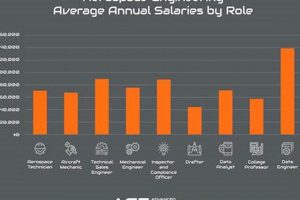
Positions focused on the maintenance, repair, and inspection of aircraft and spacecraft are essential for ensuring airworthiness and operational safety. These roles encompass a range of tasks, from routine checks and component replacements to complex troubleshooting and system overhauls. For example, an individual in this field might diagnose engine malfunctions, repair hydraulic systems, or inspect airframes for structural damage.
The availability of skilled professionals to perform these tasks is critically important for the aviation industry, impacting flight safety, operational efficiency, and regulatory compliance. Historically, these specialized skills were developed through on-the-job training. Today, formal education and certification programs contribute significantly to the competence and quality of the workforce involved in aerospace vehicle maintenance.
The following sections will provide a detailed overview of the qualifications, responsibilities, and prospects associated with pursuing a career path dedicated to ensuring the integrity and reliability of aircraft and spacecraft.
Career Advancement Strategies
Individuals seeking to excel in the field can benefit from strategic planning and continuous professional development. The following tips provide guidance for enhancing career prospects and maximizing opportunities within this highly specialized sector.
Tip 1: Obtain Comprehensive Certification: Pursue and maintain all relevant certifications, such as the Airframe and Powerplant (A&P) license. These credentials demonstrate a standardized level of competence and are often prerequisites for advanced roles.
Tip 2: Specialize in a Specific Aircraft Type: Developing expertise in a particular aircraft model or system (e.g., Boeing 737, Airbus A320, avionics systems) can significantly enhance marketability and create opportunities for specialized maintenance roles.
Tip 3: Seek Advanced Training: Participate in manufacturer-sponsored training programs and workshops to stay abreast of the latest technologies, maintenance procedures, and regulatory changes. This demonstrates a commitment to continuous improvement.
Tip 4: Develop Strong Troubleshooting Skills: Cultivate analytical thinking and problem-solving abilities to effectively diagnose and resolve complex mechanical and electrical issues. Documenting troubleshooting processes and solutions adds value to professional experience.
Tip 5: Gain Experience in Diverse Environments: Seek opportunities to work in various settings, such as commercial airlines, private aviation, or military installations. Exposure to different operational environments broadens skill sets and enhances adaptability.
Tip 6: Network with Industry Professionals: Attend industry conferences, join professional organizations, and connect with experienced colleagues to learn about emerging trends, career opportunities, and best practices.
Tip 7: Consider Supervisory or Management Roles: Acquire leadership skills and seek opportunities to advance into supervisory or management positions, such as maintenance supervisor or quality control manager. This requires strong communication, organizational, and interpersonal skills.
Adhering to these recommendations can increase the likelihood of professional success and career progression within the dynamic and demanding field.
The subsequent sections will further explore the long-term outlook and potential career trajectories for those dedicated to maintaining the safety and operational efficiency of aerospace vehicles.
1. Safety Regulations Adherence
Strict compliance with safety regulations forms the bedrock of all activities performed within aircraft maintenance. Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) regulations, along with equivalent international standards, dictate every aspect of the maintenance process, from component inspection to repair procedures and documentation protocols. The position requires a thorough understanding and unwavering application of these regulations, as failure to adhere to them can directly compromise aircraft airworthiness and passenger safety. For instance, improperly torquing a critical fastener during engine reassembly, in violation of specified torque values, could lead to engine failure during flight.
The importance of adherence extends beyond preventing immediate mechanical failures. Meticulous record-keeping, mandated by regulations, provides a complete maintenance history for each aircraft, enabling identification of potential systemic issues and tracking of component lifespan. This historical data informs predictive maintenance strategies, allowing for proactive interventions before component failures occur. An example would be tracking repeated instances of corrosion on a specific airframe section, prompting a detailed inspection and corrosion mitigation plan.
In summary, safety regulations adherence is not merely a procedural obligation but an integral component of the aerospace mechanic role. It directly influences the safety and reliability of air travel and contributes to the overall integrity of the aviation industry. The challenge lies in maintaining vigilance and continuous professional development to stay abreast of evolving regulations and best practices, ensuring the highest standards of safety are upheld in every maintenance task.
2. Aircraft System Knowledge
Comprehensive understanding of aircraft systems is foundational for proficient maintenance practices. This knowledge base enables accurate diagnoses, effective repairs, and the prevention of potential malfunctions, all critical for ensuring flight safety and operational efficiency. The following facets illustrate the breadth and depth of system expertise required.
- Hydraulic System Operation
Aircraft hydraulic systems control various functions, including landing gear deployment, flight control surface actuation, and braking. Knowledge includes understanding fluid dynamics, pump operation, valve control, and actuator mechanics. A mechanic with this expertise can troubleshoot issues like pressure loss, actuator malfunction, or fluid contamination, ensuring reliable hydraulic system performance for safe flight operations. For instance, diagnosing a faulty pressure regulator preventing proper flap extension requires detailed knowledge of hydraulic circuits and pressure regulation mechanisms.
- Engine Management Systems
Modern aircraft engines rely on sophisticated electronic engine management systems (EEMS) for optimal performance and fuel efficiency. Expertise includes understanding sensor data interpretation, fuel injection control, ignition timing, and exhaust gas analysis. A skilled mechanic can use this knowledge to diagnose engine malfunctions, optimize performance, and minimize emissions. Detecting a malfunctioning oxygen sensor causing excessive fuel consumption necessitates comprehensive knowledge of EEMS parameters and diagnostic procedures.
- Avionics Integration and Troubleshooting
Avionics systems encompass navigation, communication, and flight control elements. Knowledge includes understanding signal processing, data communication protocols, sensor calibration, and display technologies. This expertise enables the diagnosis and repair of issues affecting navigation accuracy, communication reliability, or flight control stability. Identifying the source of intermittent GPS signal loss requires thorough understanding of antenna systems, signal processing hardware, and communication protocols.
- Airframe Structure and Integrity
A solid understanding of airframe construction, material properties, and stress distribution is crucial for assessing structural integrity. Knowledge includes identifying corrosion, fatigue cracks, and impact damage, and applying appropriate repair techniques. A mechanic with this expertise can perform thorough inspections, identify potential structural weaknesses, and implement corrective actions to maintain airworthiness. Detecting hairline cracks around rivet holes on a wing spar requires careful visual inspection and knowledge of structural load paths.
These facets of aircraft system knowledge are indispensable for competent performance. Their application enables the effective performance of maintenance activities, contributing directly to the safety and reliability of aircraft operations. Possessing a deep understanding of these systems allows for efficient diagnostics, effective repairs, and proactive maintenance, solidifying the role’s critical contribution to aviation safety.
3. Troubleshooting Proficiency
Troubleshooting proficiency is a cornerstone competency for personnel in these roles. It constitutes the ability to systematically diagnose and resolve malfunctions or performance deviations in aircraft and spacecraft systems. The absence of effective troubleshooting skills directly impairs the individual’s capacity to maintain airworthiness and operational readiness. For instance, consider an aircraft experiencing unexplained fluctuations in engine RPM. A proficient technician would employ a structured approach, using diagnostic tools, reviewing maintenance records, and consulting technical manuals to identify the root cause, such as a faulty sensor or fuel delivery issue. Without such proficiency, the problem might persist, potentially leading to catastrophic failure.
The importance of these skills extends beyond simply identifying the immediate cause of a problem. It involves understanding the interconnectedness of aircraft systems and predicting potential cascading effects. For example, a seemingly minor electrical fault in the avionics system might impact navigation accuracy or flight control stability. An experienced troubleshooter would consider these potential ramifications and conduct a thorough investigation to ensure the entire system is functioning within specified parameters. Practical application includes utilizing diagnostic equipment to assess circuit continuity, analyzing waveform patterns on oscilloscopes, and interpreting fault codes from onboard diagnostic systems.
In summary, troubleshooting proficiency is integral to these roles. It directly affects the ability to maintain the safety and reliability of aircraft and spacecraft. Effective troubleshooting is not simply reactive problem-solving, but a proactive strategy for preventing future malfunctions and ensuring continued operational integrity. The challenges in acquiring and maintaining this proficiency necessitate continuous learning, practical experience, and a deep understanding of aerospace systems and their interactions.
4. Inspection Procedures
Inspection procedures are intrinsically linked to the functions within an aerospace mechanic position. These procedures are not merely a supplementary task; they form a foundational component of ensuring airworthiness and preventing catastrophic failures. The rigor and thoroughness with which inspections are conducted directly correlate with the safety and reliability of aircraft and spacecraft. For example, a detailed inspection of an aircraft engine, following prescribed protocols, can identify hairline cracks in turbine blades or corrosion within fuel lines defects that, if undetected, could result in engine failure during flight. These positions entail meticulous visual examinations, non-destructive testing (NDT) methods such as radiography or ultrasonic testing, and functional checks of various systems to verify their operational integrity.
The practical significance of understanding and adhering to proper inspection procedures is multi-faceted. First, it prevents accidents and saves lives. Second, it reduces maintenance costs by identifying minor issues before they escalate into major repairs. Third, it ensures compliance with stringent regulatory requirements mandated by aviation authorities. A failure to properly inspect and document the condition of landing gear components, for instance, could lead to a gear collapse upon landing, resulting in significant damage and potential injuries. Furthermore, the detailed records generated during inspections provide a valuable history of the aircraft’s condition, facilitating trend analysis and predictive maintenance strategies. By consistently monitoring the wear and tear of specific components, mechanics can anticipate potential failures and schedule replacements proactively, minimizing downtime and maximizing aircraft availability.
In summary, inspection procedures are an indispensable facet of the aerospace mechanic profession. Competent execution of inspections requires specialized knowledge, attention to detail, and a commitment to upholding the highest standards of safety and regulatory compliance. The challenge lies in maintaining vigilance and continuously refining inspection techniques to adapt to evolving aircraft technologies and emerging failure modes. The diligent application of inspection procedures ultimately safeguards passengers, reduces operational costs, and preserves the overall integrity of the aerospace industry.
5. Repair Techniques
Repair techniques are intrinsic to the function of an aerospace mechanic. An aerospace mechanic position involves the practical application of diverse procedures to restore aircraft and spacecraft to airworthy condition following damage, wear, or malfunction. Deficiencies in repair skills directly impact aircraft safety and operational readiness. Incorrectly performed repairs can lead to structural failures, system malfunctions, and ultimately, catastrophic accidents. For example, improper welding of a fuselage section following a minor collision can weaken the airframe, increasing the risk of structural failure under stress. Precise execution of these techniques, aligned with strict regulatory standards, forms the foundation of an aerospace mechanic’s responsibilities. This involves skills like sheet metal repair, composite patching, welding, and component replacement, all vital for maintaining structural integrity and operational performance.
The selection of appropriate repair strategies hinges on various factors, including the type of damage, the material involved, and the aircraft’s operational environment. A mechanic addressing corrosion on an aluminum wing skin would employ different techniques than one repairing a delaminated composite rudder. Proper training, coupled with adherence to manufacturer’s specifications and regulatory guidelines, is paramount in ensuring the correct repair method is chosen and implemented. In practice, this involves careful assessment of the damage, meticulous preparation of the repair area, and the skilled application of specialized tools and materials. For instance, repairing a dented engine cowling requires specialized forming tools, precise measuring instruments, and an understanding of the aerodynamic impact of surface irregularities.
In summary, repair techniques are inextricably linked to the very core of an aerospace mechanic position. The competent application of these techniques is not merely a procedural task, but a critical safeguard against potential failures and a key contributor to the overall safety and reliability of air travel. The challenges lie in mastering a diverse range of repair methods, staying abreast of evolving technologies and materials, and upholding the highest standards of precision and compliance. These attributes are essential for any individual aspiring to excel in the field of aerospace maintenance.
6. Documentation Accuracy
Documentation accuracy is integral to the function of an aerospace mechanic. Precise and comprehensive record-keeping is not merely an administrative task but a fundamental component of ensuring aircraft airworthiness, safety, and regulatory compliance.
- Maintenance Log Entries
Accurate and detailed entries in aircraft maintenance logs are crucial for tracking all maintenance activities performed. Each entry must include the date, time, description of work performed, parts used, and the signature of the mechanic completing the task. For instance, when replacing a faulty fuel pump, the log entry must specify the pump’s serial number, the reason for replacement, and any relevant test results. This information provides a complete history of the aircraft’s maintenance, enabling future mechanics to understand past repairs and identify potential recurring issues.
- Parts Traceability
Maintaining accurate records of parts used in repairs is essential for traceability and accountability. Every component installed on an aircraft must be traceable back to its manufacturer and original certification documentation. This requires meticulous tracking of part numbers, serial numbers, and batch numbers. In the event of a product recall or safety bulletin, accurate parts traceability allows mechanics to quickly identify and replace affected components, preventing potential safety hazards.
- Inspection Reports
Inspection reports provide a detailed record of the condition of aircraft systems and components at specific points in time. These reports must accurately document any defects, discrepancies, or areas of concern identified during inspections. For example, a corrosion inspection report should include the location and severity of any corrosion, along with any corrective actions taken. Accurate inspection reports enable mechanics to monitor the progression of defects and plan preventative maintenance to address potential problems before they become critical.
- Regulatory Compliance
Accurate documentation is essential for demonstrating compliance with FAA regulations and other aviation standards. Maintenance records are subject to audit by regulatory agencies, and any discrepancies or omissions can result in penalties or grounding of the aircraft. For instance, failure to properly document a required inspection could result in the aircraft being deemed unairworthy. Thorough and accurate documentation ensures that all maintenance activities meet regulatory requirements and that the aircraft is safe to operate.
These facets underscore the indispensable role of meticulous record-keeping in maintaining aircraft airworthiness and ensuring regulatory compliance. A commitment to accuracy in documentation is not merely a procedural requirement, but a professional obligation essential for safeguarding passengers and protecting the integrity of the aerospace industry.
7. Continuous Learning
The dynamic nature of aerospace technology necessitates that individuals in aircraft maintenance roles embrace continuous learning as a fundamental aspect of their profession. Rapid advancements in aircraft design, materials, avionics, and propulsion systems render static knowledge quickly obsolete. Failure to engage in ongoing education and training directly diminishes an individual’s competence and ability to effectively maintain modern aircraft. The impact is measurable; a mechanic unfamiliar with composite repair techniques may incorrectly address damage to a carbon fiber wing, potentially compromising its structural integrity. Regular engagement with technical manuals, manufacturer bulletins, and industry seminars is therefore essential for maintaining proficiency.
The practical application of continuous learning is evident in several key areas. Firstly, new aircraft models frequently incorporate advanced technologies requiring specialized training. Secondly, evolving regulations and safety standards mandate that maintenance personnel stay abreast of the latest compliance requirements. Thirdly, troubleshooting complex system malfunctions often requires a deep understanding of underlying principles and the ability to interpret diagnostic data, skills honed through ongoing education. The transition from traditional hydraulic flight controls to fly-by-wire systems exemplifies the need for constant adaptation. Mechanics trained only on older aircraft require specific retraining to understand the complexities of electronic flight control systems, their associated sensors, and the software driving their operation. Moreover, skills acquired through formal education must be constantly reinforced and updated through practical experience and continuous professional development.
In summary, continuous learning is not merely an option but a prerequisite for success and competence within the aerospace mechanic profession. The challenges of keeping pace with technological advancements and evolving regulations demand a proactive approach to skill development and knowledge acquisition. By embracing lifelong learning, aerospace mechanics can ensure they remain capable of maintaining the safety, reliability, and efficiency of modern aircraft, contributing to the overall integrity of the aviation industry. The future trajectory of air travel will be heavily reliant on highly skilled personnel, committed to staying at the forefront of their trade.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following addresses common inquiries regarding the nature, requirements, and prospects associated with roles maintaining aircraft and spacecraft.
Question 1: What fundamental qualifications are necessary for consideration?
A high school diploma or equivalent is generally required. Further credentials, like an Airframe and Powerplant (A&P) license from the FAA or equivalent international certification, are often mandated.
Question 2: What distinguishes an Airframe license from a Powerplant license?
An Airframe license authorizes work on the aircraft structure, including wings, fuselage, and control surfaces. A Powerplant license permits maintenance and repair of aircraft engines.
Question 3: What specific tasks are commonly undertaken by individuals in these roles?
Typical duties encompass aircraft inspections, component replacements, troubleshooting mechanical or electrical issues, performing repairs, and documenting maintenance procedures.
Question 4: Is prior military experience advantageous when seeking such a position?
Prior experience in aircraft maintenance within the military is beneficial. It often translates to relevant skills and an understanding of aviation regulations.
Question 5: What are the long-term career advancement possibilities within the field?
Career progression pathways include specialization in particular aircraft types, advancing to lead mechanic roles, or transitioning into supervisory or management positions within maintenance departments.
Question 6: What are the prospects influenced by technological advancement?
The aerospace industry continuously evolves. Continuous professional development is crucial. Embracing new technologies, materials, and diagnostic techniques is required to remain competitive.
The responses above offer concise information about the essential aspects of pursuing and succeeding in aerospace vehicle maintenance.
Subsequent discussions delve into the ethical considerations and professional conduct standards expected within this critical industry.
Conclusion
The preceding exploration has provided a detailed overview of the duties, qualifications, and prospects associated with aerospace mechanic jobs. It has underscored the critical importance of technical expertise, regulatory compliance, and unwavering commitment to safety within this demanding field. From routine inspections to complex repairs, these roles are fundamental to ensuring the airworthiness and operational efficiency of aircraft and spacecraft.
The aerospace industry demands meticulous attention to detail and a dedication to continuous learning. Those considering aerospace mechanic jobs should recognize the significant responsibility entrusted to them. The decisions and actions taken directly impact the safety of passengers and the success of aerospace operations. The field offers both challenges and rewards, promising a stable and meaningful career path for those who possess the requisite skills and unwavering dedication.



![Top Countries: Best Aerospace Engineering Jobs [2024] Innovating the Future of Flight with Reliable Aviation Solutions Top Countries: Best Aerospace Engineering Jobs [2024] | Innovating the Future of Flight with Reliable Aviation Solutions](https://mixaerospace.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/03/th-91-300x200.jpg)