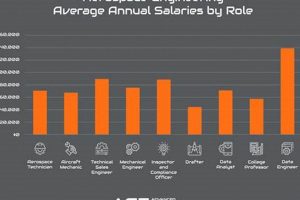
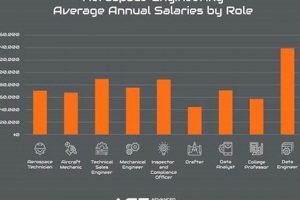
Opportunities for individuals pursuing a degree in the design, development, and testing of aircraft and spacecraft encompass a range of entry-level positions. These roles provide practical experience in applying theoretical knowledge to real-world projects within the aeronautics and astronautics fields. Examples include internships at aerospace companies, research assistant positions in university labs, and co-op programs that integrate academic study with professional work experience.
Securing practical roles during academic studies offers numerous advantages. It allows students to build professional networks, gain a competitive edge in the job market after graduation, and refine their career interests. Historically, these experiences have served as a crucial stepping stone for aspiring engineers to transition into full-time employment within the aerospace industry. The knowledge and skills acquired through such experiences supplement classroom learning and provide a deeper understanding of industry practices.
The subsequent sections will explore various types of available opportunities, provide guidance on effective application strategies, and highlight resources that can assist students in finding relevant and rewarding experiences within the field. The focus will be on maximizing the potential for professional growth and development during academic pursuits.
Successfully securing roles related to one’s academic pursuits requires a proactive and strategic approach. The following recommendations are designed to enhance prospects and maximize the potential for career advancement during university studies.
Tip 1: Cultivate a Strong Academic Foundation: A solid understanding of core engineering principles, including aerodynamics, propulsion, and structural analysis, is paramount. Employers often seek candidates with a demonstrated aptitude for technical problem-solving. Maintaining a high GPA and excelling in relevant coursework are essential.
Tip 2: Proactively Seek Out Internship Programs: Internship programs offered by aerospace companies and research institutions provide invaluable practical experience. Utilize university career services, online job boards, and professional networking events to identify and apply for relevant opportunities. Tailor application materials to align with the specific requirements of each role.
Tip 3: Engage in Relevant Extracurricular Activities: Participation in student organizations, such as rocketry clubs or design teams, demonstrates a commitment to the field and provides hands-on experience. These activities offer opportunities to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world projects and develop teamwork skills.
Tip 4: Develop Strong Technical Skills: Proficiency in industry-standard software tools, such as CAD, CAE, and programming languages, is highly valued by employers. Seek out opportunities to develop these skills through coursework, online tutorials, and personal projects. Showcase these skills in a portfolio or during interviews.
Tip 5: Network with Industry Professionals: Attend industry conferences, career fairs, and informational sessions to connect with engineers and recruiters. Networking can provide valuable insights into the industry and open doors to potential opportunities. Prepare an elevator pitch that highlights skills and career aspirations.
Tip 6: Tailor Rsums and Cover Letters: Generic application materials are unlikely to stand out. Customize rsums and cover letters to specifically address the requirements and preferences outlined in each job posting. Highlight relevant skills, experience, and academic achievements.
Effective implementation of these strategies will significantly improve one’s chances of securing valuable practical experiences during the academic journey. These experiences are crucial for building a strong foundation for a successful career in the aerospace sector.
The subsequent discussion will explore resources available to facilitate the search and application process, further enhancing the prospects of securing desired positions.
1. Internship Availability
The prevalence of internships directly impacts the accessibility of opportunities for aerospace engineering students. A higher availability of internships expands the options for students seeking practical experience in the field. This increased access enables students to apply theoretical knowledge, develop technical skills, and gain professional insights through direct involvement in industry projects. For example, the presence of numerous internship programs at major aerospace companies like Lockheed Martin and SpaceX provides students with diverse avenues for hands-on learning in areas such as propulsion systems, aerodynamics, and structural design. The absence of sufficient internship opportunities limits the potential for students to gain the necessary experience to be competitive in the job market upon graduation.
The impact extends beyond individual student development. Adequate internship availability also benefits the aerospace industry by creating a pipeline of qualified and experienced graduates. Companies that actively offer these programs are investing in the future workforce. Through internships, students bring new perspectives and ideas to the companies and can contribute to innovation. Real-world projects completed during internships often lead to valuable contributions and can significantly improve the overall productivity of a company.
Therefore, focusing on increasing internship availability is essential for enhancing the prospects of aerospace engineering students and strengthening the industry as a whole. Addressing potential barriers such as geographical limitations, funding constraints, and awareness gaps is crucial. Encouraging companies to expand their internship programs and supporting students in accessing these opportunities will foster the next generation of aerospace engineers.
2. Skill Development
The acquisition and refinement of specific skills are intrinsically linked to opportunities for individuals studying aerospace engineering. These roles necessitate a diverse skillset, and the development thereof directly influences an individual’s competitiveness and performance within these positions. Practical experience gained through internships, research assistantships, and co-op programs serves as a critical avenue for skill enhancement. For instance, participation in a design team focused on building a small satellite enhances proficiency in CAD software, systems engineering, and project managementall highly valued within the industry. Conversely, a lack of relevant skills significantly restricts access to these invaluable experiences.
Skill development within these opportunities extends beyond technical competencies. Effective communication, teamwork, and problem-solving abilities are equally crucial. For example, an intern tasked with analyzing wind tunnel data must not only possess the technical expertise to interpret the data but also the communication skills to present findings clearly to senior engineers. Furthermore, involvement in research projects often necessitates the ability to adapt to unforeseen challenges and collaborate effectively within a multidisciplinary team. The absence of these soft skills can impede project success and limit an individual’s ability to contribute meaningfully.
In summary, skill development is not merely a prerequisite but an ongoing process facilitated by actively engaging in aerospace-related opportunities. The cultivation of both technical and non-technical skills is essential for success in these roles and, subsequently, for a fulfilling career in the aerospace sector. Recognizing the importance of continuous learning and proactively seeking opportunities for skill enhancement are paramount for aspiring aerospace engineers.
3. Industry Networking
Industry networking serves as a critical component of securing positions within the aerospace engineering field during academic studies. The establishment of professional connections directly impacts a student’s access to information regarding available opportunities, company culture, and emerging technologies. Furthermore, direct interactions with engineers and recruiters provide invaluable insights into the skills and qualities sought by employers. For example, attending an industry conference, such as the AIAA SciTech Forum, facilitates direct engagement with professionals from various companies and government agencies, allowing students to learn about internship programs and entry-level positions. The absence of active networking efforts can significantly limit a student’s awareness of and access to these crucial positions.
Networking extends beyond simply acquiring information; it also provides a platform for students to showcase their skills and interests. A well-crafted elevator pitch and a professional demeanor during networking events can leave a lasting positive impression on potential employers. Moreover, participation in industry-sponsored events, such as design competitions or hackathons, offers opportunities to collaborate with professionals and demonstrate practical problem-solving abilities. These interactions can lead to direct referrals for internships or even full-time employment opportunities. Actively engaging in professional organizations, like the Society of Women Engineers, further enhances networking opportunities and provides a support system for navigating the industry.
In summary, industry networking represents a strategic investment in one’s career prospects within the aerospace sector. Proactively building and maintaining connections with professionals can significantly enhance a student’s access to opportunities, facilitate skill development, and provide a competitive edge in the job market. Addressing any potential barriers to networking, such as financial constraints or lack of confidence, is crucial for ensuring equitable access to these valuable resources. The understanding and proactive utilization of networking opportunities are paramount for aspiring aerospace engineers seeking to launch successful careers.
4. Project Experience
Project experience is a cornerstone of opportunities for aerospace engineering students. It represents a tangible demonstration of applied knowledge and practical skills, significantly enhancing a candidate’s profile and increasing their competitiveness in the job market. These experiences bridge the gap between theoretical learning and real-world application, providing a crucial advantage for students seeking employment in the aerospace sector.
- Application of Theoretical Knowledge
Project involvement allows for the direct application of classroom concepts to real-world challenges. For example, designing and testing a model aircraft wing requires students to implement principles of aerodynamics, structural analysis, and materials science. This practical application solidifies understanding and demonstrates the ability to translate theory into tangible results, a highly valued attribute for employers.
- Development of Technical Proficiency
Project activities often necessitate the use of industry-standard software and tools. Designing a satellite payload, for instance, may require proficiency in CAD software, simulation tools, and programming languages. Engaging with these technologies enhances technical competence and provides students with valuable hands-on experience that aligns with industry practices.
- Enhancement of Problem-Solving Skills
Aerospace projects inherently involve complex challenges requiring creative problem-solving. Whether troubleshooting a malfunctioning sensor or optimizing the performance of a rocket engine, students develop analytical and critical thinking skills. Successfully navigating these challenges demonstrates the ability to approach complex problems methodically and effectively.
- Cultivation of Teamwork and Collaboration
Most aerospace projects are collaborative endeavors, requiring effective teamwork and communication. Students learn to work within multidisciplinary teams, share ideas, and contribute to a common goal. Successfully collaborating on a project demonstrates the ability to function effectively within a professional team environment, an essential skill for success in the aerospace industry.
These multifaceted benefits of project experience collectively contribute to a well-rounded skill set that is highly sought after by employers. From applying theoretical knowledge to developing technical proficiency and fostering teamwork, project involvement provides aerospace engineering students with a distinct advantage in securing desired roles. The ability to articulate project experiences effectively during interviews and showcase tangible results further enhances their prospects, solidifying project participation as a critical component of professional development.
5. Career Exploration
Opportunities for students pursuing degrees in aerospace engineering are inextricably linked to proactive career exploration. The field encompasses diverse specializations, including aerodynamics, propulsion, structural analysis, and control systems. Therefore, a deliberate effort to explore these various paths is essential for informed decision-making regarding academic focus and career aspirations. For instance, a student initially drawn to aerospace may discover, through internships or informational interviews, a greater passion for computational fluid dynamics or satellite communications. This process of discovery directly influences the types of opportunities sought, aligning student skills and interests with specific industry needs.
The consequences of inadequate career exploration can be significant. Students may pursue academic tracks that do not align with their aptitudes or interests, leading to dissatisfaction or underperformance. Furthermore, a lack of exposure to different career paths can limit their awareness of available options, potentially resulting in the selection of less fulfilling or less promising opportunities after graduation. Conversely, active engagement in career exploration, through internships, research experiences, and networking events, enhances self-awareness and allows students to tailor their academic and professional development towards specific goals. Attending industry conferences and participating in company-sponsored workshops are valuable avenues for gaining insights into the evolving demands of the aerospace sector.
In conclusion, career exploration is not merely a supplementary activity but a fundamental component of academic and professional development for aerospace engineering students. It enables informed decision-making, promotes alignment between skills and interests, and enhances access to diverse opportunities within the field. Addressing barriers to career exploration, such as limited access to internships or inadequate mentorship, is crucial for ensuring that students are well-prepared to navigate the complexities of the aerospace industry and pursue fulfilling careers.
6. Financial Support
Financial support acts as a significant enabler in facilitating access to “aerospace engineering student jobs.” These opportunities, encompassing internships, research positions, and co-op programs, often require students to dedicate substantial time and effort, sometimes precluding them from pursuing traditional part-time employment. Funding through scholarships, grants, paid internships, or stipends allows students to participate without facing undue financial hardship. For instance, a student receiving a grant to support their unpaid research at a university aerospace lab can fully immerse themselves in the work, gaining valuable experience that would otherwise be unattainable due to the need to earn income.
The availability of financial assistance directly correlates with increased participation rates among students from diverse socioeconomic backgrounds. Without such support, these experiences are disproportionately accessible to students from wealthier families, potentially limiting the talent pool entering the aerospace industry. Furthermore, financial constraints can dictate the types of opportunities students pursue. Paid internships, while providing essential practical experience, may not always align perfectly with a student’s career aspirations. Financial support allows students to prioritize opportunities based on their academic and professional goals rather than purely on monetary compensation. For example, a scholarship might allow a student to accept a research position focusing on advanced propulsion systems, even if it offers a lower hourly rate than a less relevant job.
In summary, financial support is a critical element in ensuring equitable access to “aerospace engineering student jobs.” It enables students to fully engage in these experiences, develop essential skills, and explore career paths without being limited by financial constraints. Sustained investment in scholarships, grants, and paid opportunities is vital for fostering a diverse and highly skilled workforce within the aerospace engineering field. Addressing financial barriers enhances the potential for all students to contribute to innovation and advancements in the industry.
7. Mentorship Opportunities
Mentorship opportunities serve as a catalyst for successful navigation and performance within the realm of positions available to students pursuing aerospace engineering degrees. These relationships, often established with experienced engineers, researchers, or faculty members, provide invaluable guidance and support that directly enhances a student’s ability to secure and excel in relevant experiences. For example, a mentor can provide insights into the specific skills and qualifications sought by aerospace companies, assist with rsum and cover letter writing, and offer advice on interview preparation. This individualized support significantly increases a student’s chances of securing competitive internships or research positions.
The benefits of mentorship extend beyond simply acquiring a role. Mentors provide practical advice on navigating workplace dynamics, managing projects effectively, and developing professional networks. For instance, a mentor might share strategies for communicating technical information clearly to non-technical audiences or offer guidance on resolving conflicts within a team. Furthermore, mentorship opportunities often provide access to exclusive networking events or introductions to key individuals within the aerospace industry. These connections can lead to further opportunities for professional development and career advancement. A strong mentor-mentee relationship fosters confidence, encourages innovation, and provides a safe space for students to seek advice and feedback on their academic and professional progress. Consider a situation where a student is struggling with a complex engineering problem during an internship; a mentor can provide guidance and support, helping the student develop problem-solving skills and gain confidence in their abilities.
In conclusion, the availability and utilization of mentorship opportunities represent a critical factor in determining the success of aerospace engineering students seeking practical experience. These relationships provide invaluable guidance, support, and access to resources that enhance a student’s ability to secure and excel in relevant roles. Therefore, promoting and facilitating mentorship programs within universities and aerospace organizations is essential for fostering the next generation of skilled and successful aerospace engineers. The cultivation of strong mentor-mentee relationships directly contributes to the overall advancement of the aerospace industry by nurturing talent and promoting innovation.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Aerospace Engineering Student Jobs
The following questions address common inquiries and concerns related to opportunities for individuals pursuing a degree in aerospace engineering during their academic studies.
Question 1: What types of positions are typically available to aerospace engineering students?
Common roles include internships at aerospace companies, research assistant positions in university laboratories, and co-op programs that integrate academic study with professional work experience. These opportunities span various specializations, such as aerodynamics, propulsion, structures, and control systems.
Question 2: When is the optimal time to begin searching for experiential learning opportunities?
The search process should commence early in the academic career, ideally during the freshman or sophomore year. Many companies offer internship programs with deadlines that occur months in advance. Proactive networking and early application are essential for maximizing prospects.
Question 3: What qualifications are typically sought by employers offering internships or research positions?
Employers typically seek candidates with a strong academic record, relevant coursework, proficiency in industry-standard software (e.g., CAD, CAE), and demonstrated teamwork and communication skills. Previous project experience and involvement in related extracurricular activities are also highly valued.
Question 4: What resources are available to assist students in finding relevant opportunities?
University career services, online job boards (e.g., LinkedIn, Indeed), professional organizations (e.g., AIAA), and company websites represent valuable resources. Networking events and career fairs provide opportunities to connect with recruiters and industry professionals.
Question 5: Is financial support typically available for unpaid internships or research positions?
Financial support may be available through university grants, scholarships, or stipends offered by the host organization. Students should actively research and apply for funding opportunities to offset the costs associated with participating in unpaid experiences.
Question 6: How can students effectively leverage experiential learning opportunities to enhance their career prospects?
Students should actively seek opportunities to develop new skills, build professional networks, and contribute meaningfully to projects. Documenting accomplishments, seeking feedback from supervisors, and presenting project results at conferences or in publications can further enhance their competitiveness.
Successfully navigating opportunities during academic studies necessitates proactive planning, diligent preparation, and continuous professional development.
The subsequent section will address strategies for developing essential skills that enhance competitiveness within this sector.
Conclusion
This exploration of “aerospace engineering student jobs” has highlighted the critical role that practical experience plays in shaping the future careers of aspiring aerospace engineers. From skill development and industry networking to financial support and mentorship, each facet contributes significantly to a student’s preparedness and competitiveness within the field. The information presented underscores the multifaceted nature of these opportunities and their importance in supplementing traditional classroom learning.
A commitment to securing and maximizing these experiences is paramount for those seeking a successful trajectory in the aerospace sector. The long-term benefits, including enhanced career prospects and contributions to technological advancement, warrant a proactive and strategic approach. Prioritizing the pursuit of “aerospace engineering student jobs” represents a deliberate investment in a promising future.