for individuals seeking to thrive in this demanding and highly regulated industry.
4. Manufacturing Processes
Manufacturing processes are integral to the realization of aerospace designs, translating theoretical concepts into tangible aircraft, spacecraft, and components. The sophistication and precision required in aerospace manufacturing directly influence the types of engineering roles available and the necessary skill sets within Italy’s aerospace sector.
- Advanced Materials Processing
The fabrication of aerospace components increasingly relies on advanced materials such as composites, titanium alloys, and nickel-based superalloys. Italian aerospace manufacturing involves processes like automated fiber placement for composite structures, precision machining of complex metal parts, and specialized heat treatments to enhance material properties. Aerospace engineering positions in this domain require expertise in materials science, manufacturing techniques, and quality control to ensure structural integrity and performance.
- Precision Machining and Fabrication
Aerospace components often demand extremely tight tolerances and intricate geometries. Precision machining techniques, including CNC milling, turning, and grinding, are essential for producing parts that meet stringent specifications. Fabrication processes, such as welding and brazing, also require specialized expertise and adherence to rigorous quality standards. Aerospace engineering roles focused on these areas involve process optimization, tooling design, and dimensional metrology to guarantee accuracy and reliability.
- Assembly and Integration
The assembly and integration of aerospace systems, from aircraft fuselages to satellite payloads, is a complex and critical process. Italian aerospace manufacturing involves coordinating multiple disciplines and ensuring seamless integration of components from various suppliers. Aerospace engineering positions in this field require expertise in assembly techniques, project management, and quality assurance to ensure that systems are assembled correctly and function as intended.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT)
Non-destructive testing methods are crucial for detecting defects and ensuring the integrity of aerospace components without causing damage. Techniques such as ultrasonic testing, radiography, and eddy current testing are employed to identify flaws and assess material properties. Aerospace engineering roles in NDT involve developing inspection procedures, interpreting test results, and implementing corrective actions to maintain the highest levels of quality and safety.
These interconnected aspects of manufacturing processes highlight the technologically advanced and demanding nature of aerospace engineering roles within Italy. Continued innovation in manufacturing techniques, coupled with rigorous quality control measures, are essential for maintaining the competitiveness and safety of the Italian aerospace industry. The skills and expertise of engineers in these areas are critical for translating designs into reliable and high-performance aerospace systems.
5. Project Management
The discipline of project management is an indispensable component of aerospace engineering careers in Italy. Projects within this sector are typically characterized by considerable complexity, substantial financial investment, stringent regulatory oversight, and prolonged execution timelines. Effective project management ensures that these multifaceted undertakings are completed within defined parameters, including budgetary constraints, schedule milestones, and performance specifications. A failure in project management can lead to significant cost overruns, schedule delays, and, potentially, compromised safety or mission objectives. For example, the development of a new satellite system necessitates meticulous planning and coordination across various engineering disciplines, manufacturing teams, and testing facilities. Inadequate project management in such scenarios could result in delayed launch dates, reduced satellite functionality, or budget exhaustion before project completion.
Within the Italian aerospace context, project managers are responsible for orchestrating the activities of diverse teams, including design engineers, manufacturing specialists, and quality assurance personnel. These professionals must possess a strong understanding of both technical aerospace principles and project management methodologies, such as Agile or Waterfall. They are tasked with defining project scope, creating detailed schedules, managing resources effectively, and mitigating potential risks. Furthermore, they serve as the primary point of communication between project stakeholders, including clients, regulatory agencies, and senior management. The success of aerospace projects in Italy, whether the development of a new regional aircraft or the construction of a ground station for satellite communication, hinges on the project manager’s ability to effectively coordinate these diverse elements and maintain project momentum. This coordination must adhere to stringent Italian and European regulatory standards.
In conclusion, project management is not merely an ancillary skill within the Italian aerospace sector; it is a core competency that directly impacts project outcomes and the overall success of engineering endeavors. The complexities inherent in aerospace projects demand individuals with specialized training and proven experience in project management methodologies. Challenges arise from balancing innovation with regulatory compliance and managing geographically dispersed teams. A deep understanding of project management principles, combined with technical aerospace knowledge, is therefore essential for professionals seeking to advance their careers in this demanding and critical field in Italy.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding career prospects and requirements within the aerospace engineering field in Italy. The information provided aims to offer clarity and guidance to prospective professionals.
Question 1: What are the primary qualifications required for securing related positions in Italy?
Typically, a Master’s degree in Aerospace Engineering, or a closely related field such as Mechanical or Electrical Engineering with a specialization in aerospace, is a prerequisite. Proficiency in relevant software tools (e.g., CAD, CFD, FEA) and a strong understanding of aerospace principles are also essential. Fluency in Italian is often advantageous, particularly for roles involving direct collaboration with local teams.
Question 2: Which sectors within the Italian aerospace industry offer the most employment opportunities?
The design and manufacturing of aircraft components, satellite systems, and propulsion technologies are prominent sectors. Research and development roles within universities and government-funded institutions also present avenues for employment. Additionally, the growing emphasis on sustainable aviation is creating opportunities in areas such as alternative fuels and electric propulsion.
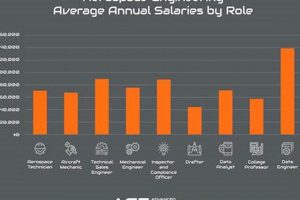
Question 3: What is the typical salary range for entry-level positions in Italy?
Entry-level salaries vary depending on the company, location, and specific role. However, a general range for recent graduates with a Master’s degree is between 28,000 and 35,000 per year. This figure can increase with experience and specialization.
Question 4: Are there specific regions in Italy where related job opportunities are concentrated?
The regions of Piedmont, Lombardy, and Lazio host a significant concentration of aerospace companies and research institutions. These areas are often associated with greater employment opportunities in the sector.
Question 5: What are the essential skills for career advancement within the Italian aerospace industry?
Beyond technical expertise, strong communication skills, problem-solving abilities, and project management capabilities are crucial for career progression. Adaptability and a willingness to embrace new technologies are also highly valued.
Question 6: What is the long-term outlook for the aerospace engineering sector in Italy?
The Italian aerospace industry is projected to experience continued growth, driven by increasing demand for air travel, advancements in space exploration, and the development of sustainable aviation technologies. This growth is expected to create ongoing employment opportunities for qualified aerospace engineers.
In summary, securing employment in the Italian aerospace industry requires a combination of strong academic qualifications, relevant technical skills, and adaptability to the evolving needs of the sector. A proactive approach to networking and continuous professional development is essential for career success.
The concluding section will provide a summary of the key factors influencing career opportunities within Italys aerospace engineering landscape.
Conclusion
The preceding analysis has explored various facets of aerospace engineering jobs in italy. The availability of these positions is influenced by factors ranging from national research funding and regulatory compliance to advances in manufacturing processes and the effectiveness of project management. The skillset demanded of professionals encompasses not only specialized technical knowledge but also adaptability and proficiency in communication and problem-solving.
The Italian aerospace sector presents a dynamic landscape for qualified individuals. Understanding the interplay of these contributing elements is paramount for those seeking to enter or advance within this field. A commitment to continuous learning and professional development will be critical for navigating the evolving demands of aerospace engineering jobs in italy and contributing to the nation’s ongoing advancements in aviation and space exploration.