Positions in the field of flight and space vehicle development located in the capital of Arizona represent a specific segment of the broader employment market. These roles encompass the design, development, testing, and production of aircraft, spacecraft, and related systems within a particular geographical area. For instance, an engineer might be involved in the creation of new drone technology or the improvement of aircraft engine efficiency for companies located in the metropolitan region.
The concentration of these opportunities in the Southwest offers potential advantages, including access to a growing technology sector, a relatively lower cost of living compared to other aerospace hubs, and proximity to key government and defense installations. Historically, the region has been a center for aviation and defense industries, contributing to a skilled workforce and a supportive ecosystem for these specialized professions. This established presence fosters innovation and collaboration between companies and research institutions.
The subsequent discussion will delve into the qualifications needed for these positions, the key industries employing aerospace engineers in the region, salary expectations, and the overall outlook for career advancement. The goal is to provide a thorough understanding of the opportunities and challenges associated with pursuing this career path in this specific locale.
The following guidelines are designed to aid professionals seeking opportunities related to aviation and space vehicle engineering in the Phoenix metropolitan area. Careful consideration of these factors can enhance career prospects and facilitate informed decision-making.
Tip 1: Target Companies Strategically: Research companies with a significant presence in the region’s aerospace sector. Identify firms involved in areas of specific interest, such as unmanned aerial systems, satellite technology, or advanced materials. Tailor applications to align with their specific needs and projects.
Tip 2: Cultivate Relevant Skills: Focus on developing expertise in areas highly sought after by employers, including computational fluid dynamics (CFD), finite element analysis (FEA), and systems engineering. Obtain certifications or complete relevant coursework to demonstrate proficiency.
Tip 3: Leverage Local Networking: Attend industry events, join professional organizations (e.g., AIAA), and connect with aerospace professionals in the Phoenix area. Networking can provide valuable insights into unadvertised openings and facilitate introductions to hiring managers.
Tip 4: Emphasize Regional Experience: If possessing prior experience, highlight projects and accomplishments relevant to the specific challenges and opportunities within the Southwestern aerospace environment. Demonstrate an understanding of the region’s industry dynamics.
Tip 5: Understand Security Clearance Requirements: Many positions require a security clearance due to the involvement of defense-related projects. Investigate clearance eligibility requirements and, if possible, pursue pre-emptive security clearance processing.
Tip 6: Optimize Online Presence: Ensure professional online profiles, such as LinkedIn, are updated with relevant experience, skills, and endorsements. Actively engage in industry discussions and share relevant content to demonstrate expertise and build connections.
Tip 7: Consider Contract Positions: Explore opportunities offered through staffing agencies specializing in aerospace engineering recruitment. Contract positions can provide valuable experience, industry connections, and potential pathways to full-time employment.
These insights provide a framework for individuals pursuing careers. A proactive approach, coupled with targeted skill development and strategic networking, can significantly increase the likelihood of securing a fulfilling position.
The following section will address the typical qualifications and salary expectations associated with engineering roles in the Phoenix area, providing a more comprehensive overview of the professional landscape.
1. Industry Growth
The expansion of the aerospace sector within the Phoenix metropolitan area functions as a primary driver for an increase in the availability of positions for engineers specializing in aircraft and spacecraft. This growth, often fueled by government contracts, private sector investment, and technological innovation, creates a demand for skilled professionals across various engineering disciplines. For example, the establishment or expansion of a manufacturing facility by an aerospace company will invariably lead to the recruitment of design engineers, manufacturing engineers, and quality control specialists.
The relationship between industry growth and employment opportunities is not merely correlational but causal. New projects, product lines, or service offerings necessitate an expanded workforce. Moreover, growth within supporting industries, such as suppliers of specialized components or providers of testing services, further amplifies the demand for engineering expertise. One notable example is the growth of companies specializing in unmanned aerial systems (UAS), leading to a demand for engineers with expertise in areas like autonomous navigation and sensor integration.
In conclusion, the sustained expansion of the aerospace sector in Phoenix directly translates into an increased demand for qualified engineers. Understanding the specific drivers of this growth, whether it be government spending, commercial activity, or technological advancements, is critical for job seekers to strategically position themselves and target companies and areas of specialization with the greatest potential for long-term career prospects. The practical implication is that prospective employees should monitor industry trends and align their skill sets to meet the evolving needs of the marketplace.
2. Salary Ranges
Compensation for aerospace engineering roles in Phoenix is a critical factor for both prospective employees and employers. These ranges are influenced by experience, education, specialization, and the specific requirements of the position, impacting the attraction and retention of talent within the region.
- Experience Level
Entry-level positions typically offer lower salaries compared to roles requiring several years of experience. An engineer with less than two years of experience might earn a salary significantly lower than a senior engineer with over ten years of experience leading complex projects. Experience gained on relevant projects directly correlates with higher earning potential.
- Educational Attainment
Advanced degrees, such as a Master’s or Ph.D., often command higher starting salaries. Positions requiring specialized knowledge or research capabilities frequently prioritize candidates with postgraduate qualifications. For instance, a research engineer with a Ph.D. focusing on advanced materials may be compensated at a higher rate than an engineer with a Bachelor’s degree in a similar role.
- Specialization
Demand for specific skill sets can significantly influence salary ranges. Specializations in areas like avionics, propulsion systems, or composite materials are often highly valued due to the scarcity of expertise. Engineers with specialized knowledge in high-demand areas often command premium salaries due to the competitive nature of the job market.
- Company Size and Type
Large aerospace corporations may offer more competitive salaries and benefits packages compared to smaller firms or startups. However, smaller companies may offer alternative benefits, such as equity or greater opportunities for rapid advancement. Government contractors often adhere to specific salary scales, which may differ from those in the private sector. Factors like the size and financial stability of an organization can impact the compensation offered.
Ultimately, salary ranges for aerospace engineering positions in Phoenix reflect the dynamic interplay of experience, education, specialization, and employer characteristics. A thorough understanding of these factors enables both job seekers and employers to navigate the competitive job market effectively. The subsequent sections will address other factors, such as required education and key employers, to provide a more complete overview.
3. Required Education
The attainment of specific academic qualifications forms the foundation for entry into aerospace engineering professions within the Phoenix metropolitan area. These educational requirements are not merely formalities but reflect the complex technical knowledge and analytical skills essential for success in this demanding field, directly influencing job opportunities.
- Bachelor’s Degree in Aerospace Engineering (or related field)
A Bachelor’s degree serves as the minimum academic threshold for most entry-level positions. Curricula typically include coursework in aerodynamics, propulsion, structural analysis, and control systems. For example, a graduate with a Bachelor’s degree may qualify for roles involving design support or testing under the supervision of experienced engineers. A solid understanding of fundamental engineering principles is critical.
- Specialized Coursework and Certifications
Certain positions may require specialized coursework or certifications related to specific software tools or industry standards. Proficiency in computer-aided design (CAD) software, finite element analysis (FEA) programs, or programming languages relevant to aerospace applications is often expected. Earning relevant certifications demonstrates a commitment to professional development and enhances competitiveness. For instance, certification in a particular composite material design software can be a distinct advantage when applying for related positions.
- Advanced Degrees (Master’s or Ph.D.)
Advanced degrees, particularly a Master’s or Ph.D., are often required for research-oriented positions or roles involving complex design and analysis. Graduate-level studies provide in-depth knowledge of specialized areas and develop advanced research skills. For example, a research engineer focusing on hypersonic aerodynamics would likely need a Ph.D. to contribute effectively to research and development efforts. These degrees often open doors to higher-level positions and leadership roles.
- Accreditation and Program Reputation
The accreditation status and reputation of the educational institution and program are significant factors in evaluating candidates. Accreditation by organizations like ABET (Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology) ensures that the program meets established quality standards. Graduates from reputable programs often have an advantage in the job market due to the rigor and comprehensive nature of their education.
In summary, acquiring the necessary educational qualifications, including a relevant degree, specialized coursework, and, in some cases, advanced degrees, is paramount for securing aerospace engineering opportunities in Phoenix. The specific requirements vary based on the position and employer, but a strong foundation in engineering principles and a commitment to continuous learning are consistently valued. Pursuing an education from an accredited and reputable institution is a strategic investment in a successful career.
4. Key Employers
The concentration of opportunities in aircraft and spacecraft development in the Phoenix area is intrinsically linked to the presence and activity of specific organizations. These companies, serving as primary drivers of the regional aerospace economy, directly influence the availability, nature, and scope of engineering positions. The operational decisions of major employers, such as expanding research facilities or initiating new production lines, are direct causal factors impacting the number of job openings, the skill sets demanded, and the overall economic health of this employment sector. The prominence of key employers, therefore, is a critical component of the professional landscape being examined.
Examining the specific companies contributing to these positions yields practical insights. For example, a multinational defense contractor with a significant Phoenix presence might specialize in missile systems, thus creating demand for engineers with expertise in guidance and control or aerodynamics. Conversely, a smaller firm focused on commercial drone technology will likely prioritize engineers skilled in autonomous navigation or sensor integration. Understanding the business focus of these key employers is therefore essential to tailoring job applications and focusing skill development efforts. Furthermore, knowledge of employer-specific projects and contracts allows candidates to demonstrate informed interest and relevance during the application process.
In summary, key employers constitute the cornerstone of employment opportunities in the Phoenix aerospace sector. Awareness of these companies, their specialization, and their current projects is essential for professionals seeking to navigate this job market successfully. This understanding enables job seekers to target their applications, develop relevant skills, and ultimately, increase their chances of securing a desirable engineering position.
5. Skill Demands
The skills required to secure positions related to aircraft and spacecraft engineering in Phoenix directly influence the career prospects of professionals seeking employment. The demand for specific skills, often dictated by technological advancements and industry trends, functions as a gatekeeper, determining which candidates are best positioned for success. A demonstrable mastery of required skills is a prerequisite for entry into this competitive job market. For example, the increasing reliance on composite materials in aircraft design necessitates proficiency in areas such as composite analysis, manufacturing techniques, and non-destructive testing. Candidates lacking these skills may find their employment opportunities severely limited.
Practical examples further illustrate this connection. Employers engaged in the development of unmanned aerial systems (UAS) in the Phoenix area seek engineers with expertise in areas such as autonomous navigation, sensor integration, and embedded systems programming. Engineers lacking these specialized skill sets may struggle to compete with candidates who possess the required expertise. Furthermore, the growing emphasis on model-based systems engineering (MBSE) requires a proficiency in simulation software and systems modeling languages. These “soft skills” are not necessarily inherent talents, but skills that can be improved in a very short time through focused online education or personal study.
In conclusion, the convergence of specialized engineering abilities and the evolving demands of Phoenix’s aircraft and spacecraft engineering sector shapes career trajectories. The competitive nature of this landscape demands active acquisition and refinement of skills tailored to the specific needs of local employers. Professionals who proactively address these demands enhance their employment prospects and contribute to the region’s technological advancement. The continuing professional’s capacity for skill adaptation remains a critical factor for sustainable career progression within this sector.
6. Regional Advantage
The concentration of opportunities in the Phoenix area relating to aerospace engineering is significantly influenced by a confluence of geographical, economic, and infrastructural factors, collectively termed “Regional Advantage.” These advantages shape the nature of the industry within the area and contribute to the desirability of the region for both companies and engineering professionals.
- Proximity to Government and Military Installations
The presence of Luke Air Force Base and other government facilities provides a stable source of demand for aerospace engineering services. Companies located near these installations benefit from proximity to potential clients and collaborative research opportunities. This translates into more positions focused on defense-related projects and testing, a distinct characteristic of employment in the region.
- Favorable Business Climate and Lower Operating Costs
Arizona’s pro-business policies, including lower taxes and reduced regulatory burdens compared to other major aerospace hubs, attract companies seeking to minimize operating expenses. This economic advantage fosters investment and expansion, leading to the creation of additional engineering positions across a range of specialties.
- Access to a Skilled Workforce
The presence of reputable universities and technical colleges in the Phoenix metropolitan area contributes to a steady supply of qualified engineering graduates. This local talent pool reduces recruitment costs for aerospace companies and provides a foundation for innovation and growth. The continuous stream of new graduates fills entry level positions and allows more senior personnel to focus on higher level innovation.
- Strategic Geographic Location
Phoenix’s geographic location offers favorable weather conditions for flight testing and research, a significant advantage for aerospace companies involved in aircraft development. The region also provides convenient access to other major markets and suppliers, facilitating efficient logistics and supply chain management. This strategic positioning makes the region attractive for the aerospace industry.
These regional advantages, taken together, create a favorable environment for the aerospace industry in Phoenix, resulting in a distinct concentration of engineering opportunities within the area. The interaction of these factors is critical to understanding the specific characteristics and benefits associated with pursuing careers related to aircraft and spacecraft development in this region.
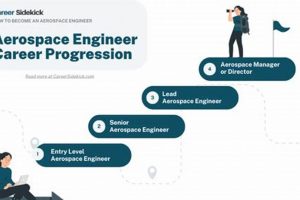
7. Career Trajectory
The anticipated progression of an engineer’s professional life is a critical factor when evaluating employment prospects in the Phoenix aerospace sector. Understanding potential career paths provides valuable insight for both aspiring and established engineers, influencing decisions related to education, specialization, and strategic job selection. The viability of aerospace engineering positions in Phoenix hinges on the availability of opportunities for advancement and skill development.
- Entry-Level Positions and Initial Skill Development
Entry-level roles, such as design engineers or testing engineers, serve as a foundation for career advancement. These positions provide opportunities to acquire fundamental skills and gain practical experience under the supervision of senior engineers. For example, a recent graduate might begin by assisting with CAD modeling or conducting component-level testing, gradually assuming more responsibility as expertise grows. The availability of these foundational positions is crucial for nurturing talent and building a sustainable workforce.
- Progression to Specialized Roles
With experience, engineers can specialize in areas such as propulsion systems, avionics, or structural analysis. These specialized roles demand in-depth knowledge and advanced technical skills. For example, an engineer who initially focused on structural design might transition to specializing in composite materials, requiring additional training and certification. The existence of opportunities for specialization allows engineers to deepen their expertise and contribute to specific areas of technological advancement.
- Management and Leadership Opportunities
Experienced engineers may advance into management or leadership positions, overseeing engineering teams and projects. These roles require strong communication, problem-solving, and decision-making skills. For example, a senior design engineer might become a project manager, responsible for coordinating the efforts of multiple engineers and ensuring the successful completion of complex projects. The availability of leadership roles is essential for retaining experienced engineers and fostering a culture of innovation.
- Opportunities for Research and Development
Some aerospace engineers pursue careers in research and development, contributing to the advancement of aerospace technology. These roles require a strong understanding of scientific principles and advanced research skills. For example, an engineer with a Ph.D. might work on developing new propulsion technologies or designing more efficient aircraft structures. Research and development positions are crucial for driving innovation and maintaining a competitive edge.
In conclusion, the availability of clear and attainable career trajectories significantly influences the attractiveness of aerospace engineering positions in Phoenix. A robust aerospace sector offers a variety of opportunities for engineers to develop their skills, specialize in specific areas, and advance into leadership roles. The presence of both established companies and innovative startups creates a diverse range of career paths, contributing to a dynamic and thriving engineering community. This environment, in turn, strengthens the region’s position as a hub for aerospace engineering innovation and employment.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Aerospace Engineering Positions in Phoenix
This section addresses common inquiries and misconceptions regarding career prospects and opportunities in aircraft and spacecraft engineering within the Phoenix metropolitan area. The information presented aims to provide clarity and informed guidance to prospective job seekers and those interested in understanding the dynamics of this regional sector.
Question 1: What are the primary qualifications required to secure an entry-level aerospace engineering position in Phoenix?
A minimum of a Bachelor’s degree in Aerospace Engineering, or a closely related field such as Mechanical Engineering with a focus on aerospace topics, is generally required. Demonstrated proficiency in relevant software tools (e.g., CAD, FEA) and a strong understanding of fundamental engineering principles are also essential.
Question 2: Which specific industries within the Phoenix area are most likely to employ aircraft and spacecraft engineers?
Key industries include defense contractors involved in missile systems and aircraft maintenance, commercial aerospace companies specializing in aircraft components and manufacturing, and technology firms focused on unmanned aerial systems (UAS) and related technologies. Research institutions and government agencies also provide employment opportunities.
Question 3: How does the cost of living in Phoenix compare to other major aerospace hubs, and how does this impact salary expectations?
The cost of living in Phoenix is generally lower than in major aerospace hubs such as Los Angeles or Seattle. While salaries may be somewhat lower in Phoenix compared to these areas, the reduced cost of living can result in a comparable, or even higher, standard of living.
Question 4: What are the most in-demand skills for aerospace engineers in the Phoenix job market?
Skills in areas such as systems engineering, composite materials, avionics, propulsion systems, and autonomous systems are consistently in high demand. Proficiency in modeling and simulation software is also highly valued.
Question 5: Is a security clearance typically required for aircraft and spacecraft engineering positions in Phoenix?
Many positions, particularly those involving defense-related projects, require a security clearance. The specific level of clearance required depends on the nature of the project and the level of access to classified information. Prospective applicants should be prepared to undergo a background check and security screening.
Question 6: What are the prospects for career advancement for aircraft and spacecraft engineers in Phoenix?
Career advancement opportunities exist in areas such as specialized engineering roles, project management, research and development, and leadership positions. The presence of both established companies and innovative startups provides a diverse range of career paths.
These frequently asked questions highlight the key considerations for individuals exploring career options related to aircraft and spacecraft engineering in Phoenix. A thorough understanding of these factors is crucial for making informed decisions and maximizing career potential.
The following section will address resources for job seekers and professional development opportunities, offering practical guidance for navigating the Phoenix aircraft and spacecraft engineering landscape.
Aerospace Engineering Jobs Phoenix
This analysis has explored the specific dynamics of the employment market for aerospace engineers within the Phoenix metropolitan area. Key aspects examined included industry growth patterns, salary expectations, educational prerequisites, prominent employers, in-demand skills, regional advantages, and potential career trajectories. The goal was to provide a comprehensive understanding of the opportunities and challenges associated with pursuing engineering careers in this specific geographic location.
The information presented serves as a resource for individuals considering or currently pursuing careers in this field. Continued monitoring of industry trends, proactive skill development, and strategic networking remain crucial for success. The future of “aerospace engineering jobs phoenix” will depend on sustained economic growth, technological innovation, and the ability of engineers to adapt to the evolving demands of the industry.